Despite the similar names of diseases, pathogens, symptoms and drugs against them are different.
| signs | powdery mildew | downy mildew |
| Pathogen | Mushroom oidium | peronospore mushroom |
| Mycelium | From the top side of the leaves | On the underside of the leaves |
| Manifestations | White powdery coating | On the underside - a white-purple coating, on top - yellow oily spots |
| What strikes | More often greenhouse cucumbers | It spreads most strongly in greenhouses. Rarely found outdoors |
| favorable conditions | Sharp changes in day and night temperatures | Rainy and cold summer |
| Spreads | With soil, water, plant residues. During sporulation, the spores are dispersed by the wind. | With plant residues, water, infected seeds |
Drugs for the treatment of diseases are also different.
Powdery mildew (ashtray)
This is perhaps the most common. In protected ground, it spreads instantly and its harmfulness is enormous. In open ground, powdery mildew is less common, does not spread so rapidly, and therapeutic measures give a much greater effect than in a greenhouse.
Description of the pathogen.

Conditions for the onset of the disease
Favorable factors for the development of the disease on cucumbers are strong temperature drops - more than 10 ° C. Increased humidity promotes the spread of powdery mildew. It spreads most strongly in wet summers. Even if the weather is hot, but rainy, with high humidity, powdery mildew still affects plants, though not as much as in a cold and damp summer. The first foci appear:
- in the greenhouse - at the doors, vents, film breaks;
- outdoors - in the wettest places of the borage. Most often, lesions appear a few days after heavy rains;
- thickened plantings, both in open and protected ground, are the first to be affected by powdery mildew.
The incubation period lasts 3-5 days, when the cucumbers are already infected, but there are no signs of the disease yet.
Signs of powdery mildew damage to cucumbers

- Leaves, petioles and stems of cucumbers are affected.
- Spots of white powdery coating appear on the leaves from the upper side, which are initially easily erased from the surface. But after a few hours they appear again.
- The spots gradually merge with each other, the edges of the leaves are slightly bent down and dry.
- Severely affected leaves become wavy, dry and fall off.
- With a wide distribution of powdery mildew, the stems are affected. Pads of white fluffy coating appear on them, but not as thick as with white rot. The lashes begin to dry.
Zelentsy do not suffer from powdery mildew, but the yield when affected by a pathogen is reduced by 40-50%. Zelentsy themselves become small and bitter.
Fighting disease with chemicals
Treatment is carried out immediately upon detection of the first signs. It should be taken into account that the infection of healthy plants occurs rapidly, and the slightest delay can lead to a shortage of crops and death of plants.
- Colloidal sulfur - the main drug against powdery mildew - is not used in the greenhouse. In a greenhouse, where the temperature and humidity are high, even a normal concentration of the drug can cause severe burns of cucumbers, and if the concentration is exceeded, even slightly, plants can be killed. In open ground, treatment with sulfur preparations is best done in cloudy weather. Prepare the working solution strictly according to the instructions. When processing with sulfur and its derivatives, the air temperature should be at least 20°C and not more than 32°C. At low temperatures, the drugs will not work, at high temperatures they are phytotoxic, that is, they kill plants. Colloidal sulfur is sold in pure form in garden stores, a preparation based on it is Thiovit Jet. All cucurbits, and cucumber in particular, are very sensitive to sulfur, so a single treatment is carried out. It is impossible to spray cucumbers with sulfur-containing preparations several times during the growing season.
- Application of fungicides: Rayok, Tilt, Topsin-M, Topaz, Bayleton. Re-treatment is carried out after 14 days, changing the drug, since the pathogen very quickly becomes resistant to drugs.
- At an early stage, the biopreparation Alirin B. is used. The soil bacteria contained in it at a very early stage are able to destroy the pathogen. It is usually used if there is a high risk of disease. Processing is carried out 2-3 days after heavy rains.
Folk remedies
Used for the prevention and treatment of the initial stage of the disease.
With any method of treatment, all affected leaves are removed necessarily.
Disease prevention
- If from year to year powdery mildew appears in the greenhouse, then a layer of earth of at least 10 cm is removed, replacing it with a new one.
- In autumn, all plant residues are removed.
- The greenhouse is disinfected by burning sulfur bombs in it, or the structures are washed using disinfectants.
- Thinning thickened crops, since it is there that the first foci of the disease most often appear.
- Thorough ventilation of greenhouses. Reducing humidity also reduces the risk of powdery mildew.
- Removal of weeds around the perimeter of the borage.
Varieties resistant to powdery mildew
Currently, a sufficient number of them have been bred, both hybrids and bee-pollinated varieties. Resistant means that if the pathogen spreads slightly, cucumbers are not affected. With a strong outbreak of the disease, only individual leaves on the cucumber are affected, while the main part of the cucumbers does not get sick.
| Powdery mildew resistant hybrids | |
|
|
| Varietal bee-pollinated cucumbers with disease resistance | |
|
|
Downy mildew (downy mildew)
A disease similar to the previous one only in name. There is little in common between the MR and the LMR. More often it affects greenhouse cucumbers. In open ground it is less common than MP. It does not spread as quickly as the real one if the pathogen is on plant debris. If the seeds are infected, then the entire borage may die in a few days. 

Downy mildew appears in cold, damp summers. In greenhouses where cucumbers are grown for several years in a row, it may also appear in hot summers, but this happens much less often. More often it affects soil suffer from it less. 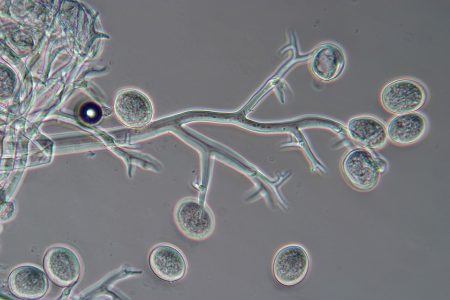
The peak incidence of plants occurs in early to mid-July, although it may appear earlier. In the southern regions, with greenhouse cultivation of cucumbers, it appears on plants even in winter. Appears 1-2 days after heavy cold dew or rain, as well as when watering with cold water.
Signs of defeat
It affects only leaves and petioles. The first signs appear in the morning. The disease begins with young upper leaves. The lower leaves are the last to be affected. 

- Oily yellow spots appear on the upper side of the leaf, which then merge.
- White-violet areas appear on the underside - this is a mycelium.
- After 5-7 days, the spots become brown, the leaf dries up.
- In the absence of protection measures, the entire greenhouse may die in a few days.
The harmfulness of downy mildew is much greater than the real one. With untimely measures, you can be left without a crop.
If the first signs appear on individual leaves, then the pathogen got to the cucumbers from the outside. If at the same time spots appear on all plants under unfavorable conditions, then the seeds were infected.
Control measures
Measures should be taken in advance, 1-2 days after the rains. And in the greenhouse, cucumbers must be treated prophylactically.
- Bordeaux mixture in the fight against LMR is ineffective.
- When the first signs of the disease appear, they immediately begin to treat with fungicides. No folk remedies will help. Use drugs Strobi, Quadris. Processing is done 2 times per season. The first after rains or heavy cold dew, the second - at the first sign of the disease. More than 2 treatments cannot be carried out, since the pathogen very quickly develops resistance to the active substance.
- At the first sign, cucumbers are treated with copper-containing preparations, except for those containing copper sulfate, this substance does not affect the peronospore. Usually use HOM, Ordan, Abiga-Peak.
- The use of drugs Consento, Revus, Previkur.
- All seeds must be dressed before planting. Even if they have been treated, it is recommended to pickle them again, since the protective effect of the fungicide has already ceased by the time of sowing. At home, the seeds are soaked in a strong solution of potassium permanganate for 20-30 minutes. You can use the drug Maxim or biologics Trichodermin, Gamair.
- Removal of diseased leaves, they are cut off, leaving no stumps. After removal, the cucumbers are sprayed with a solution of Trichodermin.
- Treatment with Planriz in the initial stage of LMR.
- Thorough ventilation of the greenhouse. It is undesirable to allow dripping moisture from the leaves in the morning. To do this, the greenhouse is left open at night.
When signs of the disease appear, at least 3 treatments are carried out with an interval of 3-5 days. Each time the drug is changed. Cucumbers can be treated with one preparation no more than 2 times per season, but not in a row, but alternating it with other chemicals. If the substance is effective, then after the first treatment, the spots lose their oily tint, dry out, and sporulation stops.
With LMR, spraying is carried out on the underside of the leaves, since it is there that the mycelium develops and spores ripen. The spots on the upper side are simply manifestations of the disease, there are no mycelium or spores at the top.
Folk methods of struggle
Folk methods are mainly preventive. 
- Use of soda ash. Having a strong alkaline reaction, the chemical prevents the development of the pathogen. Preparation of a working solution: 25-30 g of the drug is diluted in 5 liters of hot water, 20-25 g of solid or 5 g of liquid tar soap are added. Processing is carried out in the morning on the underside of the leaves.
- Spraying cucumbers with a strong solution of potassium permanganate.
Folk remedies are used in places where the disease is expected to develop. If the first signs appear, especially when they appear simultaneously on all plants (which indicates infected seeds), they immediately switch to chemical protection.
Disease prevention
- Before sowing, all cucumber seeds are treated.
- If there were outbreaks of downy mildew in the greenhouse last year, then replace the earth to a depth of 10 cm.
- Complete removal of plant debris.
- Disinfection of greenhouses des. means or setting fire to sulfur bombs. In the greenhouse, where foci of downy mildew were observed, sulfur bombs are set on fire both in autumn and in spring.
- When watering cucumbers, it is undesirable for water to get on the leaves.
- Preventive treatment with biopreparation Gamair.
Prevention, unless the infection is in the seeds, is quite effective and can reduce the risk of downy mildew by 1.5-2 times.
Varieties and hybrids resistant to the disease
There are quite a few hybrids and varieties resistant to downy mildew.
| Downy mildew resistant hybrids | |
|
|
| Resistant bee pollinated varieties | |
|
|