Accounting can be maintained in different forms. In this case, the options are divided based on various characteristics, including the number of accounting registers, features of the documentation structure, appearance nuances, communication sequence, and recording methods.
The enterprise has the right to independently choose the accounting system that is most suitable, focusing on the acquired skills and knowledge. Since the 1950s, it has been customary to use a journal-order system for recording documentation with various modifications, including simple, simplified, complete or standard.
It is mandatory to use special documents, which are known as a journal order. At the same time, there is an opportunity to download a sample in order to understand the features of the filling process.
The basis is the principles of accumulation and systematization of primary documentation in accounting registers. There is the possibility of carrying out synthetic and analytical accounting, data on business transactions. At the same time, memorial order files do not need to be compiled, since a correctly completed form initially contains all the important information.
Chronological and systematic records must be carried out simultaneously, and the order journal does not imply a chronological recording of the organization’s business turnover.
Records should be made on the basis of indicators that indicate the state of the enterprise. The data allows you to create monthly, quarterly and annual reports. For a rational approach, the use of specially designed tables is provided.
Nuances of entering information
Each form must be filled out correctly. You can first download an example file and carefully study the nuances of formatting the information.
- The order journal is a free large sheet with a large number of details.
- It is possible to open a document to a synthetic account or a group of them.
- Each form must have a specific permanent number.
- Entries must be made every day. For registration, it is customary to use primary documentation or auxiliary statements if there are problems with obtaining analytical data.
- The basis for registration is the credit attribute of registration of business transactions. A correctly completed form, an example of which it is advisable to download in advance, allows you to closely monitor data on the operation of the enterprise.
- The results for the month, which are entered into the order journal, are a reflection of the total amount of credit turnover of the account, as well as the amount of debit turnover.
- A journal order can be used to inventory business transactions, but information is entered into the form only as such events are completed. For this reason, the recording becomes not only systematic, but also chronological.
The results obtained must certainly be compared with each other and with all indicators. The final data entered into the form is always prepared at the end of the month in two documents: the journal order and the General Ledger.
The journal-order accounting system is a classic form of accounting in which information from primary documents is systematized in special registers - journals-orders, which monthly record all transactions carried out by the company.
Each journal order is intended to reflect transactions performed on the loan of one or more economically similar, and therefore synthetic accounts combined in one register. The form has a section or a separate column for each account. Order journals for accounts that require analytical accounting along with accounts credit entries have two sections: the main one (the order journal itself) - for entries on the account credit, and an additional one (statement for the order journal) - for recording the necessary analytics. Debit turnover on the account is recorded in other journals along with the corresponding credit accounts, ensuring the basic principle of accounting science - double entry on accounts. correspondent accounts. In the statements, detailed analytical indicators for accounts are grouped, and then their results are transferred to order journals. At the end of the month and after all entries have been entered into the order journals, the data is summed horizontally and vertically, the results of which must match.
Total information on accounts from order journals (beginning and ending balances) is transferred to the general ledger, which is the basis for compiling the enterprise’s balance sheet. Systematization of accounting information and a clear chronology of records are the principles for constructing these accounting registers. The use of a journal-order system significantly simplifies labor-intensive accounting work, facilitating the formation of financial statements and monitoring its proper preparation. Let's look at what order journals are used in Russian companies.
Journal order 1
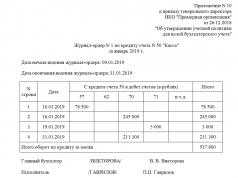
Journal order number 1 for account number 50 “Cash” is filled out on the basis of cash reports with primary documents attached to them - PKO and RKO. Journal order 1, the form (word) of which can be downloaded below, is one of the most common documents and is necessary to control the use of cash. The credit balance of the account is formed by all payments from the cash register, the debit balance is formed by funds received. The final line informs about the amounts of the accounts for which money was issued from the cash register: in our example, 108,652 rubles for salary payments. (D 70), accountable amounts 72,000 rubles. (D71), etc. Often in this register, for convenience, the balance of money as of the reporting date is displayed, subsequently checking with the data in the cashier’s report.
|
Journal order No. 1 for account loan. 50 "Cashier" from 01/01/2016 to 01/31/2016 to the debit of the account. |
||||||||
|
from-to as of 01/01/2016 98300 |
||||||||
|
from to 02/01/2016 |
||||||||
The debit balance, i.e. cash receipts, is recorded in the account statement. 50 to w/o 1. Journal order 1 and statement 1 , samples of which are presented in the article systematize all operations at the company’s cash desk for the month.
|
Statement for railway station No. 1 on the debit of the account. 50 |
|||||
|
Perv. doc |
Wiring |
Amount, rub. |
|||
|
Revenue received for sold operating systems |
|||||
|
Payment received for long-term securities |
|||||
|
Received DS for salary payment |
|||||
|
Payment received for services rendered |
|||||
|
Revenue received from products sold |
|||||
Journal order 2
Journal order 2 takes into account transactions reflected in the credit account. 51. Entries are made on the basis of bank statements and attachments to them - payment orders, letters of credit, etc. On the back of w/o 2, information on the debit of the account is collected in the statement. 51, i.e. according to receipts to the account. Journal order 2 (you can download the form below ) , is filled in according to the same principle as journal order 1.
Let's look at an example:
|
Journal order No. 1 for account loan. 51 from 01/01/2016 to 01/31/2016 to debit accounts |
||||||||
|
D s-to 01/01/2016 100000 |
||||||||
|
from to 02/01/2016 158300 |
||||||||
Order logs 3, 4, 5
When conducting operations with accounts 54, 55, 56, which take into account capital costs, special accounts and other funds, it is necessary to maintain such a register as journal order 3.
Journal order 4 is provided for recording transactions on credits and borrowings on the account. 66 and 67. Journal order 5 is rarely used by Russian enterprises, since offsets of mutual claims between debtors and creditors are today considered an exclusive operation. However, such a register exists and is used if necessary.
Journal warrant 6
Settlements for supplies supplied and services rendered are reflected in journal order 6 – a combined register recording the receipt of goods and services and further payments for them.
Journal order 6 (filling sample attached) is maintained according to account. 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors” for each counterparty.
|
Provider |
Check |
From K/ta account. 60 in D/t accounts |
From to the beginning of the month |
Paid |
from-to to the end of the m-tsa |
||||||
|
K/t 51 |
K/t 91 |
||||||||||
|
LLC "Temp" |
No. 100458 dated 01/18/2016 |
||||||||||
|
No. 000145 dated 01/05/2016 |
|||||||||||
Journal warrant 7
Journal order 7 records the issued accountable amounts in the context of each responsible person. Journal order 7, the form of which combines synthetic accounting with analytical information, is convenient for monitoring the timely submission of employee expense reports.
Introducing journal order 7: sample filling
|
Balance at the beginning of the month |
Issued on report |
according to advance report |
|||||||
|
date of presentation |
approved amount of expenses |
||||||||
|
Ivanov I.I. |
|||||||||
|
From the account 71 in d/t accounts |
overexpenditure was reimbursed to the employee |
unused amounts are withheld |
||||
Journal order 7, the form of which can be downloaded below, reflects all accountable amounts and carry-over balances.
Journal warrant 8
Accounting for settlements with creditors and debtors is carried out on accounts 62, 68, 73, 75, in the order journal 8. All values for these accounts are summarized in this register, noting advances received and payments received from counterparties.
Journal order 10
Journal order 10 (filling sample just below) is intended for accounting for production costs. The register receives all information from accounts 02, 04, 05, 10, 11, 15 16, 19, 20, 21, 23, 25, 26, 28, 29, 40, 46, 68, 69, 70, 76, 94, 97.
|
In D/t accounts |
Turnovers on correspondent accounts |
||||||||
The abundance of information reflected in this register makes it the most informative. The basis for filling out is a variety of forms - production reports and summary statements that form the journal order 10. The form can be downloaded below.
Journal warrant 11
This accounting register - journal order 11, is necessary to record the shipment, sale of products, and is filled out on the basis of auxiliary statements No. 15 and 16, which reflect the prices for inventories applied in accordance with the accounting policy - actual or accounting.
Journal warrant 12
Systematizing information about changes in the reserve, additional or authorized capital of the company, as well as in the accounts of target receipts and retained earnings, this accounting register is based on data from accounting certificates, bank statements, and cash reports. The debit turnovers accumulated in decoding from various registers are entered into the journal order 12. The form can be downloaded below.
Journal warrant 13
Accounting for fixed assets and intangible assets is reflected in journal order 13. The basis for filling it out are depreciation calculations, certificates, and disposal acts. Journal order 13 – sample filling:
|
Journal order No. 13 for credit account. 01 to debit accounts |
||||||
Journal warrant 15
Accounting for the use of profit and future income for accounts 84, 91, , 99 is kept in the journal order 15 (the form can be downloaded below). Turnovers are entered into the register for the reporting month in the context of analytical accounting items and on a cumulative basis from the beginning of the year. At the end of the reporting period, the total values of the order journal become the basis for the preparation of the annual financial report.
Journal warrant 16
Accounting for capital investments in accounts 07, 08, 11 is carried out in journal order 16. Credit turnover of these accounts is recorded as monthly results based on information from analytical statements and primary documents, presenting data about each object combined in the register.
Note that accounting automation has eliminated the maintenance of independent forms of order journals. With appropriate program settings, this register is generated automatically when posting primary documents.
ZhO is responsible in accounting for the systematization of primary documentation. Using a journal-order accounting system, business transactions that each organization performs monthly are recorded.
ZhO are filled out on unified forms (OKUD code No. 0504071), approved by the Ministry of Finance through Orders No. 123n dated September 23, 2005 and No. 25n dated February 10, 2006. However, if necessary, an institution can use independently developed JO forms, having previously approved them by order and secured them in its accounting policies.
Each form of liquidation is used to reflect one or another loan transaction, then all the transactions performed are combined in a single register of synthetic accounts, highlighting the totals for each individual account.
Credit liquidations consist of two sections:
- main - for CT records;
- additional (statement) - for maintaining analytical records.
DT turnover is entered into special JOs together with corresponding CT accounts, which ensures the implementation of the double entry principle in accounting. Balances at the beginning and end of the period from the JO for each account are transferred to the general ledger of the organization.
Each institution has the right to choose the type of form with which accounting will be carried out:
- journal-order;
- memorial order.
However, the use of a journal-order form leads to simplification of the work of accounting, since its main principle is the systematization of accounting data and the automation of the preparation of periodic and final reporting.
Journal order 1 and statement 1
Journal-order No. 1 and the statement to it are filled out by the institution in account 50 “Cash” in accordance with incoming and outgoing cash orders. The balance on the CT account reflects all payments made from the cash desk, on the DT account - those funds that were received. The total line shows the amounts for which funds were paid. JO 1 should reflect cash balances as of specific dates. These balances must necessarily coincide with the final balance on the specified day in the cashier’s report. The final line of the JO should be similar to the turnover for CT account 50 in the general ledger for the selected period.
The statement for ZhO No. 1 is filled out in a similar manner. The final turnover must necessarily coincide with the indicators of the cash register. At the end of the reporting month, the accountant needs to reconcile the final balance against JO No. 1, statement No. 1, and the indicators of the institution’s cash book.
Journal order 1: download the form in Word
Journal order 1: sample filling

Journal order 2: form
ZhO 2 reflects all transactions recorded on CT account 51. All information is indicated on the basis of statements and attachments to statements from the bank, including payment orders. The reverse side of ZhO No. 2 serves to reflect information about receipts from DT account 51. The algorithm for filling out ZHO-2 is similar to ZO No. 1.
Journal warrant 2: download form

Journal order 2: sample filling

ZhO No. 3-5
Operations on CT accounts 54-56, recording capital costs and special accounts in banks (letters of credit, check books, monetary documents), are formed in ZhO No. 3.
Journal warrant 3: form

Journal order 3: sample filling

Journal order 4: form
Movements on short-term and long-term loans, borrowings (accounts 66 and 67) are recorded in journal order 4.

Journal order 4: sample filling

Offsets of mutual claims between debtors and creditors are formed by journal order 5.
Journal warrant 6: form
All settlement transactions for goods and services supplied are recorded in ZhO No. 6. It also reflects the direct receipt of goods and provision of services. Settlements for the supply of goods and services are recorded in account 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”. ZhO No. 6 is filled out for each counterparty and agreement.

Journal order 6: sample filling

Journal warrant 7: download form
Journal-order 7 is responsible for systematizing accounting data for settlements with accountable persons based on transactions on account 71. Journal No. 7 contains information in the context of all advance reports of employees, all amounts of funds issued to the accountable persons, as well as carry-over balances for the selected period . The lines in ZhO No. 7 are not subject to grouping or merging.

Journal No. 7: sample filling

Journal warrant 8: form
ZhO No. 8 is a register for accounting settlements with debtors and creditors in accordance with analytical data for the following special accounts:
- 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”;
- 62 “Accounting for settlements with customers”;
- 68 “Accounting for calculations of taxes and fees”;
- 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations”;
- 75 “Settlements with founders”;
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors.”
JO No. 8 contains generalized data on mutual settlements with the above-mentioned counterparties, indicating funds received from such counterparties, including advance payments.

Journal order 8: sample filling

Journal warrant 10: download form
ZhO No. 10 is used to account for the costs of own production. ZhO No. 10 reflects summary data from multiple accounts for each financial and economic operation of the organization. Information is entered into ZhO No. 10 on the basis of a number of accounting reporting registers and statements.

Journal order 10: sample filling

Journal warrant 11: form
ZhO No. 11 is intended for recording accounting data on the shipment and sale of finished products. Registers that serve as the basis for the formation of ZhO 11 - statements No. 15,16. These accounting reports indicate actual or accounting prices for inventories, as specified in the accounting policies of the organization.
Documentary support for cash withdrawal
In our time of total dominance of banks and bank transfers, no organization can do without actual funds. This article discusses an example of filling out an expense cash order (RKO) and issues related to its use.
Any organization or individual entrepreneur is obliged to conduct settlements with counterparties, make payments to the budget and funds through a current account. But there are still many cases when you need cash:
- issuance to an accountable person
- calculation of wages
- issuance for business needs
- advance payment to supplier
The Federal legal act entrusts the Central Bank with determining step by step cash transactions. This procedure is outlined in the Bank's Directive, which states that all cash and cash transactions are executed by orders: incoming and outgoing. The names of standard forms are also indicated there. These forms are enshrined in legislative regulations. Form KO-2 is intended for an expense cash order.
Thus, the creation of a cash document when issuing money is a mandatory procedure.
An example of filling out a cash receipt order will help you draw up the document correctly. In addition, it must be recorded in journal form, where all incoming and outgoing documents of the cash register are recorded. This magazine, in turn, has a KO-3 standard form.
Registration of an order
An accountant prepares an expense cash document. At the legislative level, there are no clear requirements on how to fill out an order. But since there is a unified form for the order, the responsible person fills out the order form in accordance with the requirements of the corresponding fields in the form:

- The name of the organization is written on the top line
- below it is a structural unit; if there is no division, then a dash is put
- in the “Codes” plate, the OKUD code 0310002 is entered automatically, and the OKPO code must correspond to the code from the classifier
The accountant must then enter the accounts. The account credit will always be 50, but the debit depends on the business transaction in accordance with which money is issued:
- 70 – issuing salaries to employees
- 60 - payment to suppliers and customers
- 71 - settlements with accountable persons
- 51 - transfer of a certain amount to the organization’s current account
In the next column the amount of the transaction is entered; below is the name of the employee who receives the money. The line “Base” records the business transaction on the basis of which money is withdrawn. This is most often:
- employee remuneration
- issuance for business needs
- cash is transferred to the account (settlement)
- payments under lease agreements, etc.
In the next line “Amount” the amount is written in words. The line “Attachment” is documents confirming ongoing business transactions. It could be:
- payment statement
- written application for business needs
- receipt for the advertisement for cash contribution, respectively, etc.
The leadership of the organization signs below. If there is no accountant in the organization, then the manager signs for him.
Requirements for registration of RKO
An example of filling out a cash flow order confirms that cash settlement order is a financial document, therefore:
- records should not contain blots, corrections or errors
- It is impossible to certify a consumable with an electronic digital signature
- the document must be in paper form
Issuing money at the cash register via cash register

Procedure for issuing money at the cash register
The cashier of the organization issues the money according to the expense order. It is his responsibility to check the correctness of the order and make sure that the manager and chief accountant have signed in the appropriate lines. The order contains a line where the recipient’s passport details are written:
- last name, first name, patronymic must be in the dative case
- Before issuing, the cashier must check the passport data in the order with the original, which the recipient must provide
In the “Received” line you need to write the amount from the cash register, put the current number below and sign for the person who directly receives the money. After receiving the appropriate amount, the cashier must put his name and sign.
Now all documents are filled out on a computer. Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U notes that the consumable can also be filled out by hand.
There is also no mention that you cannot combine automatic and manual filling. Thus, if necessary, you can fill in by hand those lines that were not included in the consumables automatically. The expense document is filled out in the singular and filed in the cash book.
Cash settlement services in credit institutions

Drawing up cash settlements in a bank
- Tear-off coupon for RKO No. - the number is indicated in numbers, which must correspond to the RKO
- debit and credit are formed as required by the Bank's regulations
- free field - filled in as required by the rules of the so-called analytical accounting in cases of transactions with precious metals. This procedure is enshrined in the internal document of the organization, the accounting policy
- symbol - symbols are written in numbers
- document code is the designation of the document in numbers
- cash dispensing direction – write the dispensing direction, taking into account the reporting symbols
- free field - details are written in accordance with the requirements of the accounting policy of a specific banking organization
Accountant's Guide
The new legal act allows entrepreneurs to create and use primary forms of documents from 01/01/2013. But for RKO you need to use previously approved forms and fill them out in accordance with the above rules.
Thus, as can be seen from the example, drawing up a RKO document is quite simple. When drawing up, you must carefully fill out all fields of the document without errors or omissions, otherwise the document may be declared invalid.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and click Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
I’ve never worked as an accountant, but as a cashier-seller, I had to print out such a form when issuing funds. The form is very simple, the only drawback is that you cannot make mistakes in cash documents - otherwise you had to redo it, and in addition we were fined for this...
prednalog.ru
Just another WordPress site
Recent Entries
Recent comments
- admin to the entry Transfer of a pregnant employee to light work
- admin to the entry Purchasing goods from an individual: accounting, documents, taxes
- Alexander on Purchasing goods from an individual: accounting, documents, taxes
Filling out cash receipts and cash vouchers. Cash book.
Filling out an expense cash order (RKO).
An expenditure cash order is used to issue cash from the cash register. This is a unified document (form KO-2). It is written out by the cashier or other authorized person in one copy.
How to fill out an expense cash order correctly?
At the top of the consumable is written the name of the organization, its structural unit (if any). If there is no structural unit, then put a dash. At the top right side, the organization codes are written based on a certificate from the State Statistics Committee.
The “Document Number” is assigned in order as money is issued from the cash register. Numbering starts from the beginning of the year.
Document date – the date the money was issued from the cash register. It coincides with the date in the journal for registering incoming and outgoing cash orders (KO-3). The date is indicated in the format - DD.MM.YYYY.
The columns “Debit” and “Credit” indicate the accounting accounts of the cash transaction. They are filled out by an accountant. The column “Debit, structural unit code” is filled in if the enterprise has such a unit and money is issued in it.
In the column “Debit, analytical accounting code” the code is indicated if it is used in the organization, or a dash is placed.
“Credit” are the cash register accounts from which money is issued. In synthetic accounting, this is account 50 “Cash”.
“Amount, rub. cop." — the amount dispensed from the cash register is indicated in numbers.
In the column “Purpose code” the codes are indicated if they are accepted by the enterprise.
In the “Issue” line, fill in your full name. employee of the organization to whom the money is given, in the genitive case.
The content of the financial transaction is written in the “Base” line.
The “Amount” line repeats the amount indicated above for the cash receipt order. It is written with a capital letter first in words. Kopecks are indicated in numbers.
In the “Appendix” - the documents on the basis of which money is issued from the cash register are indicated. If an employee of a third-party organization receives money, it is necessary to indicate the data in the power of attorney, according to which the money is issued from the cash register. The power of attorney is attached to the cash receipt order.
RKO is registered in the register of cash documents KO-3 and certified by the signatures of the head of the organization and the chief accountant.
The “Received” line is filled in by the recipient of the money. It includes the amount received in words and kopecks in numbers. The recipient of the funds then signs and dates it. Below is the name of the document on the basis of which the money is issued to the recipient. Most often this is a passport or identity document. Why do you need passport data in a consumable? This is necessary if a conflict situation arises regarding receipt of money. Let’s say an employee makes a claim to you that it was not he who received the money, then you can prove this with his passport details and signature. This is especially important when you give out money under a power of attorney, since the power of attorney may be fake, for example, when an employee quits, but he still has the power of attorney form (yes, this happens in practice).
The line “Issued by cashier” is filled in by the cashier or an authorized person after issuing money under the cash register. According to it, the cashier certifies the consumable with his signature and its transcript.
RKO is not handed over to the recipients of the money. It remains with the cashier.
The cash receipt form can be downloaded here.

Filling out a cash receipt order (RKO).
A cash receipt order is used to process cash when it arrives at the organization's cash desk. This is a unified document (form KO-1). It is written out by the cashier or other authorized person in one copy.
How to fill out a cash receipt order correctly?
A cash receipt order (PKO) consists of two parts: the receipt order itself and a receipt, which, after filling out, is issued to the person who deposited the money into the cash register. The consumable can be issued either manually or electronically. Marks and corrections in receipts are not allowed. In this case, they need to be rewritten.
At the top of the RKO, fill in the name of the organization and its structural unit (if any). If there is none, a dash is added.
“Codes” are filled in based on a certificate from the State Statistics Committee.
The receipt number is indicated according to the order of cash transactions. Numbering starts from the beginning of the year. RKOs are registered in the KO-3 registration log.
“Date of compilation” is the date of receipt of money (receipt of money at the cash desk). Consumable date format is DD.MM.YYYY (for example, 05/25/2012).
The columns “Debit” and “Credit”, as in the cash receipt order, are filled out by the accountant. The Account Debit always includes an account for cash transactions (synthetic account 50 “Cash”).
In the column “Amount, rub. cop." The amount of money deposited into the cash register is written. It is indicated in numbers. The column “Purpose code” is filled in if the organization uses a coding system.
In the column “Accepted from___” the full name of the person who deposited the money into the cash register is written in the genitive case, and if the payment was made by a representative of a third-party organization, then “Name of the organization” and the full name of the authorized person.
In the “Base” column – the content of the financial transaction or the document on the basis of which the payment is accepted is shown.
The “Amount” line indicates the amount of payment accepted at the cash desk. The amount is written from the beginning of the line with a capital letter in words, and kopecks in numbers. If the “Amount” line is not completely filled in, then the empty spaces are crossed out.
In the “Including” line, enter the VAT amount in figures, or enter “excluding tax (VAT).”
The “Appendix” indicates the primary documents that must be attached to the order.
The same entries are made in the receipt for the PKO as in the PKO. The “PAID” stamp is placed on the receipt and PKO. The receipt is torn off and given to the person who deposited the money.
The cash receipt order is signed by the cashier and endorsed by the chief accountant or other authorized person.
The cash receipt form can be downloaded here.

Filling out the Cash Book.
A cash book is a consolidated document that records all cash transactions: both the receipt of cash and its issue. The unified form of the book is form KO-4.
The book can be filled out either manually or electronically.
The procedure for maintaining a cash book electronically.
On the morning of each next working day, the cashier needs to prepare two printouts: “Cashier’s Report” and “Cash Book Loose Sheet”. They contain the same details to fill out. They are numbered in order from the beginning of the year.
The printout of the last loose sheet of the month and year indicates the total number of sheets for each month (year). The cashier needs to check the printouts for accuracy, then sign them. The loose sheets of the cash book remain in the cash register and are stored for a year, and the report with attached cash receipts and expenditure orders is transferred to the accounting department.
All loose sheets of the cash book, as necessary or at the end of the year, are stitched and sealed, certified by the signatures of the chief accountant and manager, indicating the total number of sheets.
The procedure for maintaining a cash book manually.
When manually maintaining a cash book, it is opened for a certain period, based on the number of transactions. Even before use, the sheets of the book are laced, numbered, sealed and certified by the signatures of the manager and chief accountant on the last page. The cash book is sealed with wax or regular seal.
If the sheets of the cash book are not completely filled out, they are crossed out.
At the end of each day, the cash book displays the total amount of receipts and the total amount of expenditure documents posted during the day, and also calculates the balance at the end of the day. Maintaining the cash book is controlled by the chief accountant.
The cash book form can be downloaded here.

Read about checking cash transactions here.
Free book
Go on vacation soon!

To receive a free book, enter your information in the form below and click the “Get Book” button.
Filling out an expense cash order form KO-2
The operation for issuing cash is formalized by a cash receipt order form KO-2, the form and sample of filling out this form can be downloaded for free below. The form is drawn up according to a unified form and does not allow errors or corrections when filling out.
The order is drawn up by the person responsible for maintaining the cash register; the document is drawn up in one copy. A completed cash order must be certified by the cashier's signature. The signature of the director of the organization is not required if the document is accompanied by other documentation that contains the signature of the director.
The reverse operation of accepting cash at the cash desk is formalized by cash receipt order KO-1. Completed samples of cash orders are used as justification for making entries in the KO-4 cash book.

Sample of filling out form KO-2
A standard cash receipt order form is filled in with information in the following sequence:
- basic information about the organization filling out form KO-2 is filled in (name, OKPO, division);
- the cash receipt order is assigned a number; it should not be repeated within a year;
- the date of the consumable must correspond to the day the cash is issued;
- the “debit” field is filled in by the accountant, the department code is indicated here, the account where the cash is credited (60 when paying a supplier, 76 when paying another counterparty, 71 when issuing a report, 70 when paying wages, etc.), if analytics is carried out on specified account, then the analytical account code is entered;
- the “credit” field is also filled in by the accountant; in this field of the KO-2 form the account number from which cash is debited is entered (account 50, subaccount can be indicated);
- the amount - in numbers - is paid in full, down to kopecks;
- the intended purpose code is filled in only when funds are spent for the intended purpose;
- in the “issue” line, you should fill in the information about the person to whom the money is issued, this can be an employee of the organization receiving a salary or accountable funds, or a representative of the organization receiving money for goods and services supplied;
- in the “grounds” field, you need to explain the purpose of the amount paid under the cash receipt order - for example, payment to ABS LLC for the supply of goods under supply agreement No. 1-p dated 04/01/2017, or “issuance on account for payment of goods under invoice No. 12 dated 04/01/2017";
- capital form of the amount of money issued;
- appendix - documents accompanying the transaction, on the basis of which the KO-1 cash order is issued (For example, an application from an accountable person, an invoice, etc.);
- signature of the manager and cashier;
- At the bottom there is space for a receipt of receipt of cash in the specified amount, in this section of the KO-2 form you need to confirm the fact of receipt and indicate your full name and passport details, the recipient confirms receipt with his signature.
Representatives of other organizations to which cash is issued are required to submit a power of attorney to receive money (if this is not the director of the company). Raising is unacceptable. The details of the power of attorney are entered into the KO-1 cash receipt form, and the original power of attorney is attached to the consumable form.
Documents accompanying transactions and attached to the order are marked with a “paid” stamp indicating the date of the transaction. Next, form KO-1 is submitted to the accounting department.
Form and sample design
Cash order form form KO-2 - download.
Sample of filling out cash receipt order KO-2 - download.
Expense cash order (form KO-2) in 2017
What it is
Expenditure cash order (RKO)- this is one of the cash discipline documents that is drawn up at each extradition cash from the cash register. The RKO is formed in one copy by an accounting employee and signed by the head of the organization, the chief accountant, the cashier and the person receiving the funds.
note, starting from June 1, 2014, a simplified procedure for maintaining cash discipline is in effect, according to which individual entrepreneurs are more not obliged draw up cash documents (PKO, RKO and cash book).
RKO form (form KO-2)
Expense cash order (form KO-2), valid in 2017:
How to fill out RKO
Instructions for filling out the cash receipt form
In line "Organization" the legal form is indicated (LLC, CJSC, etc.) and the name of the organization (for example, LLC “Company”).
In line "OKPO code" it is necessary to indicate the OKPO code in accordance with the notification received from Rosstat. If the code has not been assigned, put a dash.
In field "Document Number" the serial number of the cash register is indicated (the numbering of incoming and outgoing cash documents during the year must be continuous, and start anew from the beginning of the next year).
In field "Date of preparation" the date of issue of money from the cash register is indicated in the format DD.MM.YYYY (for example, 03/05/2016). RKO must be issued on the day the money is issued from the cash register, so the date of issue of money and the day the order is generated coincide.
In the column "Structural unit code" indicate the code of the division of the organization issuing cash settlements (if the organization does not have structural divisions, put a dash).
In the column “Corresponding account, sub-account” the account number is indicated, the debit of which reflects the issuance of money from the cash register in accordance with the chart of accounts:
- 51 – delivery of money to the bank for crediting to the current account;
- 60 – settlements with suppliers and contractors;
- 70 – settlements with employees regarding wages;
- 71 – settlements with accountable persons;
- 73 – settlements with employees for other transactions;
- 75-2 – settlements with founders for payment of income.
Count "Analytical Accounting Code" filled in only if the corresponding codes are available.
In the column "Credit" the number of the accounting account is indicated, the credit of which reflects the issue of money from the cash register (as a rule, this is the account 50.1 – “cash desk”).
In the column "Sum" The amount of money dispensed from the cash register is indicated in numbers.
Count "Destination code" filled out if the organization uses the appropriate coding system in its activities. In this case, the code for the purpose of using the retired funds is indicated.
In line "Issue" The full name of the individual is indicated (in the dative case, for example, Ivanov Ivan Ivanovich) or the name of the organization to which funds must be issued.
In line "Base" it is necessary to indicate the basis for issuing money from the cash register, for example: "Issue of financial assistance" or "Depositing money to the bank" etc.
In line "Sum" The amount of money dispensed from the cash register is indicated in words. In this case, rubles are written with a capital letter, and kopecks with numbers. In empty fields you must put a dash.
In line "Application" the attached primary documents are reflected, indicating their numbers and dates, on the basis of which money is issued from the cash desk (powers of attorney, receipts, orders, statements, etc.).
Note: the manager does not have to sign for the cash register if he makes an authorization inscription on the attached documents to the cash receipt order.
String "Received" filled out by the person to whom money is given from the cash register. In it, he indicates the amount of money received (in this case, he must write rubles in words with a capital letter, and kopecks in numbers). Next is his signature and the date of receipt of the money.
When issuing money via cash register, the cashier must check identity document recipient (passport or other document). The cashier indicates the name, number, date and place of issue of this document in the corresponding line of the cash register.
Line "Given out by the cashier" filled in by the cashier only after the cash is issued via cash register. In it he puts his signature with a transcript (last name and initials).
Fully filled the order remains in the cash register enterprise (and not handed over to the recipient of the money) and serves as confirmation that the funds were issued legally.
note, it is prohibited to make corrections in the cash receipt order.
Samples of filling out cash registers in 2017
Below are examples of filling out the cash receipt order form in 2017:
How is the KO-2 cash receipt order filled out?
If the receipt of cash at the cash desk is formalized using the KO-1 receipt order, then when issuing funds from the cash register, the unified form KO-2 is filled out. Once completed, this document is also subject to mandatory registration in the KO-3 journal, and the money issuance operation itself is reflected in the KO-4 cash book, indicating the number and date of the “consumables”.
An order is a monetary document that does not allow any kind of errors, corrections are not allowed, so be careful.
The KO-2 form is filled out at the time of issuing money to the recipient; the recipient can be an individual - an employee of the organization to whom the amount is issued on the basis of his application, as well as a third-party individual, a representative of another organization - in this case, the recipient must present a passport or power of attorney for receiving the money.
Sample filling
Filling out the standard form KO-2:
When registering an expense cash order, you need to fill in the following lines:
- name of the organization filling out the form;
- its OKPO code;
- structural unit - for example, a retail outlet, the name of one of the stores, you can put a dash here;
- expense order number – serial number from the beginning of the year, taken from the KO-3 registration journal;
- date – the date of compilation of the consumables, coinciding with the date of issuance of money from the cash register to the recipient;
- debit – in this column you need to fill in the code of the structural unit (if you indicated this unit above and your organization uses a coding system), debit of the account in which the amount issued will be reflected (depending on who the money is given to and for what purpose), analytical code accounting (if such accounting is maintained for this account);
- credit – cash accounting account number – account 50 “Cash”;
- amount – we write in numbers the amount given to the recipient;
- designated purpose code - depending on the purpose and to whom the cash is issued, the appropriate code must be indicated here; if the organization does not provide such a coding system, then a dash is added;
- issue – surname, name, patronymic of the individual in the dative case to whom the money is issued;
- basis - the document that served as the basis for drawing up the cash order is indicated, this can be a payroll when issuing wages, a statement from the employee when issuing money for reporting, sales documents, a check;
- amount - the amount is written in words with a capital letter, if there are kopecks, then they are indicated in numbers;
- application – here the primary documents accompanying the operation of issuing money from the cash register are reflected;
- signatures of the manager and chief accountant.
After the above information is entered into the cash receipt order, the money is transferred to the recipient. After they are recalculated, the recipient must fill out the following lines of the form:
- received - writes the amount received in words, kopecks in numbers;
- date of receiving;
- recipient's signature;
- by – name of the recipient’s identity document.
After all this, the cashier who issued the money also signs the document.
The standard KO-2 form has been filled out, see a sample cash receipt order below, and at the very end of the article you will find a link where you can download the KO-2 form.

Download the form and sample
Cash receipt order form KO-2 - download.
The article was written based on materials from the sites: pravodeneg.net, prednalog.ru, blandoc.ru, www.malyi-biznes.ru, buhland.ru.