Hypoglycemia in a woman during pregnancy can occur for several reasons, such as:
- A change in the amount of food taken, while either a decrease or an increase in the amount may result in a lack of sugar;
- During pregnancy, a woman's body consumes more nutrients than usual;
- A decrease in plasma glucose, causing type 2 diabetes, characterized by a chronic form of the disease;
- Liver dysfunction.
As a rule, during pregnancy, hypoglycemia develops in the early stages due to the intensive growth of the child in the womb.
Among the provoking factors for the appearance of this disease, it is worth noting the following:
- The use of insulin by a woman, as well as its possible overdose, while patients with diabetes mellitus usually suffer from hypoglycemia;
- Failure of organs such as the heart, liver and kidneys.
Symptoms
The appearance of symptoms during hypoglycemia can be either rapid or, conversely, expressed in the long-term appearance of individual symptoms that occur gradually. These may include discomfort, fatigue and slight dizziness, as well as symptoms such as:
- Loss of consciousness;
- High fatigue;
- The appearance of headaches;
- Increased sweating;
- Trembling in arms, legs;
- State of anxiety and restlessness;
- Frequent heartbeat;
- Increased feeling of hunger;
- Changing the color of the skin to a paler shade.
Diagnosis of hypoglycemia during pregnancy
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out by doctors when a woman contacts her, in case of complaints about her health, as well as during periodic medical examinations. In this case, the diagnosis of hypoglycemia is carried out based on the data obtained from several studies, such as visual examination, palpation, etc., as well as from laboratory blood tests, so when the concentration of blood sugar level decreases below 2.8 mmol/l, hypoglycemia is diagnosed.
Also, an instrumental research method is used, which consists in the use of certain instruments, such as an electrocardiograph, computed tomograph, etc.
Complications
Hypoglycemia is a disease that can affect both the health of the woman and the health of the unborn child. At the same time, if blood circulation is impaired during pregnancy, problems with memory and thinking occur in the child. For the unborn child, hypoglycemia can be expressed in the following:
- Disruption of the nervous system in the unborn child, underdevelopment of the nervous system, cardiovascular or other;
- A sharp increase in fetal weight, facilitating a cesarean section;
- The appearance of polyhydramnios;
- Threat of miscarriage.
It is worth noting that before pregnancy it is necessary to diagnose the woman’s existing diseases and carry out the necessary preventive measures necessary to prevent complications, as well as pre-determine treatment in the presence of hypoglycemia in the period before pregnancy.
Treatment
What can you do
Treatment of hypoglycemia is aimed, first of all, at reducing the symptoms of the disease and can be carried out either with or without the use of medications, with a mild degree of the disease.
Thus, with stage 1 hypoglycemia, maintaining normal blood sugar levels is achieved through a balanced diet, including foods containing carbohydrates, such as sweet tea.
The manifestation of the disease in the second stage requires immediate intake of foods with easily digestible carbohydrates, such as jam or compote. As a rule, with timely normalization of blood sugar levels, it is possible to avoid visiting a doctor.
It is important to understand that eating foods such as ice cream, cakes, etc. does not have a positive effect on the body; with a high sugar content, these products contain fats that slow down the absorption of carbohydrates.
What does a doctor do
In the third stage of the disease, it is necessary to consult a doctor to provide effective emergency assistance, which consists of intravenous administration of a glucose solution to prevent cerebral edema. At this stage, the pregnant woman is hospitalized in order to monitor the consequences of hypoglycemia and correct the blood condition.
Prevention
To prevent the disease, a woman must consult a doctor before pregnancy to conduct research and make an accurate diagnosis of the presence or absence of the disease. It should be understood that the disease directly affects the health and well-being of the child. Therefore, in the very early stages of pregnancy, a woman needs to register with doctors and undergo examinations carried out on a regular basis.
Among the additional measures necessary to prevent the onset of the disease, it is necessary to monitor the blood sugar level and use a glucometer, while it should be understood that at different stages of pregnancy, the blood sugar level may fluctuate, even in the absence of the disease.
It is worth noting that blood sugar is one of the most common causes of the development of other diseases, such as visual impairment, the appearance of gangrene, and tumors.
If there are symptoms of the disease, it is necessary to urgently provide the woman with first aid, which may include the following:
- Intramuscular injection of a substance containing sugar in cases where vomiting, cramps and pain occur. At the same time, it is worth keeping medications containing these substances as accessible as possible in your home.
- It is recommended to take apple or orange juice with the addition of a weak glucose solution. At the same time, products such as milk and fruits must be excluded from your diet, because. they contain enzymes.
- Monitor your glucose status several times an hour until your blood sugar levels return to normal.
During pregnancy, women often develop health problems that they have never heard of before. In particular, with a probability of up to 10%, a carbohydrate metabolism disorder develops. To identify these pathological changes, all women expecting the birth of a baby undergo multiple studies of glycemic levels. We will tell you in this article what tests the expectant mother should undergo and how to decipher their results.
Sugar tests during pregnancy
If the patient does not have risk factors for diabetes, then she can only undergo the mandatory minimum tests. If a woman is at risk for pathology of carbohydrate metabolism, then more tests are prescribed.
Mandatory glycemic studies:
- fasting glucose level (, sugar during the day) upon registration;
- oral glucose tolerance test at 24-28 weeks.
Additional tests are needed if there are risk factors (complicated heredity, obesity, age over 25 years, glycosuria, history of glycerglycemia, gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy, a large fetus or a history of stillbirth, fetopathy and polyhydramnios on ultrasound).
Additional samples include:
- determination of daily glycemic profile;
- re-determination of fasting glucose;
- oral glucose tolerance test up to 32 weeks.
Blood sugar levels in pregnant women
When assessing carbohydrate metabolism, all blood tests for sugar and glycosylated hemoglobin are taken into account.
Normally, fasting blood sugar in a pregnant woman is no higher than 5.1 mmol/l. Even a single detection of higher values allows a diagnosis to be made.
The level of glycosylated hemoglobin in healthy people does not exceed 6%. Diabetes is diagnosed at rates of 6.5%.
During the day, glycemia should not be higher than 7.8 mmol/l. Diabetes mellitus is diagnosed when blood glucose is more than 11.1 mmol/l.
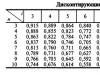
The most accurate way to identify disorders of carbohydrate metabolism is considered to be a glucose tolerance test. Its methodology and interpretation of the results are discussed in a separate article -.
The type of disease is determined by the level of glycemia and other tests.
High blood sugar during pregnancy
During pregnancy can be found:
- gestational diabetes;
- overt diabetes.
The reason for the increase in glycemia in the first case is a relative deficiency of insulin against the background of poor tissue sensitivity to this hormone. In fact, this is a manifestation of metabolic syndrome and a harbinger of type 2 diabetes.
Manifest diabetes is a severe disorder of carbohydrate metabolism associated with a severe absolute or relative deficiency of insulin. The cause may be autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells or insulin resistance of peripheral tissues.
High blood sugar is dangerous for the expectant mother and baby. Hyperglycemia disrupts the normal blood supply to the fetoplacental complex. As a result, the fetus lacks oxygen and nutrients. In addition, glucose in high doses disrupts the normal formation and development of the child’s organs and systems. Hyperglycemia is especially dangerous in early pregnancy.
 Risks for the child if the mother has diabetes:
Risks for the child if the mother has diabetes:
- increased likelihood of intrauterine death;
- intrauterine infection;
- premature birth;
- births with developmental anomalies;
- birth with fetopathy (large size, swelling, functional immaturity).
For a woman, hyperglycemia during pregnancy is also unfavorable. This metabolic disorder can lead to:
- infectious complications during pregnancy and after childbirth;
- polyhydramnios;
- trauma during childbirth, etc.
Even a slight increase in glycemic levels can lead to adverse outcomes. Therefore, for any hyperglycemia, a pregnant woman must urgently consult an endocrinologist and begin treatment. Typically, therapy only includes a special diet. But it must be prescribed by a specialist. During pregnancy, it is especially important to take responsibility for your health and not self-medicate.
Low blood sugar during pregnancy

During pregnancy, many women tend to experience hypoglycemia. Low blood glucose levels can manifest as weakness, tremors, sweating, and rapid pulse. In rare cases, low blood sugar leads to serious consequences. Adverse outcomes:
- intrauterine fetal death;
- mother's coma.
Such serious consequences occur with hypoglycemia caused by drugs (insulin) or tumors. Typically, such drops in glycemia are benign.
To undergo further examination and receive recommendations, you need to consult an endocrinologist. Treatment most often consists of fractional meals and limiting simple carbohydrates in the menu. If a hypoglycemic state has already occurred, then the woman is recommended to take 12-24 g of simple carbohydrates (1-2 XE). Liquid sweet drinks (a glass of juice, tea with two tablespoons of sugar or jam) best relieve symptoms.
Inna Tsvetkova, endocrinologist, especially for the site
Useful video:
Hypoglycemia in newborns is a rather rare condition, unless we are talking about the transient category of this pathology.
Most pregnant women do not realize that a decrease or increase in glucose to critical levels poses a huge danger to the development of the baby.
However, problems can be avoided if you know what symptoms a newly born person has. It is important to know what measures are used to normalize the condition.
Any mother during pregnancy certainly thinks about the health of the baby. However, she does not always pay attention to the dependence of the fetus on her own condition.
Due to excessive weight gain, a woman may have complexes and refuse to eat or go on a diet without consulting a specialist. In this case, the carbohydrate balance can change greatly.
Women's hormonal background undergoes great changes during pregnancy, for example, the pancreas begins to produce more insulin under the influence of estrogen and prolactin, while people who are far from such women do not always manage to understand that glucose levels are inexorably falling.
In severe cases, if there is a danger of developing a condition such as hypoglycemia in pregnant women, all internal organs will suffer, and there is a high probability of a threat to the physical and mental state of not only the fetus, but also the mother.

Or, on the contrary, mommy, due to a constant desire to eat something unusual, gains weight and independently upsets the balance of hormones, thereby provoking the development of diabetes. And just as in the first case, it is not always possible to notice an increase in sugar - hyperglycemia during pregnancy is also dangerous.
But the child develops and receives all the necessary substances from the mother; an excess or lack of glucose can have a detrimental effect on his health. Because he still cannot control his sugar level with help.
Hyperglycemia in pregnant women can lead to hyperglycemia in newborns and the development of diabetes mellitus in babies from birth.
For reference!
Hyperglycemia, like hypoglycemia, during pregnancy can lead to underdevelopment and even death of the fetus.
This is why it is so important to control the diet of the expectant mother and monitor her sugar levels, especially if she is already diagnosed with diabetes or there is a possibility of disruption of other metabolic processes.
You also need to listen to the state of your own body, if you notice excessive fatigue, constant thirst, you need to seek advice from a doctor managing your pregnancy.

Just born - already problems
Blood sugar problems are less common in healthy newborns. Typically, neonatal hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia affects premature babies with low body weight.
In children, a glucose level of 2.6 mmol/l is considered critical; lower levels indicate the development of hypoglycemia.
It is necessary to take into account the fact that there is a newborn (which is transient) - a normal condition in the first hours of a child’s life.
Since the body has not yet produced its own glucose, in the first minutes of life it uses the reserve accumulated in the liver. When the supply runs out and feeding is delayed, a sugar shortage develops. Usually after a few hours or days everything returns to normal.
You can immediately see when there is not enough glucose
A premature newborn is most susceptible to developing hypoglycemia, and there are a number of signs of this condition.

Symptoms that may indicate hypoglycemia are as follows:
- weak cry at birth;
- weak sucking reflex;
- regurgitation;
- cyanosis;
- convulsions;
- apnea;
- decreased tone of the eye muscles;
- incoherent movements of the eyeballs;
- general lethargy.
Hypoglycemic symptoms also include increased sweating with dry skin, high blood pressure, and heart rhythm disturbances.
Since the symptoms of hypoglycemia may not always manifest themselves, regular blood sampling is required for diagnosis, since such signs may indicate other serious pathologies.
In addition, hypoglycemia may be present in a newborn without symptoms.
What are the causes of the pathology?
Risk factors for diseases are always taken into account when managing any pregnancy and at the birth of a child.
If there are signs of hypoglycemia, specialists, first of all, determine the causes of the development of a dangerous pathology in order to select the correct treatment based on the information received.

Hypoglycemia usually develops for the following reasons:
- The presence of diabetes mellitus in a woman in labor, as well as her use of hormonal drugs. Early transient hypoglycemia is observed, starting from 6-12 hours of the infant’s life.
- Premature or multiple pregnancy with children weighing up to 1500 g. May occur within 12-48 hours. The most dangerous is considered to be the birth of a baby in the 32nd week of pregnancy.
- Problems at birth (asphyxia, brain injury, hemorrhage). Hypoglycemia can develop at any time.
- Problems with the child’s hormonal levels (adrenal dysfunction, hyperinsulism, tumors, impaired synthesis of proteins and carbohydrates). Typically, sugar levels decrease a week after birth.
In children at risk, blood is taken for analysis every 3 hours during the first 2 days of life, then the number of blood collections is reduced, but sugar levels are monitored for at least 7 days.

Normalization of the condition
Usually, no therapeutic manipulations are required, but in critical situations, when a lack of glucose can lead to nervous system disorders, emergency help is sought.
If the condition does not return to normal after a few days, we are no longer talking about transient, but about chronic hypoglycemia, which can be hereditary or congenital in nature, or be the result of a difficult birth with trauma.
If hypoglycemia in newborns is transient and does not have obvious signs that interfere with life, according to the articles of the AAP (American Academy of Pediatrics), the treatment used gives the same result as no therapy.
According to established WHO treatment measures, it is necessary that the newborn regularly receives the required amount of nutrition, regardless of therapy with glucose-containing drugs.
At the same time, if the child constantly spits up or has no sucking reflexes, tube feeding is used.
In this case, the newborn can be fed either breast milk or formula.

When sugar levels are below the critical norm, intramuscular or intravenous administration of drugs is used to increase sugar.
In this case, the minimum possible amount of glucose is initially used intravenously at the minimum infusion rate; if no effect is observed, the rate is increased.
Individual medications and their dosages are selected for each child. If intravenous administration of glucose does not give the desired result, therapy with corticosteroid drugs is carried out.
For reference!
After establishing a normal state, it is important not to abruptly discontinue glucose medications; it is necessary to gradually reduce the dose.
At the same time, if normoglycemia is not established for a long time, the child is not discharged from the neonatal department, additional tests are taken and the necessary therapy is selected.
Normoglycemia is established if the glucose level does not change for 72 hours without the use of drugs.
Attention! Danger!
Transient hypoglycemia in newborns usually does not have dangerous consequences for the body and goes away quickly.
Then, persistent hypoglycemia during pregnancy and immediately after birth can seriously affect the physical, mental and mental development of children.

Typically pathologically can lead to the following outcome:
- mental retardation;
- brain tumors;
- development of epileptic seizures;
- development of Parkinson's disease.
Also, the most dangerous thing that can result from low sugar is death.
Pregnancy is a wonderful period of life and an opportunity to give the child all the necessary beneficial elements, while protecting him from danger.
The same applies to preventing hypoglycemia or maintaining the necessary condition of both mother and fetus during pregnancy and newborns.
Low blood sugar levels are an alarming symptom, and this is especially dangerous during pregnancy. Such a deviation can be threatening not only for the expectant mother, but also for her child. That is why low sugar during pregnancy is not recommended to be left without attention and appropriate treatment.
The importance of blood sugar during pregnancy
Blood sugar plays a special role not only during pregnancy, but throughout life. Glucose allows you to regulate processes associated with carbohydrate metabolism, metabolism, and other significant conditions from a physiological point of view. Reduced or, especially, increased blood sugar levels indicate a high likelihood of developing complications and some pathological conditions. The most severe in this case is gestational diabetes.
A normal glucose level allows a woman to carry a child to term without any problems, give birth to him and ensure further breastfeeding. In addition, it is blood sugar that is responsible for the protective forces of the body. Thus, the causes and symptoms of hypoglycemia during pregnancy should not be ignored.
Causes and symptoms of low sugar during pregnancy
Women in the following risk groups are most at risk of developing hypoglycemia:
- hereditary predisposition to the development of diabetes;
- first birth after 30 years;
- being overweight;
- pathologies during previous pregnancies.
If glucose is low in a pregnant woman, the reasons for this should be considered non-compliance with the diet or insufficient nutrition, lack of vitamins, essential mineral components and trace elements. Low sugar in pregnant women occurs due to exhausting exercise, frequent consumption of sweets, as well as carbonated or alcoholic drinks.
The level of glucose in the blood during pregnancy decreases if a woman lives in a locality with a poor environmental situation and often faces stress. That is why it is very important for pregnant women to closely monitor their health and follow all the recommendations of a specialist.
 When sugar levels drop, it is always accompanied by quite specific symptoms. Speaking about this, they pay attention to the feeling of weakness and fatigue, headache, severe trembling and active sweating. Symptoms of this pathology should be considered drowsiness, constant hunger and the same degree of irritability. We should also not forget about the likelihood of a woman developing visual impairments, for example, double vision.
When sugar levels drop, it is always accompanied by quite specific symptoms. Speaking about this, they pay attention to the feeling of weakness and fatigue, headache, severe trembling and active sweating. Symptoms of this pathology should be considered drowsiness, constant hunger and the same degree of irritability. We should also not forget about the likelihood of a woman developing visual impairments, for example, double vision.
Experts call frequently recurring fainting and clouding of consciousness other pronounced symptoms. Similar signs are characteristic of later stages of development of the condition. Given the unpleasant symptoms, it is recommended to understand in more detail why hypoglycemia is dangerous for the woman and the fetus as a whole.
How dangerous is hypoglycemia for pregnancy and the fetus?
Hyper- and hypoglycemia are dangerous for a pregnant woman and fetus. They negatively affect the condition and development of the latter. So, low blood glucose during pregnancy can lead to a lack of nutrition for the fetal cells. As a result, the fetus may be born with a deficiency of body weight, prematurity is likely, as well as the presence of certain endocrine disorders.
The effect on the fetus can be expressed as follows:
- worsened health with minor fluctuations until spontaneous termination of pregnancy in the most difficult cases;
- premature aging of placental tissues, which can provoke hypoxia and even intrauterine fetal death;
- incorrect fetal presentation, entanglement of the umbilical cord and other no less serious diagnoses.
Among other things, low blood sugar can lead to early insulin secretion in the unborn child. As a result, the fetus may experience abnormal formation. The likely consequence is a sudden increase in fetal weight, leading to a difficult birth for the mother and injury to the baby. Another consequence of hypoglycemia should be considered a violation of the metabolism of other components, which as a result provokes late gestosis, aggravation of the general condition of the fetus and mother. Thus, there is no doubt about the danger of hypoglycemia, and therefore it is necessary to ensure its treatment and prevention at the initial stage.
What to do with low glycemia?
 The main action is to normalize the diet. This diet involves limiting the use of easily digestible carbohydrates. During pregnancy, it is advisable to consume as little sugar and sweets as possible, and it is also recommended to limit the use of sweet juices, which include, for example, peach, grape or apple. The same applies to certain fruits and dried fruits (for example, prunes or dried apricots).
The main action is to normalize the diet. This diet involves limiting the use of easily digestible carbohydrates. During pregnancy, it is advisable to consume as little sugar and sweets as possible, and it is also recommended to limit the use of sweet juices, which include, for example, peach, grape or apple. The same applies to certain fruits and dried fruits (for example, prunes or dried apricots).
In order for glucose to normalize during pregnancy, it is necessary to reduce the ratio of foods in the diet that contain slowly digestible carbohydrates. The presented list includes pasta, potatoes and rice. A special table has been developed not only for pregnant women, but also for diabetics, which indicates the carbohydrate composition of specific foods. It should be understood that it is the presented diet that allows you to maintain optimal sugar levels, which allows a woman to give birth to a healthy child without any pathologies.
.Hypoglycemia in pregnant women can be eliminated through gentle exercise. They are useful because they allow the female body to be provided with oxygen, which will reach the child in optimal quantities. It is no secret that this is one of the most important conditions for the normal development of the fetus. At the same time, the expectant mother’s metabolism is normalized and excess calories are burned.
However, low glucose levels during pregnancy cannot always be restored through diet or exercise. Speaking about this, experts point out that:
- if the measures presented are insufficient, the specialist prescribes additional injections of the hormonal component;
- there is no need to be afraid of this, because insulin is harmless for a woman and a growing child;
- another advantage is the absence of an addictive effect;
- after childbirth, when the insulin production algorithm in the mother’s body stabilizes, the introduction of the hormonal component can be abandoned without any problems.
One of the conditions determining the success of such treatment should be considered the timely start of treatment. The sooner therapy is carried out, the more positive the effect on the body will be. In addition, it is necessary to remember the complexity of measures and the provision of adequate preventive intervention.
Preventive measures
Without prevention, low sugar and, in principle, problems with glucose levels in a pregnant woman will appear throughout this period.
Pay attention to maintaining a healthy lifestyle, namely eliminating alcohol and nicotine addiction, maintaining proper nutrition and exercising.
In order for diet and exercise to be effective and safe, they must first be agreed upon with a specialist. A woman should feel much better after just a few days from the start of such changes.
Next, experts pay attention to controlling the level of sugar, cholesterol, and glycated hemoglobin for preventive purposes. From the point of view of preserving your own health and the condition of your child, it would be right to take care of purchasing a glucometer. This will allow you to constantly monitor your sugar levels and adjust your diet and exercise accordingly.
It is very important not to self-medicate and refuse to use traditional recipes unless they have been previously agreed upon with a specialist. All this will allow the expectant mother to maintain her health and give birth to a child without any pathologies.
Monitoring the compliance of all vital parameters with the norm is very important during pregnancy.
After all, the significantly increased load on a woman’s body during this period forces the main systems and organs to work much more actively, which can lead to health problems.
Even small disturbances in homeostasis in the body can cause unpleasant and painful sensations. In particular, it is a fairly common occurrence during pregnancy.
This condition not only provokes unpleasant sensations, but can also be dangerous for the fetus and the woman carrying it. What are the signs indicating low blood sugar during pregnancy, what could this condition indicate, and how should it be dealt with?
Signs
Signs of decreased glucose in pregnant women are absolutely no different from the symptoms that accompany other cases.
 Low sugar levels cause:
Low sugar levels cause:
- irritability and anxiety;
- nausea;
- sweating
In addition, tremors of the limbs and rapid heartbeat often appear.
Of course, many of the symptoms presented above may not be associated with a drop in glucose and may be caused by other diseases or, for example, food poisoning.
However, if several symptoms are simultaneously observed for a week or longer and occur after eating or due to a relatively long break between meals, or occur after eating a large amount of food, this most likely indicates problems with sugar levels.
Reasons for low sugar
 There are three main ones for pregnant women.
There are three main ones for pregnant women.
The first, internal reason is high activity, leading to the production of excessive amounts of insulin.
The second, external – malnutrition. Especially often, a decrease in sugar is observed when a pregnant woman follows a diet that is not recommended by the attending physician and is unbalanced and poor in nutrients.
Finally, fetal development also requires a certain amount of glucose. In this regard, a drop in blood sugar levels may be observed, since the expectant mother’s body first of all provides the child with the necessary substances, often to the detriment of her own health.
The most serious and worrisome is the first reason that contributes to low sugar during pregnancy.
After all, abnormally active functioning of the pancreas often indicates the presence of a disease, for example, a benign or malignant tumor.
The development of pathology leads to the fact that cells produce more insulin than the body needs.
However, poor nutrition is much more common, along with the expectant mother’s increased need for glucose. The process of restructuring the body during pregnancy is quite slow - all organs and systems need time to better adapt to maintaining the life and development of the fetus.
Added to this is poor nutrition, when a woman either consciously limits herself to food due to the inevitable weight gain during pregnancy, or eats an unbalanced diet, receiving few nutrients.
 By the way, paradoxically, excessive consumption of sweet foods can also cause a rapid drop in sugar.
By the way, paradoxically, excessive consumption of sweet foods can also cause a rapid drop in sugar.
This occurs because the intake of large amounts of glucose activates the pancreas.
If excessive consumption of sweets occurs often enough, the body gets used to this diet and begins to constantly produce excess insulin. There are certain risk factors for hypoglycemia. Low blood glucose during pregnancy is observed more often if the expectant mother eats irregularly and prefers low-calorie foods.
Hypoglycemia can also develop as a result of certain diseases. In particular - ulcers.
Particularly harmful is the constant consumption of sweeteners and various products with artificially reduced calorie content. When they enter the body, the production of “excess” insulin begins, and as a result, glucose in the blood drops.
 Active during pregnancy also reduces sugar levels, especially when combined with a strict diet.
Active during pregnancy also reduces sugar levels, especially when combined with a strict diet.
After all, muscles that work with full dedication need energy, which is provided by glucose. Accordingly, its amount in the blood decreases.
Finally, an imbalanced diet and excessive indulgence in sweets and carbonated sweetened drinks can also lead to hypoglycemia. A diet high in simple foods is especially dangerous for an expectant mother who has problems with the pancreas.
How to avoid hypoglycemia?
 If there are no problems in the functioning of the pancreas, you can bring low blood sugar during pregnancy back to normal by following a number of fairly simple recommendations that have a beneficial effect not only on glucose levels, but also on the general condition of the body of the mother and the unborn child.
If there are no problems in the functioning of the pancreas, you can bring low blood sugar during pregnancy back to normal by following a number of fairly simple recommendations that have a beneficial effect not only on glucose levels, but also on the general condition of the body of the mother and the unborn child.
First of all, you need to get your nutrition in order. A pregnant woman's diet should be as balanced as possible, with a predominance of healthy foods. It is better to avoid food with a significant amount of simple carbohydrates or minimize its amount.
But it is imperative to consume sources of complex carbohydrates. These include starch, glycogen and fiber - substances containing long molecular chains of glucose. The main difference between these substances and simple or monosaccharides is their ability to accumulate in human muscle cells.
 Thus, when the body works normally, these substances are not active.
Thus, when the body works normally, these substances are not active.
As soon as intense work begins and additional energy is required, special enzymes break down polysaccharides and glucose is formed, which, through interaction with insulin, provides energy to the cells.
At the same time, the caloric content of the diet should be at a fairly high level. It must be remembered that a pregnant woman should receive an additional twenty-five to thirty calories for every kilogram of her body weight. Shortage turns on the mechanism of their production from glucose and reduces sugar levels.
In addition to diet, diet is also important. It is best to eat at least four times a day, without snacking, but also without allowing breaks longer than four hours between meals.
 Thus, the total amount of food consumed will not increase, the load on the digestive system will decrease, and the absorption of nutrients will improve.
Thus, the total amount of food consumed will not increase, the load on the digestive system will decrease, and the absorption of nutrients will improve.
Organs and glands, in particular the pancreas, will work more smoothly, without peaks of activity after rare but plentiful meals. Accordingly, the production of insulin is stabilized, and therefore the level of glucose in the blood.
Very important during pregnancy. However, if there is a tendency for glucose to drop excessively, it is better to avoid complex exercises that put stress on the body. It is better to prefer physical education that provides normal physical activity, but does not overload the muscles and cardiovascular system.
Long walks in a forested area will also be useful. It is worth remembering the correct alternation of physical activity and rest, sleep and wakefulness. It is very important to avoid excessive fatigue, both physical and mental - it can also cause a significant decrease in sugar.
If a pregnant woman still continues to play sports, it is very advisable to follow a simple rule.
Moderate tiredness and tiredness should only be felt after training, at home.
If fatigue is felt during exercises, they must be stopped, and next time be sure to reduce the load. Otherwise, such physical activity can cause significant harm, including hypoglycemia.
With a significant decrease in sugar, it is advisable to have lollipops with you - their use will help to quickly, but relatively briefly, increase your glucose level if necessary.
Video on the topic
About the symptoms and treatment of low blood glucose during pregnancy in the video:
In general, you need to understand that a serious decrease in sugar levels is no less dangerous than its excess, and can lead to very serious consequences for the health and even life of both the pregnant woman and the unborn child.
Therefore, it is necessary to monitor this parameter, follow recommendations for its stabilization and, if necessary, immediately seek medical help. Consultation with a specialist at the first signs of hypoglycemia will preserve the health and life of mother and child.