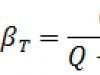A diploma of graduation from a university (college, vocational school) is just documentary evidence that its bearer was trained in a particular specialty during a certain period of time. But this says nothing about the level of his practical skills. Everything related to the maintenance of various electrical/technical devices (equipment, power or switching lines) under voltage has its own specifics.
That is why independent work, especially its organization, cannot be entrusted to a person who is not sufficiently prepared professionally. The level of qualification is determined by electrical safety clearance groups. Let's figure out what they are and how they are assigned.
All workers who are in one way or another connected with electrical installations are classified into groups, depending on the specifics of their activities, and therefore the requirements for them are different. Including by type of admission.
Personnel categorization
Electrotechnical
- Administration representatives (chief engineer, department heads, etc.). That is, persons involved in planning and organizing work related to electrical equipment.
- Operational, repair and operational repair services of the enterprise. These include personnel involved in various transfers, admission of employees to workplaces, and supervision of their activities. If they have undergone special training, then in emergency cases they can take a direct part in eliminating emergency situations or complex malfunctions at the site, and provide practical assistance to repairmen.
- Subject matter specialists of the departments (engineers, electrical installers, welders, electricians and a number of others).
For electrical/technical personnel there are several groups on electrical safety - from the second (primary) to the fifth (independent work without restrictions).

Non-electrical
In short - all other categories of workers. For example, a cleaner who is responsible for keeping order in the machine shop (compartment). The specific list of positions is determined by order of the organization. It includes personnel who, due to the nature of their activities, may (even briefly) be in the area of electric shock.
For this category of persons, Group I is provided. That is, they must have the minimum knowledge of electrical equipment and safety rules that is necessary to perform their official duties without risk to health and life.
Electrical safety groups
The first one is initial
It is assigned after an introductory briefing to the employee on the basis of tests, and does not provide for any special training.
What is being checked? Knowledge of the provisions of the TB instructions (both general and in relation to the position held), the ability to provide first aid to a colleague in case of electric shock.
Who conducts it?
A specialist with an electrical safety group of at least third. For example, a workshop engineer (laboratory, etc.) can instruct an electrician.

All other groups are for electrical personnel.
Second group
The second is the minimum acceptable for specialized specialists and does not involve independent work on electrical installations. Only under the leadership of a senior (partner) or as part of an emergency (adjustment) team. But this applies to the operational and repair staff. For those who are not directly involved in troubleshooting or connecting equipment, the second group is often sufficient.
Examples are a thermal operator, a crane (gantry) operator, and persons engaged in loading/unloading operations using electric mechanisms. Employees who have completed two weeks of training (72 hours) according to a program developed at the enterprise are allowed to take the exam for obtaining Group II, if they do not have a specialized education.
For persons under the age of majority (students, trainees), this is the limit group. It is also automatically assigned to employees who were unable to confirm the existing higher one within the established time frame. In essence, this means a temporary loss of qualifications and limitation in work.
Third - you can take this electrical safety group no earlier than a month after assigning the second. It provides the right to independent work, but only on equipment (in circuits) with voltage up to 1 kV. At most enterprises (institutions) this is the most common qualification for specialized specialists.
To obtain admission group III, you need to know the theory of electrical engineering (at least to a basic extent), safety rules, design and maintenance features of electrical installations, as well as. To obtain this admission group, you must have at least a secondary specialized education, or a long tenure in the position.
Fourth group
 This category of persons has the right to work on installations with voltages over 1,000 V. Engineering personnel who have this electrical safety group are appointed responsible for electrical facilities. Such specialists are entrusted with training young employees directly at the place of repair work. Submission for admission is possible only if the employee has already been certified for Group III and has worked in his position for at least three months.
This category of persons has the right to work on installations with voltages over 1,000 V. Engineering personnel who have this electrical safety group are appointed responsible for electrical facilities. Such specialists are entrusted with training young employees directly at the place of repair work. Submission for admission is possible only if the employee has already been certified for Group III and has worked in his position for at least three months.
During the examination, more stringent requirements are imposed on personnel applying for advanced training. Questions on electrical engineering are asked from the entire college course (vocational school). The employee must be well aware of all the instructions (on labor protection, maintenance and operation of facilities in a specific area), the requirements of industrial safety rules, the provisions of the PUE, and the diagrams of all electrical installations located in his area of responsibility.
In addition, be able to competently organize the work of subordinates, control their actions, and teach the necessary professional techniques and skills. This category of persons is allowed to instruct personnel and allow them to work on installations.
Fifth group
Everything is the same as for the fourth group on electrical safety. Additionally, it is required to know the structure of all units and equipment available at the production site, and be able to identify any malfunction and how to eliminate it. Certification for admission group V is carried out no earlier than three months after the assignment of the fourth and practical work in the specialty.

Where is the delivery for the electrical safety group?
- In the relevant department of Rostechnadzor, which carries out training and certification of employees. As a rule, in the direction of the enterprise (institution), indicating the position held, length of service in it and the required admission group.
- In an organization, if it has a PDK (permanent commission). She accepts exams and submits a draft order for the assignment of qualifications to management for consideration.
When is delivery to the electrical safety group?
- Upon expiration of the established period (depending on the group and level of education).
- When moving within the organization to another position that differs in the specifics of performing official duties.
- When changing place of work (when moving to another enterprise, institution, etc.).
Based on the testing of the subject’s knowledge, a protocol is drawn up and a certificate of the established form is issued.
> "ELECTRICAL SAFETY Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)" > Publication date: 2017-03-01 14:15:00
How many people should be on the enterprise commission for personnel certification?
In order to test the knowledge of the electrical and electrical engineering personnel of the organization, the head of the Consumer must appoint by order of the organization a commission consisting of at least five people.
The chairman of the commission must have electrical safety group V for Consumers with electrical installations with voltages up to and above 1000 V and group IV for Consumers with electrical installations with voltages only up to 1000 V. The chairman of the commission is usually appointed as the person responsible for the electrical equipment of the Consumer.
All members of the commission must have an electrical safety group and pass a knowledge test in the commission of the state energy supervision body.
Who assigns electrical safety group 1 to non-electrical personnel?
Employees from among electrical technical personnel with an electrical safety group of at least III group. up to 1000 V
Group 1 is assigned to one person who has a group of at least three (without creating a commission and with an entry in the registration log of group 1), cleaners of electrical premises working with power tools, auxiliary workers of non-electrical personnel, etc.
No certificate will be issued.
What kind of electrical safety group should managers have who are directly subordinate to electrical personnel?
The group is no lower than that of subordinate personnel, since they provide technical guidance and control over its work.
What is an "electrical safety permit"?
This is sometimes called electrical safety certification. Electrical safety permit - the right to work in electrical installations.
Which electrical safety group should a person allowed to perform work in electrical installations with voltages up to 1,000 V have?
Not lower than IV group.
Who can be appointed responsible for electrical equipment in electrical installations up to 1000 volts?
Responsible for electrical equipment in electrical installations up to 1000 volts can be assigned to a person who, after testing knowledge and instructions, is assigned group IV, certified as administrative and technical personnel.
Who can carry out maintenance of electrical installations of consumers in the organization?
Operation of Consumers' electrical installations must be carried out by a special service staffed by qualified electrical personnel. It is allowed to operate electrical installations under an agreement with a specialized organization.
What responsibilities for organizing the operation of electrical installations are assigned to the person responsible for electrical facilities?
The responsible person is obliged:
- Organize the development and maintenance of the necessary documentation on the operation of electrical installations;
- Organize training, instruction, testing of knowledge and permission to work independently for electrical technical personnel;
- Organize the safe performance of all types of work in electrical installations, including with the participation of seconded personnel;
- Ensure timely and high-quality performance of technical maintenance, preventative maintenance;
- Organize calculations of consumer needs for electricity and monitor its consumption and rational consumption;
- Participate in the development and implementation of measures for rational energy consumption;
- Monitor the availability, timeliness of inspection and testing of protective equipment in electrical installations, fire extinguishing equipment and tools;
- Ensure the establishment of a procedure for admitting specialists to electrical installations to carry out work on connecting new and reconstructing existing electrical installations;
- Organize prompt maintenance of electrical installations, prevent and eliminate emergency situations;
- Must:
a) check the compliance of power supply diagrams with actual operational diagrams and check them at least once every 2 years;
b) control the quality of supplied electricity at least once every 2 years;
c) improve the qualifications of electrical technical personnel at least once every 5 years; - Monitor the availability and compliance with the permit requirements of construction, installation and specialized organizations involved in work in existing electrical installations and in the security zone of power lines;
Note: The rights and responsibilities of the person responsible for electrical equipment must be specified in his job description.
In what case is electrical personnel required to undergo an internship (industrial training)?
A) Before being assigned to independent work.
B) When moving to another job or position related to the operation of electrical installations.
C) If there is a break in work for more than 1 year.
What type of electrical personnel are divided into?
A) Administrative and technical personnel.
B) Operations personnel.
B) Maintenance personnel.
D) Operations and repair personnel.
How is the 1st electrical safety group assigned to non-electrical personnel?
This is done through instruction. Knowledge acquisition is carried out in the form of oral questioning and testing in practice the acquired skills of safe methods of carrying out work and providing first aid to victims.
What type of testing is established for an employee if there is a break in testing knowledge for more than 3 years?
Primary. Only group II.
What type of testing is established for employees who increase their knowledge to a higher group?
Extraordinary inspection.
Where are the results of testing the knowledge of electrical workers documented?
Based on the results of the knowledge test: a protocol is drawn up; a journal entry is made; a certificate is issued.
What is necessary for certification according to PTEEP?
1. Completed electrical safety logbook (“Logbook for testing knowledge of norms and rules of work in electrical installations”, see IPBEE Appendix No. 7).
2. A completed certificate issued by the organization upon hiring or in case of loss of the previous certificate. The certificate must be filled out on the 1st page, certified by the seal of the organization, have the signature of the manager or person responsible for electrical equipment, the Certificate must have a number assigned by the organization. (See IPBEEAppendix No. 2).
3. In case of certification for a group higher than II, it is necessary to provide documents (magazine or certificate) confirming the previous certification.
What group can be assigned to an employee who did not present documents indicating previous certification, but only stated that he:
1. has been previously certified or
2. has extensive work experience?
In the absence of documents confirming a previously conducted certification, the employee is certified only for group II.
What is the maximum period allowed between assessments?
If there is a break in testing knowledge for more than 3 years, only the primary knowledge test for group II up to 1000 V is carried out (see PTEEP clause 1.4.19).
Can the group be promoted during an extraordinary certification in connection with a change in position or a change of place of work?
When changing a position or place of work, the previous (extraordinary knowledge test, see PTEEP clause 1.4.23) group is first confirmed, and then, if necessary, an extraordinary certification is carried out to increase the group.
Minimum time between certifications, if it is necessary to increase the group?
- During the initial certification for group II, certification for group III is carried out no earlier than two months later.
- After certification for group III for the first time, certification for group IV is carried out no earlier than three months later.
- If the employee being certified from among managers and specialists has a higher electrical engineering education, the intervals between certifications are reduced by 1 month each (a copy of the diploma must be attached to the documents listed above)
What must be reported about an employee in an application for electrical safety certification?
- Fully indicate the full name and position of the employee as it is recorded in personnel documents,
- length of service in this position at this enterprise,
- date of the last electrical safety certification and
- group that was previously assigned. (The same information should be recorded in the log).
- In the column about the upcoming certification, you must write which group should be assigned to the employee and as which personnel.
Who has the right to service batteries and chargers?
Specially trained personnel with electrical safety group III
Who in the organization monitors the operation of measuring and accounting instruments for electrical energy, including recording devices and devices with automatic acceleration of recording in emergency modes?
Operational or maintenance personnel
Who does the Labor Safety Rules apply to when operating electrical installations?
For employees from among electrical, electrical and non-electrical personnel, and for employers, regardless of ownership and organizational and legal forms), engaged in maintenance of electrical installations, carrying out operational switching in them, organizing and performing construction, installation, adjustment, repair work, testing and measurements
Who is covered by the Rules for the Technical Operation of Consumer Electrical Installations?
For organizations, regardless of ownership and legal forms, individual entrepreneurs operating existing electrical installations with voltages up to 220 kV inclusive, and citizens - owners of electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V
In which electrical installations is a person responsible for electrical equipment appointed?
In all electrical installations, except those where the owners of electrical installations above 1000 V are citizens or the electrical equipment includes only ASU, lighting installations and electrical equipment with a voltage not exceeding 380 V
Who approves the List of positions and professions of electrical personnel who need to have an appropriate electrical safety group?
Head of the organization
Where is the electrical safety knowledge of those responsible for electrical facilities and their deputies tested?
In the territorial commission of Rostechnadzor
Which electric current is more dangerous for humans: direct or alternating?
Up to 380 V, alternating current is more dangerous, and above 500 V, direct current is more dangerous than alternating current.
What are electrical safety groups?
SCROLL
positions (professions) of non-electrical personnel,
requiring assignment to electrical safety group I
|
№ p/p |
Position (profession) |
Structural subdivision |
| 1. | Accountant | Administration |
| 2. | Economist | Administration |
| 3. | Secretary | Administration |
| 4. | Cleaning woman | AXO |
| 5. | Driver | AXO |
Access groups II to V are assigned to workers whose daily work is associated with the operation or adjustment of electrical equipment.
characteristics of electrical safety approval groups
II tolerance group assigned to personnel whose work involves the operation of electrically driven equipment. Professions that require group II: electric welder, elevator operator, dispatcher, cook, heat operator, turner, etc. Personnel with clearance group II do not have the right to independently connect equipment to the electrical network. This can only be done by an employee with access group no lower than III.
III tolerance group gives the employee the right to independently connect/disconnect to the electrical network, inspect or maintain electrical installations. Professions that require group III: electrician, electrician, electrician, installer of low-current systems.
IV tolerance group assigned to employees who already have significant experience working in electrical installations.
Workers with group IV have significant competencies: they have the right to carry out organizational measures for the admission of personnel to work in electrical installations, provide control and supervision of the progress of work, and conduct electrical safety briefings.
Specialists who need Group IV: chief power engineer, work foreman, site manager.
V tolerance group assigned to engineering and technical personnel performing work in electrical installations up to and above 1000 V, as well as to workers authorized to perform special work, for example, testing equipment with high voltage.
Persons with qualification group III-V have the right to service electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V and up to and above 1000 V. The voltage limit is indicated in the certificate.
The list of positions and professions requiring assignment to electrical safety groups II-V is determined by the person responsible for electrical equipment and approved by the manager.
SCROLL
positions (professions) of electrical and electrical engineering personnel,
requiring assignment to groups II-V for electrical safety
|
No. |
Electrical Safety Group |
Position (profession) |
Structural subdivision |
| 1. |
III up to 1000 V |
Department head | Technical department |
| 2. |
III up to 1000 V |
Engineer | Technical department |
| 3. |
III up to 1000 V |
Senior Engineer | Technical department |
| 4. | Department head | Construction department | |
| 5. | Producer of works | Construction department | |
| 6. | Electrician | Construction department | |
| 7. |
III up to 1000 V |
Electrician | Construction department |
| 8. |
III up to 1000 V |
Installer of low current systems | Construction department |
| 9. |
V up to and above 1000 V |
Head of Electrical Laboratory | Electrolaboratory |
| 10. |
V up to and above 1000 V |
Engineer | Electrolaboratory |
Important! Managers who are directly subordinate to personnel with electrical safety groups II-V must have an electrical safety group no lower than that of subordinate personnel (clause 1.4. 3. Regulation dated January 13, 2003 N 6 PTEEP).
Who is the person responsible for electrical equipment?
The work of personnel in the company is inextricably linked with the use of equipment powered from the mains. Workers use power tools - hammer drills, grinders, and portable lamps. Office workers perform work duties surrounded by computer equipment and peripheral devices.
To organize control over the safe operation of electrical equipment, each company must appoint a person responsible for electrical equipment (clause 1.2.3).
The responsible person ensures that the necessary measures are taken to allow personnel to work in electrical installations, controls the implementation of scheduled preventive maintenance, periodic testing of protective equipment, and ensures the uninterrupted operation of electrical equipment.
If the company has electrical installations with a capacity of 10 kVA or higher, a deputy responsible for electrical facilities is also appointed by order of the manager.
The person responsible for electrical equipment and his deputy are appointed by order of the manager.
A sample order is shown in the figure:

The person in charge of electrical equipment and his deputy must have IV tolerance group if the company has electrical installations with voltages up to 1000 V and V tolerance group if there are electrical installations with voltages above 1000 V (clause 1.2.7. Etc. dated January 13, 2003 N 6 PTEEP).
The regulatory document allows not to appoint a person responsible for electrical equipment in cases where the company does not have equipment powered from a mains voltage higher than 380 V (clause 1.2.4 Etc. dated January 13, 2003 N 6 PTEEP).
In this case, the manager assumes responsibility for the safe operation of electrical installations. However, such a decision requires approval from the territorial bodies of Rostechnadzor.
What is electrical safety training and who provides it?
Assignment to group I is carried out in the form of instructions; special training for personnel is not required.
The instruction is conducted by a company employee with an electrical safety group of at least III. Usually this is the person responsible for the company's electrical facilities.
Registration of assignment of group I is carried out in the “Register of assignment of group I for electrical safety to non-electrical personnel”.
A sample of a completed journal is shown in the figure.


To initially obtain the II group of admission, personnel with secondary education or without secondary education must undergo training in electrical safety at the training center under the program “Norms and Rules of Work in Electrical Installations” for at least 72 hours and pass exams at the certification commission of Rostekhnalzor.
Those who successfully pass the knowledge test are assigned admission group II and issued a certificate in the established form.
How often is the group confirmed?
The next test of knowledge of personnel with qualification group I is carried out annually.
The next test of knowledge of personnel with qualification groups II-V is carried out:
- for electrical personnel directly organizing and carrying out work on servicing existing electrical installations or performing adjustment, electrical installation, repair work or preventive tests in them, as well as for personnel who have the right to issue orders, orders, and conduct operational negotiations - once a year;
- for administrative and technical personnel not belonging to the previous group, as well as for labor protection specialists authorized to inspect electrical installations - once every 3 years.
Important! Do not miss the deadlines for the next electrical safety certification, since if there is a break between knowledge tests of more than three years, the group is lost irretrievably and you will have to start again, with the assignment of admission group II (clause 1.4.19. Etc. dated January 13, 2003 N 6 PTEEP).
When changing place of work, the employee must undergo an extraordinary re-certification to confirm the current group and receive a certificate indicating the new place of work and position. The certificate from the previous place of work is not valid at the new place of work.
An employee can take the next knowledge test either at a training center or at a commission formed within the company.
The commission must consist of five people, three of whom (including the chairman) must be certified by Rostechnadzor. As a rule, the chairman of the commission is the person responsible for electrical equipment.
When conducting a knowledge test, at least three members of the commission must be present, incl. chairman
Knowledge testing is carried out according to developed and approved programs, taking into account the specifics of the enterprise’s activities.
Confirmation of the admission group of the person responsible for electrical equipment is carried out only by the Rostechnadzor commission.
How to improve the electrical safety group?
Testing employees' knowledge is divided into primary and periodic (regular and extraordinary).
An initial knowledge test is carried out for workers who first entered a job related to the maintenance of electrical installations, or when there is a break in knowledge testing for more than 3 years; next - in the order established in clause 1.4.20. Etc. dated January 13, 2003 N 6 PTEEP); and extraordinary - in the manner established in clause 1.4.23. Etc. dated January 13, 2003 N 6 PTEEP).
clause 1.4.20. The next inspection should be carried out within the following periods:
For electrical personnel directly organizing and carrying out work on servicing existing electrical installations or performing adjustment, electrical installation, repair work or preventive tests in them, as well as for personnel who have the right to issue orders, orders, and conduct operational negotiations - once a year;
For administrative and technical personnel not belonging to the previous group, as well as for labor protection specialists authorized to inspect electrical installations - once every 3 years.
The time of the next test is set in accordance with the date of the last knowledge test.
clause 1.4.23. An extraordinary knowledge test is carried out regardless of the date of the previous test:
When the Consumer introduces new or revised rules and regulations;
- when installing new equipment, reconstruction or change of main electrical and technological circuits (the need for an extraordinary check in this case is determined by the technical manager);
When assigned or transferred to another job, if new responsibilities require additional knowledge of rules and regulations;
If employees violate the requirements of labor protection regulations;
At the request of state supervisory authorities;
According to the conclusion of commissions that investigated accidents with people or disruptions in the operation of an energy facility;
- when increasing knowledge to a higher group;
When testing knowledge after receiving an unsatisfactory grade;
If there is a break in work in this position for more than 6 months.
clause 1.4.38. Based on the results of testing knowledge of device rules electrical installations, these Rules, safety rules and other regulatory and technical documents for electrical engineering, electrotechnological personnel are assigned an electrical safety group.
What risks does an employer face if employees are not trained in electrical safety?
An employer who allows uncertified personnel to perform work on electrical installations may be subject to administrative punishment.
From article 9.11. Code of Administrative Offenses: “Violation of the rules for operating electrical installations entails the imposition of an administrative fine:
For officials - from 2000 to 4000 rubles;
For persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from 2000 to 4000 rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days;
For legal entities - from 20,000 to 40,000 thousand rubles or administrative suspension of activities for up to 90 days.”
Officials who are required to organize timely training and ensure proper access to work for electrical and electrical engineering personnel are the head of the company and the person responsible for electrical equipment (clause 1.2.9 Etc. dated January 13, 2003 N 6 PTEEP).
Other persons who have committed violations in the operation of electrical installations may also be held liable.
In addition to administrative liability, officials may be held criminally liable for industrial accidents if, through their orders, actions or inactions, they failed to fulfill their official responsibilities for labor protection or did not take proper measures to prevent an accident.
From Article 143 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation:





our clients
Our advantages
Competent and professional construction of teaching methods
Discounts for budgetary and government institutions
Free consultations before the State Labor Inspectorate
To work with electrical installations of any type, you must have sufficient qualifications and possess certain skills. If to confirm your professional education it is enough to present a diploma, then with the certificate of the electrical safety group, not everything is so simple. What is the peculiarity of the permit and what is the procedure for assigning it, we will describe in detail in the publication below.
Access groups for various categories of personnel
According to the IPBEE (Inter-industry Occupational Safety and Health Rules), production personnel whose professional activities are related to electrical installations of any type are usually divided into three categories:
- Electrotechnical.
- Electrotechnological.
- Non-electrical.
Let's consider the features of assigning an electrical safety permit.
Electrotechnical
For this category, electrical safety approvals from II to V are assigned, depending on the specific requirements for personnel. It, in turn, according to the IPBEE, is usually divided into the following subcategories:
For independent activities, the last three subcategories must have a tolerance of at least 3, if the work is carried out with a voltage class of up to 1000 V. Accordingly, to carry out work with a higher voltage, it is necessary to have at least the IV tolerance group.
Electrotechnological
This category includes personnel whose professional activities involve the use of equipment powered by electrical energy. Examples include welding machines, as well as manual and stationary electrical equipment. Personnel are allowed to work after being assigned the 2nd qualification safety group.
Non-electrical
This definition includes personnel not included in the two previous categories. They are assigned the 1st clearance group. Which professions are included in this category is determined by the head of the enterprise.
Purpose and order of assignment
All employees of the enterprise must undergo certification of knowledge of electrical safety standards within the framework of their professional activities. A specialist cannot begin work duties without being assigned the appropriate qualification group. How a permit is assigned is indicated in PTEEP or other technical literature, which contains excerpts from regulatory documents.

We will briefly introduce you to the procedure for assigning each qualification group.
1 group
The group in question should be assigned to employees whose activities are not related to the use of electrical equipment. In essence, assignment is a preliminary (primary) briefing, at the end of which an oral interview is conducted, which is recorded in the briefing log. Workers are taught the basics of TB, the dangers of electrical voltage and how to provide first aid in cases of electric shock.

According to safety standards, instruction with the subsequent assignment of the 1st qualification group can be carried out by an employee appointed by order of the head of the enterprise. A mandatory requirement for an instructor is clearance group 3 and above.
After a group is assigned to non-electrical personnel, they are still required to undergo regular and extraordinary briefings, which is recorded in the log.
Video: electrical safety briefing (assignment to group 1)
2 groups
Assignment of qualification group 2 is carried out to employees of electrical and electrical engineering personnel. According to the Rules, an employee applying for certification must complete 72-hour theoretical knowledge training courses. This requirement does not apply to those who have received an electrical engineering education, since the vocational training program includes obtaining the necessary knowledge, including electrical safety.
To assign an access group to electrical engineering personnel, the latter must have 1-2 months of production experience. For employees included in this category, group 2 is the maximum.
As for employees belonging to the electrical category, for them the group in question is minimal. Without receiving it, they cannot start work. For example, persons undergoing industrial training or practice are in the first group, and, according to the current Rules, are not allowed to operate any electrical installations, even under supervision.
After employees are assigned the 2nd electrical safety clearance, they can begin maintenance of de-energized equipment and electrical facilities of the enterprise, but only under the supervision of employees with a qualification clearance of at least 3rd.
Certification for the assignment of a permit is carried out by a special qualification commission of a production organization or a local branch of Rostechnadzor. The commission checks theoretical knowledge of the principle of electrical equipment on which the employee will work, as well as skills in providing first-aid care.
Obtaining this qualification permit is not necessary for non-electrical personnel, but in some cases, by decision of management, even loaders may be required to receive group 2.
Please note that the Rules do not allow employees to be assigned a group higher than 2 if they have not reached the age of majority (18 years old).
Recertification, in order to test knowledge of safety standards, is carried out every year.
3 groups
Only a commission appointed by the management of the enterprise or the regional branch of Rostechnadzor can assign the 3rd qualification group, as well as the 2nd. This permit is issued to electrical technical personnel, which gives workers the right to independently service electrical equipment with voltages up to 1.0 kV.
To obtain the 3rd permit, a certain amount of work experience in the 2nd electrical safety group is required. The duration of training is set depending on the qualification level. For example, assignment to an engineer is usually made after a month of work, while college graduates receive the 3rd group no earlier than six months later.
The commission checks knowledge of electrical engineering, the design of electrical equipment, and the features of its maintenance, the ability to free the victim from and provide first aid.

4 groups
The main difference from the previous approval is that it allows maintenance of installations above 1.0 kV, that is, it is allowed to work with any high voltage. In addition, persons with appropriate qualifications can train personnel, conduct instructions, and also test knowledge after special industrial training. Engineering and technical workers with this category of admission can be appointed responsible for the technical condition of the electrical equipment of the enterprise.
Qualification group 4 is assigned only to those persons who have worked for at least a quarter with a 3rd electrical safety approval. Quite serious requirements are placed on applicants to take the exam. The examinee must have information on the entire basic electrical engineering course and the main provisions of the PUE. Know general and job instructions for safety, maintenance of entrusted electrical equipment, as well as know its electrical circuits and understand the principle of operation.
5 groups
This level of highest clearance implies maximum responsibility. Therefore, applicants are subject to all the above special requirements, plus knowledge of the design of equipment used in the entrusted electrical equipment. The certified person must understand the principle of operation of any electrical installation on his site, and, if necessary, be able to determine the cause of the malfunction and find the optimal way to solve the problem.
To obtain a 5th qualification permit, you must have the required qualifications and a certain amount of work experience with the 4th security group (from 3 months to two years, depending on the internal regulations).
How and where do you take the electrical safety exam?
There are two options for carrying out the certification procedure:

What is contained in the electrical safety group certificate?
This document confirms technical training and permission to work in consumer electrical installations. The employee must always have the certificate and present it if such a requirement follows, for example from the security of the facility. The certificate contains the following information (see Fig. 5):
On the left inner side:
- Document Number.
- Full name of the employee to whom the certificate was issued.
- Employee's position.
- Permissible voltage class.
- Which personnel does the employee belong to?
- The date of issue of the certificate and the name of the organization to which the permit is authorized to be assigned.
- Round seal and signature of the head.
On the right inside side of the ID there is a table with the results of the knowledge test.

Designations:
- Date of inspection.
- Reason for inspection (for example, regular, unscheduled, etc.).
- Assigned group.
- Grade.
- Indication of the date of the next (next) certification.
- Signature of the person who conducted the certification.
- electrotechnical;
- electrotechnological;
- non-electrical.
Electrotechnical
It includes:
- Administrative staff. For example, chief engineer, workshop manager, etc. These are workers who are responsible for planning and organizing work related to electrical equipment.
- Operational, repair and operational repair services of the enterprise. These include personnel involved in various transfers, admission of workers to workplaces, and supervision of their activities. If they have special training, they can participate in eliminating accidents and various malfunctions at the site, and they also have the right to provide assistance to employees engaged in repair work in production.
- Subject matter specialists of the departments. This category includes engineers, electricians, welders, electricians, etc.
For electrical personnel, there are several electrical safety groups - from the second (primary) to the fifth (the 5th electrical safety clearance group gives the right to independent work without restrictions).
Electrotechnological
This includes the following categories of personnel:
- if in the controlled technological process the main component is electrical energy (for example, electric welding, electric arc furnaces, electrolysis, etc.);
- using hand-held electric machines, portable power tools and lamps;
- other employees for whom the job description requires knowledge of industrial safety.
It can be:
- Administrative and technical employees, that is, managers and specialists whose work is related to operational and technical maintenance, commissioning, repair and installation work in installations.
- Operational employees who carry out routine maintenance and management of installations. They are engaged in inspection, preparation of workplaces, operational switching, admission, supervision of other workers, and performance of tasks within the framework of the ongoing operation of equipment.
- Operations and repair workers. These employees are specially trained to service the installations assigned to them.
- Maintenance workers who are responsible for maintenance, installation, testing, and commissioning of equipment.
Non-electrical
This category includes all other employees during whose work the possibility of electric shock cannot be completely excluded (the specific list of positions is determined by order of the employer). For example, a secretary working at a computer.
Persons included in this category are assigned electrical safety group 1. That is, they must have the minimum knowledge of electrical engineering and safety regulations that is necessary to perform the work entrusted to them without risk to health and life.
Electrical safety groups
This classification allows a worker to perform various types of work in electrical installations, and also determines the level of his training.
Workers are usually divided into five categories.
Electrical safety group 1 is assigned to non-electrical workers. Their work is not related to working with electrical installations.
Groups 2 to 5 are assigned to electrical personnel. The levels of knowledge that employees must have are described by the Order of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated July 24, 2013 No. 328n (as amended on February 19, 2016) “On approval of the Rules for labor protection during the operation of electrical installations” (registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on December 12, 2013 No. 30593) and the Order Ministry of Energy of Russia dated January 13, 2003 No. 6 “On approval of the Rules for the technical operation of consumer electrical installations” (registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on January 22, 2003 No. 4145).
First, initial, admission group
This applies only to non-electrical personnel. Before starting work, employees in this category must undergo training. A specialist with an electrical safety category of at least third is appointed responsible for its implementation.
After the employee completes the training, a record of this is made in a special journal. The citizen gets acquainted with her under his personal signature. The instructor also signs the log.
Second admission group
Assigned to workers who are not directly related to electrical installations, but who use electric tools when performing work, where electrical safety is important.

Third group of admission
A specialist who has been assigned group 3 electrical safety clearance receives an electrical safety permit up to 1000 Volts. This gives the right to work independently or the opportunity to work in a team that works with electrical installations over 1000 Volts. In this case, the corresponding explanation must be indicated in his certificate.

Fourth admission group
This category of persons has an electrical safety permit to work on installations with voltages over 1000 V. An employee with this right can be responsible for electrical facilities and train young employees.

Fifth admission group
As a rule, it is owned by engineering and technical personnel. This is the highest category, the presence of which gives permission to manage and manage tasks on equipment under any voltage and perform the duties of a manager of electrical facilities.

Where do they take the electrical safety class?
The exam for electrical safety clearance groups 2-5 takes place in the Rostechnadzor division that conducts training and certification of employees.
Training is carried out in the direction of the enterprise, in which it is necessary to indicate:
- employee position;
- his length of service in this position;
- required level of clearance.
Some organizations have their own permanent commission. She accepts exams and submits a draft order for the assignment (or upgrade) of qualifications to management for consideration. The commission must include:
- Chairman with electrical safety approval 5 (at voltages above (up to) 1000 V) and 4 (at voltages only less than 1000 V). As a rule, this is the person responsible for the electrical part;
- vice-chairman;
- secretary;
- at least 3 commission members.
After completing the training program and successfully passing the exam, employees are assigned categories of electrical engineering personnel (from 2 to 5). The corresponding mark is made in the certificate, the form of which is presented in Appendix No. 3 to the Rules on labor protection during the operation of electrical installations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated July 24, 2013 No. 328n. The certificate is valid until the position changes.
Duration and price of education
Applications for training are accepted by licensed training centers. We will show in the table the time it will take for training and the estimated cost.
| Access group | Academic hours | price, rub. | Timeframe for obtaining admission, working days |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 to 1000 V | 72 | From 4700 | 7 |
| 3 to 1000 V | 72 | From 4700 | 7 |
| 3 up to and above 1000 V | 40 | From 5700 | 7-10 |
| 4 to 1000 V | 72 | From 4700 | 7-10 |
| 4 up to and above 1000 V | 40 | From 5700 | 7-10 |
| 5 up to and above 1000 V | 40 | From 5700 | Up to 7 |
After the training, students will know everything that, according to the standards, is required for the corresponding category of clearance.
When is delivery to the electrical safety group?
The exam is taken:
- upon expiration of the previous certification. The validity period of certification for electrical safety up to and above 1000 V: for engineering personnel - 3 years, and for operating personnel - 1 year from the date of certification;
- when moving within the organization to another position that differs in the specifics of performing official duties;
- when changing jobs.
After testing the employee’s knowledge (if he successfully passes the exam), a protocol is drawn up and a certificate of the established form is issued.