Tomatoes can be grown both outdoors and in greenhouse conditions. To obtain a high-quality harvest, this vegetable crop requires special care and prevention of various diseases in any growing conditions.
If you look at the diseases of tomatoes in the photo, you will notice that many diseases affect not only the leaves and stems, but also the fruits. Diseases of tomatoes can be conditionally divided into infectious and non-infectious. Infectious diseases include fungal, bacterial and viral lesions, brief information about which you can see here and below. We will also talk about tomato lesions that are non-infectious.
Some infectious diseases
Mosaic is one of the most common viral diseases of tomatoes. Moreover, this disease can affect not only greenhouse plants, but also those plants that grow in open soil. The mosaic affects the leaves, changing their color and shape. First, yellowish-green spots appear on the leaves, while they begin to wrinkle and curl. As a result, tomatoes practically do not bear fruit, turn yellow and die.
Plants affected by the mosaic are recommended to be pulled up and burned. To prevent the appearance of this disease, the seeds should be treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and subsequently also water the seedlings with it once every three weeks. Passionate also refers to the preventive measures of this disease.
Some tomato diseases in the photo give a clear idea of the course of the disease. For example, the brown spot of tomatoes is characteristic of film greenhouses and manifests itself in the formation of brown spots with a velvety gray bloom on the underside of the leaf. Accordingly, the plant dies. The disease is spread by spores of the fungus, therefore it is easily transferred to other healthy plants.
Brown spot develops actively at high humidity. Therefore, as a preventive measure, it is necessary to stop abundant watering and ventilate the greenhouse well. And after removing ripe fruits, spray the plants with foundation.
Non-communicable diseases
Watering errors
Signs of suboptimal watering are often confused with infectious diseases.
With a lack of moisture, tomatoes slow down growth, abundantly throw off ovaries and flowers. The leaves fall down, turn yellow at the tips and wrinkle. To bring the plants to their senses, it is not recommended to flood them with large amounts of water at once. It is better to give them some settled water and water it after a couple of days as expected.
Excess water also affects the development of the tomato. Most often, stagnant water causes decay of the roots, the leaves on tomatoes fade (old and young at the same time) and they begin to fall off. The root collar may develop watery or brown spots. If it is immediately impossible to carry out drainage work in such areas, then it is better to transplant the bushes, slightly cleaning the roots from rot.

Improper watering can lead to cracking of tomato fruits. This usually happens when, in the heat, summer residents suddenly appear on the site and, seeing a dull picture in the garden, rush for a hose. Plants are shocked by the sharp supply of water and quickly supply it to the ovaries. The integumentary tissues burst and infections can enter. It happens that the tissues overgrow in time, create a new coating. It has been noticed that tomatoes are prone to cracking when overfeeding with mineral water.
Sunburn
Burnt areas on tomato fruits are whitish spots of various sizes. It happens that solar radiation burns a very large part of the fetus. The wounds that appear under the influence of rays dry out over time and do not allow the fruit to develop. Then they wilt, and the taste of such fruits is greatly deteriorated.
Top rot
This non-infectious form of the disease is very typical for greenhouse tomato cultivation. It manifests itself at low humidity (about 40%) and high temperatures, as well as with an excess of nitrogen. Such extreme conditions for the development of tomatoes cause the outflow of nutrients from the fruit, metabolism is disrupted, tissues are destroyed.
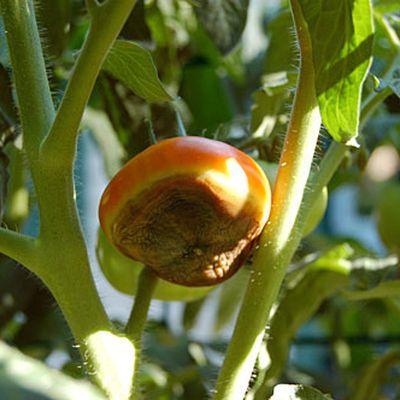

Initially, green oily-watery spots appear on unripe fruits (as a rule, on the first set clusters). Then they acquire a brown hue and, as it were, are pressed into the fruit and thicken, having a concentric shape at its top. Affected fruits begin to ripen faster, become a place of penetration of secondary infections, and can rot and fall off.
If you have not previously encountered such a disease, then it can be easily identified from the photo, unlike many other diseases, where you have to analyze the symptoms in a complex. To prevent the appearance of apical rot, the following measures are necessary:
- Greenhouse ventilation;
- Regular watering;
- Introduction of calcium into the soil before planting;
- Strict control of applied nitrogen doses.
If the greenhouse is installed in the country and during the week there is no way to control the level of moisture in the soil, then it is better to install an automatic water supply. There are all kinds of sensors and programmable relays (timers) that will help ensure at least daily watering. Such devices work both from the mains and from alkaline batteries.
For automatic ventilation of greenhouses, special transoms are installed, which, depending on the ambient temperature, rise by themselves, providing an influx of fresh air. They are autonomous and volatile.
So, when you determine the causes of deviations in the development of a tomato from a photo, keep in mind that diseases can be infectious and non-infectious. In the latter case, it is important to observe the dosage of mineral water, observe the modes of lighting, watering and airing.
OgorodSadovod.com
Diseases of tomatoes and their treatment - from A to Z about diseases of tomatoes
Fungal diseases of tomatoes and their treatment
The most common are fungal diseases, which can appear at low temperatures, due to heavy rainfall, due to improper care of seedlings.
Fight against tomato diseases:

The main thing is that you must carefully read the instructions for each of the listed drugs, so as not to oversaturate the plants with them. After all, this can also harm tomatoes no worse than diseases.
Tomato bacterial diseases and their treatment
There are various bacterial diseases of tomatoes and control measures. It is advisable to know in advance what sores threaten your garden in order to prevent the appearance of diseases. Otherwise, you are in danger of losing your crop, and diseases can spread to other crops in your garden.

Protection and treatment of tomatoes from diseases: prevention
As you understand, there are a wide variety of diseases, and their treatment is a rather complicated process. That is why it is much easier to prevent the appearance of an infection in your garden than to fight it. And gardeners should know the basic preventive measures to protect the beds from disease. For example, tomato seeds should not be planted near potatoes, or in the beds where you previously grew eggplants and peppers.
And if the crops were sick with something, then it is not advised to plant any horticultural crops on this site for at least three years.
Try not to thicken the planting, remove the lower leaves, carry out weed control. It is also important to water the plants in doses without overmoistening them, because a high level of humidity is one of the reasons for the appearance of fungal diseases. Loosen the soil more often, do not overdo it with nitrogen fertilizers, and avoid using fresh manure as fertilizer. It is necessary that the planting of vegetables takes place according to all the rules: choose the seed material correctly and take care of the plants.

Preventive protection of tomatoes against diseases:
- Before planting, treat the seedlings with a 0.5% solution of Bordeaux liquid, and after a week, repeat the work.
- Treatment with copper chloride helps (40 grams of the drug is used for a 10-liter bucket of water), however, work must be carried out at least 20 days before harvesting.
- You can sprinkle the soil with ash or prepare an ash infusion (200 g of ash is boiled for about 10 minutes in a liter of water, filtered through cheesecloth, and then the liquid is poured into 10 liters of water).

Preventive measures taken in advance will help you reduce the risk of not only diseases, but also various pests on your site. The main thing is to carry out all the work in a timely manner so that the infection does not have time to penetrate the plant.
nasotke.ru
How to deal with tomato top rot. What is this disease, photo
Summer residents and avid gardeners often grow tomatoes. They know that in order to get a good result, you need to have information about all diseases of the culture. Therefore, the question is: "How to deal with the top rot of tomatoes?" - is quite common. This disease can affect vegetables both outdoors and in greenhouses.
Infectious spot
Top rot very quickly captures most of the tomato. The disease first begins to manifest itself on the green fruit below. Then a watery spot becomes visible on the top of the tomato. It is darker than a green vegetable. Over time, the stain will change and be dry and greyish brown. It will take on a dense skin, which will crack and affect the entire fruit. Therefore, you need to know how to deal with the top rot of tomatoes. Otherwise, there will be no harvest.
 The dry skin of the spot is pressed into the depth of the tomato. The disease affects the entire vegetable with mold. The tomato pulp is populated with saprophytic mushrooms. They damage the tissue, which then simply rot. Sometimes it happens that the fruits do not rot, but dry out. In some cases, no signs of the disease are visible on the tomatoes. The vegetable is damaged inside, ripens earlier than healthy fruits and falls off. Such tomatoes are not suitable for consumption. They have low taste, you cannot process and use seeds as planting material.
The dry skin of the spot is pressed into the depth of the tomato. The disease affects the entire vegetable with mold. The tomato pulp is populated with saprophytic mushrooms. They damage the tissue, which then simply rot. Sometimes it happens that the fruits do not rot, but dry out. In some cases, no signs of the disease are visible on the tomatoes. The vegetable is damaged inside, ripens earlier than healthy fruits and falls off. Such tomatoes are not suitable for consumption. They have low taste, you cannot process and use seeds as planting material.
Conditions for the spread of the disease
Before you start growing tomatoes, you need to learn how to deal with tomato top rot. It is also advisable to understand from what conditions it can begin. What should be done in advance?
The most important cause of the disease is the violation of water equality. This is if there is a lack of moisture in the cells of the vegetable at an external high temperature. When the crop grows outdoors and in hot climates, evaporation increases. From tomatoes, moisture will mix into the leaves, this leads to dehydration and death of the fetus. Tomato (top rot) disease is very common and is well known among gardeners. Indeed, in our country in the summer there is a lack of moisture, and the air temperature reaches 30 degrees above zero.
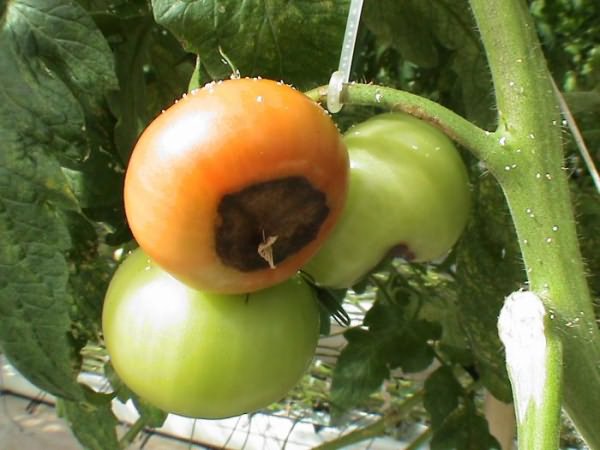 Before you deal with tomato apical rot, you need to find out all the reasons for the appearance of this disease. For example, lack of calcium and uneven watering. Therefore, to prevent rot, you can spray the culture with calcium nitrate. Such actions must be performed a couple of times every seven days. It is worth diluting forty to fifty grams of calcium nitrate for five liters of water.
Before you deal with tomato apical rot, you need to find out all the reasons for the appearance of this disease. For example, lack of calcium and uneven watering. Therefore, to prevent rot, you can spray the culture with calcium nitrate. Such actions must be performed a couple of times every seven days. It is worth diluting forty to fifty grams of calcium nitrate for five liters of water.
Root dressing
The most common disease is tomato apical rot. The treatment of the culture is to process the plant at the stage of fruit set. If rot is not stopped, it will become a source of new infections: gray and brown rot, fungal diseases.
 When brown spots appear, root top dressing should be done immediately. It is desirable that these were complex fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. Ash can also be added under the root. Calculation: dilute 250 grams of ash per 10 liters of liquid. Ash contains zinc and iron, sulfur and calcium, phosphorus and potassium. When planting, a fresh solution is added to the dug hole. When feeding an adult plant, add 5 grams of superphosphate to the water with ash.
When brown spots appear, root top dressing should be done immediately. It is desirable that these were complex fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium. Ash can also be added under the root. Calculation: dilute 250 grams of ash per 10 liters of liquid. Ash contains zinc and iron, sulfur and calcium, phosphorus and potassium. When planting, a fresh solution is added to the dug hole. When feeding an adult plant, add 5 grams of superphosphate to the water with ash.
Presowing processing methods
The disease most often affects tomatoes that are grown in greenhouses. Top rot of tomatoes in a greenhouse is a very common occurrence, the disease quickly begins to destroy the fruits. In the open field, the nightshade plant is also susceptible to disease. Methods for saving tomatoes must be taken in advance.
Often summer residents and gardeners buy more resistant varieties of tomatoes. This method is the safest, it is environmentally friendly and profitable. Also, hybrid varieties are very resistant to top rot. For example: Bolshevik F1 and Glombe master F1, Benito F1 and Pharaoh F1, Rotor F1 and the Grand Canyon and many others.
 After the final harvest, you need to carefully dig up the site. Collect the roots of affected tomatoes. Then carry out deep plowing again. For the next season, do not plant tomatoes in this place, this can be done only after three years.
After the final harvest, you need to carefully dig up the site. Collect the roots of affected tomatoes. Then carry out deep plowing again. For the next season, do not plant tomatoes in this place, this can be done only after three years.
Disinfection of seeds
Top rot of tomatoes in a greenhouse is very common. Experienced gardeners take measures in advance to prevent it.
You can soak them in a solution of one percent potassium permanganate or twenty percent hydrochloric acid three months before sowing seeds. This will disinfect the planting material. The prepared seeds are placed in cheesecloth and tied. Then they put it in a container and fill it with a solution. You need to hold the planting material in the liquid for about half an hour. In this case, the solution should fill the seeds completely. Then the planting material is washed in water for 15 minutes and allowed to dry.
Succinic acid solution
Almost all measures to combat top rot of tomatoes consist in pretreating the seeds. After all, you need to take care of a healthy plant by taking care of the planting material.
 This approach increases the percentage of plant resistance to infectious diseases. It can be not only the top rot of tomatoes. Photos of the infection on tomatoes show how it affects the entire fetus. So, let's figure out in what solution you can still soak the seeds. Dissolve 17 milliliters of succinic acid in one liter of water. You can also use 1% zinc sulfate solution. It is necessary to keep the seeds in liquid for at least a day. This method will not only make the plant more resistant to infectious diseases, but also accelerate the process of fruiting and ripening of the tomato itself.
This approach increases the percentage of plant resistance to infectious diseases. It can be not only the top rot of tomatoes. Photos of the infection on tomatoes show how it affects the entire fetus. So, let's figure out in what solution you can still soak the seeds. Dissolve 17 milliliters of succinic acid in one liter of water. You can also use 1% zinc sulfate solution. It is necessary to keep the seeds in liquid for at least a day. This method will not only make the plant more resistant to infectious diseases, but also accelerate the process of fruiting and ripening of the tomato itself.
syl.ru
Diseases of the tomato. Fight Tomato Disease
Types of tomato diseases. Prevention of tomato diseases. How to fight tomato diseases?
It is known that tomato leaves have insecticidal properties, so their infusions and decoctions are used against aphids, leaf-eating pests, caterpillars of the apple moth, caterpillars of the cabbage scoop and onion moth, against the gooseberry sawfly and moth. Planting tomatoes in the aisles of gooseberries also scares off the sawfly and moth. All this is true, but the tomatoes themselves are attacked by pests and the invasion of various diseases.
Late blight
This is the most common and dangerous disease affecting tomatoes. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus that infects fruits, leaves and stems. At first, the disease usually manifests itself on the leaves of the potato and, if it grows nearby, then after a couple of weeks the infection can spread to the tomatoes. First, spots appear on the leaves of tomatoes, and then they dry out and die off (do not confuse with the natural death of leaves in determinant varieties). Damp and cool weather contributes to the development of late blight. However, the development cycle of the fungus, fortunately, is quite long, and even in cool summers, damage to plants in our climatic conditions in open ground does not appear until the beginning of August. Therefore, early ripening varieties generally have time to ripen before the onset of the mass spread of the disease. Such varieties can be grown every year without chemical treatments, without fear of a decrease in yield due to late blight.
To prevent the disease, it is imperative to isolate the potatoes from the tomatoes, and to deeply dig the soil every season. Control measures are spraying the plants with an infusion of garlic during the period of fruit setting every two weeks (grind 50-100 g of cloves, leave for a day, dilute with water up to 10 liters), regular treatment of plants with 1% Bordeaux liquid, and at the first signs of the disease - treatment 10 % sodium chloride solution. If spots appear on the fruits, it is necessary to remove all formed tomatoes and warm them for 1-2 minutes in hot (not higher than +60 ° C) water. In this case, the skin of the fruit will become wrinkled, ugly, but the fruit will ripen and have a normal taste.
Apical rot of the fruit
With this disease, a watery, yellowish-green spot appears at the top of the fruit, then a brownish spot, indicating the beginning of decay. Top rot is caused by bacteria that persist on plant debris and on weeds of nightshade. The disease spreads in damp weather, mostly affecting large-fruited varieties with delicate skin. In greenhouses, this disease develops at high temperatures and low humidity. The disease is aggravated by a lack of potassium in the soil. The application of phosphorus-potassium fertilizers increases resistance to disease.
An effective method of combating top rot is the treatment of plants with phytosporin. Spraying with 0.3-0.4% calcium chloride, Bordeaux liquid or its substitutes helps. For the prevention of disease, it is recommended to process seeds before planting.
Spotted fruit ripening
This disease is characterized by the appearance of yellow spots on the surface of the fruit, which become almost transparent by full ripeness; there is dead tissue under the skin. Disease prevention is considered to be feeding with potassium nitrate.
Hollowness of fruits
Signs of the disease - when pressed, the fruits shrink like a ball, empty chambers are visible on the cross section. This is the result of poor pollination of the flowers. Disease prevention - additional pollination (shaking plants in the morning), feeding with potassium sulfate.
Blackleg
Seedlings are affected, its root collar darkens, becomes thinner and rots. In this case, the plant withers and dies. The disease spreads with plant debris, lumps of soil, partly with seeds.
Control measures are moderate watering of plants, sufficient distance between shoots. To prevent the disease, trichodermin is introduced into the soil before planting.
Brown leaf spot
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus that infects leaves, stems, and less often fruits. The first signs of the disease appear on the lower leaves during flowering and fruit setting. Then the disease spreads to the upper leaves, this happens during the ripening of the fruit. The fungus spreads at high air humidity, while several hours of high humidity are enough to infect plants. The incubation period of the disease is 10-12 days. The spores of the fungus tolerate dryness and freezing well and remain viable for up to 10 months. At humidity below 70%, the disease does not spread. To prevent the disease in greenhouses and greenhouses in the fall, plant waste is burned, the soil is changed.
A good means of combating this fungus is the treatment of plants with solutions of basezol and phytosporin.
Dry spot, or macrosporiosis
She is also a brown spot. This is a fungus that infects leaves, stems and, less often, fruits. Round brown spots with concentric circles form on the leaves. Gradually, they merge and the leaves die. Then the stems die off, depressed round spots appear on the fruits, very dark, mainly at the stalk. The fungus spreads well with watering, rain and wind.
The spots are treated with a copper-soap emulsion, taking 20 g of copper sulfate and 200 g of soap per 10 liters of water. The affected tops are mowed 7-10 days before harvesting, collected in heaps and burned.
Fusarium wilting
It develops in young plants in greenhouses. The veins of the leaves brighten, the petioles droop, the leaf turns yellow, withers, and shoots can wither. At the same time, plant growth dies out. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus that develops at high temperatures, low soil moisture and poor lighting. The causative agent of the disease remains in the soil for a long time. The fungus penetrates through the roots and water-carrying vessels of the plant. Plants wither, as the mycelium clogs blood vessels and poisons the plant with toxins released during its life. To prevent the disease, it is necessary to maintain the optimal temperature regime in the greenhouse, and at the first signs of the disease, remove the affected plant along with the roots and a lump of earth.
To combat the disease, plants are sprayed with a solution of foundationol or phytosporin.
Gray and white rot of fruit
These rot usually develop at the base of the fruit. Gray mold is a watery gray spot that quickly spreads to the entire fruit. When affected by white rot, the fruit is covered with white mycelium. Fight these diseases with phytosporin.
Streak, or streak
This disease is caused by the tobacco mosaic virus. Irregular spots appear on the leaves of tomatoes. On the petioles, stems and peduncles, surface intermittent stripes of a red-brown color are formed. Brown streaks can also be seen on the fruit. As a result, the leaves of plants die off, the stem becomes fragile and easily breaks, sometimes the top of the plant dies off. Streak develops at a temperature of 15-20 ° C, at 24 ° C and above, the disease stops. The incubation period of the disease is 10-14 days. The streak virus persists on post-harvest residues and on seeds.
In order for the virus to spread less, the affected plants and plant debris must be burned, and the plants must be treated with phytosporin.
Tomato bacterial cancer
It is a bacterial disease. The optimum temperature for the development of bacteria is 25-27 ° C, bacteria die at 50-53 ° C. Bacteria enter the plant through wounds and first affect the vascular system. Sources of infection are seeds and last year's plant debris. Bacteria in the soil persist for no more than a year, and on seeds for 2.5-3 years. During the growing season, cancer can be transmitted by insects, watering and equipment. Small brown sores appear on the leaves, stems, petioles and stalks of tomatoes, and spotting appears on the fruits. On green fruits, the spots are white with dark small cracks in the center, and on ripe ones they are brown, surrounded by a light halo. The spots are located closer to the stalk.
Cancer prevention: burning plant residues in the fall and treating seeds before sowing, which consists in soaking them for 12-24 hours in a phytosporin solution.
ped-kopilka.ru
Diseases of tomatoes (with photo)
What tomatoes are sick with
Top rot of fruit 
This attack appears even on green fruits - in the form of a brown or black top. All this is due to a lack of calcium, or its conflict with potassium, when one blocks access to the plant for the second.
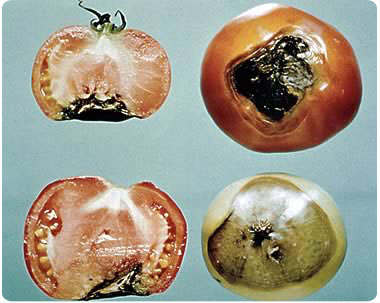
To prevent this disease, even when planting seedlings, 1 tbsp. calcium nitrate and some charcoal. Or, as an option, spray already green fruits with a solution of calcium nitrate.
Fusarium wilting
This fungal disease affects seedlings and young plants. The infection gets through the roots, and is masked by the alleged lack of water to the plants. As a result, the tomatoes wither, the lower part of their leaves turns yellow, and the stem turns black and becomes cracked. 
In order to prevent this, it is important to observe crop rotation, and the disease can be treated with the drugs Trichodermin and Previkur.
Gray rot
This fungus appears in cold, rainy weather, affecting leaves, stems, inflorescences and fruits. You can recognize it by its dark gray patches. 
At the time of bad weather, 2-3 lower leaves on the plants should be cut off - this will increase the air circulation of the lower tier, and after the weather improves, everything will pass.
Late blight or brown rot of tomatoes.
This most dangerous disease can be calculated by the brown spots of yellowing on the drying leaves.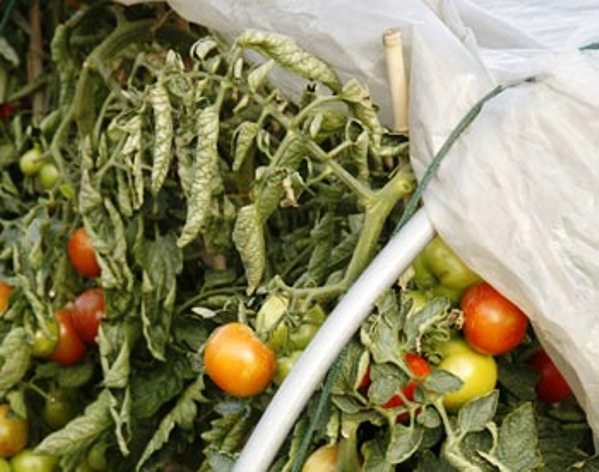 
Soon these spots spread to the fruits themselves, until the entire crop is affected. And all because of the high humidity - that's why only drip irrigation or root watering is suitable for tomatoes. 
After phytophthora has already put its marks on the plant, it is very difficult to change the situation. The best thing, of course, is not to forget about prevention.
If there is nothing at hand, and the tomatoes turn black, use the Bordeaux liquid, proven for decades - spray every week.
It is very effective against late blight tomato disease and processing tomatoes with freshly prepared garlic infusion. It can be sprayed up to five times per season at intervals of 15-18 days. 1.5 cups of mashed garlic, 1.5 g of potassium permanganate and 2 tbsp. l. Dissolve the grated laundry soap in 10 liters of water, stir, strain and process the bushes, spending 100-150 g of the mixture for each m2.
And here is the advice of an experienced gardener: "In mid-June I spray the tomatoes with a weak solution of potassium permanganate. After a week, with a solution of boric acid (1 tsp of boric acid per 10 l of water). A week later, with a solution of iodine (1 tsp for 10 l of water). This is quite enough for the whole summer." ...
This tomato variety never suffers from late blight. 
Watch the weather. As soon as the thermometer begins to hang at around +10 ° C at night, it is undesirable to leave the tomatoes on the bushes. It is better to remove unripe, then the chances of saving and preserving them will be much greater. And so that the apparently healthy tomatoes that have been removed do not turn black, immediately after harvesting, immerse them in hot (up to 60 degrees) water for 1.5-2 minutes. At the same time, the skin will wrinkle, become ugly, but the fruits will ripen and will have a normal taste.
There is another forecast method: if late blight appeared on potatoes, then wait for its appearance in 5-7 days on tomatoes. The fact is that the pathogen is mainly stored in the potato tubers, therefore, during the entire growing period, the infection accumulates and under the first favorable conditions the disease appears on this crop. Then it is transferred with air currents to the tomatoes.
Tomato septoria, or white spot
It can appear on seedlings in greenhouses and greenhouses in the form of separate foci, white spot is found almost everywhere where tomato is grown, but especially in areas with sufficient moisture. 
Disease of tomatoes Septoriosis manifests itself on the leaves, first of the lower tier, and then of the middle and upper ones in the form of small, first brown, later off-white spots with a dark brown border. Spots appear throughout the growing season, especially on mature plants.
Early varieties are especially strongly affected by septoria. 
Control measures:
1. Careful collection and destruction of dry leaves while removing severely damaged green leaves.
2. Correct agronomic care of plantations.
3. Selection of varieties that are more resistant to the disease.
4. Carrying out three times spraying with 1% Bordeaux liquid in the following terms: the first - at the moment of exposing the buds, the second - 10 days after the first, the third - immediately after harvesting.
When spraying, make sure that the solution also falls on the underside of the leaves.
Tomato mosaic
The primary source of infection is infected seeds. Individual plants also become infected through infected soil. The tobacco mosaic virus quickly spreads from plant to plant during care, when the hairs (pubescence) of leaves and stems are injured - when picking, planting seedlings, pinching, tying plants, cutting leaves, harvesting.
 |
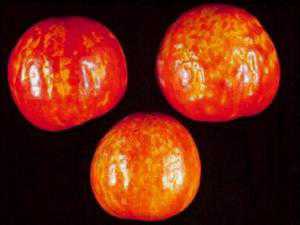 |
Control measures
To avoid mosaic disease, tomatoes should not be planted in the same place next year. For growing seedlings, only pickled seeds should be used.
For preventive purposes, healthy seedlings should be watered once every 2 decades with a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 2 months after planting in a permanent place.
Hybrid "Evpator" does not get sick at all, a brush of even beautiful fruits. 
Here's what they write about him:
promising tomato hybrid recommended for extended turnover. One of the earliest among the indeterminate hybrids of the latest selection, sets fruit well at early planting dates. Suitable for both ground greenhouses and low-volume cultivation. Plant with an open habit, vigorous, vigorous. The average fruit weight is 130-150 g, it contains 4-6 seed chambers. The hybrid is genetically resistant to all tomato diseases.
Black leg of tomatoes 
Upon reaching about 1 cm, the plant falls and dies.
Tomato blackleg is a tomato disease caused by fungi. It manifests itself most often due to improper regime and poor ventilation of greenhouses and greenhouses during growing seedlings. The lower part of the tomato stem (root collar) turns black, becomes thin and rots.
Blackleg is a fungal disease. There are almost no tomatoes in normal soil. Try spilling your throat with furacilin solution.