The almond plant is a small but very valuable fruit tree or shrub that is a relative of the plum. Contrary to popular belief, almonds are not a nut, they are a hard stone fruit. Asia is considered the homeland of this plant, but currently almonds grow in many parts of the world, it is successfully grown from some states of the USA, in the Tien Shan mountains, China, in Europe, almonds are widespread in the Mediterranean countries and in the Crimea, as well as in the Caucasus, which is known to be located at the junction of Asia and Europe.
Almonds grow in small groups on rocky slopes rather high above sea level. Prefers sunny places and is not afraid of drought, having a well-developed root system. The plant is frost-resistant, but it does not tolerate frosts during the growing season. The soil for almonds must be high in calcium. It begins to bloom with light pink five-petal flowers in late winter - early spring, and fruits appear in early summer. The average lifespan of a tree is one hundred years, but sometimes almonds live much longer. The fruiting period is from five to thirty to fifty years. Almonds are cross-pollinated plants. 
Almond fruits are green seeds covered with short villi, similar in shape to apricot ones, which, when fully ripe, crack along the inner seam. Thus, in almonds, the fruit is similar to a nut, although the plant itself is not a nut. The fruits of almonds are very tasty, dietary and at the same time highly nutritious - the amount of oil in some tree species reaches almost 70%, protein - up to 35%. In terms of nutritional value, almonds surpass not only all the fruits and vegetables we are used to, but even wheat, beef, milk and fish.
Also in almonds there are many vitamins and trace elements, thanks to which the famous medieval healer Ibn Sina (Avicenna) used this plant in the treatment of liver, spleen and kidneys. Due to its composition, almonds are indicated for diabetics, asthmatics and ulcers, it is also taken for gastritis, headaches, nervous exhaustion. This plant has the ability to calm and stimulate the brain at the same time.
 Almond oil cleanses the bladder and kidneys, reduces the content of bad cholesterol, is used for pneumonia, various sprains, and even helps in the treatment of certain cancers. It is popularly believed that almond oil helps to get rid of age spots, freckles and dandruff (if you mix it with wine and rub it into your hair), and it is also taken for a strong cough.
Almond oil cleanses the bladder and kidneys, reduces the content of bad cholesterol, is used for pneumonia, various sprains, and even helps in the treatment of certain cancers. It is popularly believed that almond oil helps to get rid of age spots, freckles and dandruff (if you mix it with wine and rub it into your hair), and it is also taken for a strong cough.
Almond fruits are high in calories, so they should not be overused. Nevertheless, the balanced composition of these fruits allows even people suffering from overweight to take it without any fears for their figure.
Important! Unripe almond seeds contain cyanide, in addition, poisonous hydrocyanic acid is present in some varieties. Such fruits should be eaten with care and only after pre-roasting. Glycoside and amygdalin, contained in large quantities in almond fruits, are fatal to humans; for a lethal outcome, it is enough to eat only a few dozen grains.
 Almonds are an excellent addition to confectionery. It sets off and enhances the taste of chocolates and other sweets; it is also added to various marmalades and preserves, pastas, curd cheeses and ice cream. Almond flour as a substitute for wheat flour is used in the recipes of exquisite cakes and pastries. A paste is prepared from crushed almond kernels, which is an independent delicacy, as well as an ingredient for enhancing the taste of other products and saturating them with a unique almond aroma.
Almonds are an excellent addition to confectionery. It sets off and enhances the taste of chocolates and other sweets; it is also added to various marmalades and preserves, pastas, curd cheeses and ice cream. Almond flour as a substitute for wheat flour is used in the recipes of exquisite cakes and pastries. A paste is prepared from crushed almond kernels, which is an independent delicacy, as well as an ingredient for enhancing the taste of other products and saturating them with a unique almond aroma. Did you know? Almond flour and marzipan made from it were previously used to treat psychiatric diseases. In years of famine, due to its high calorie content, it was daily used for making bread as a substitute for the absent conventional flour.
Where is the best place to plant almonds
Although almonds can tolerate drought, dehydration can seriously harm the plant - it slows down growth and begins to shed leaves, as a result, the yield decreases, not only this year, but also the next. Also, productivity drops in low light when almonds grow in places shaded by other plants or buildings.
These features must be taken into account when deciding on the cultivation of almonds.
What types and varieties are best to plant
 Before growing almonds, you need to decide for what purpose the plant will be planted, and depending on this, choose the most suitable variety.
Before growing almonds, you need to decide for what purpose the plant will be planted, and depending on this, choose the most suitable variety.
There are more than forty types of almonds, but the common almond is considered the most common. Its height can reach six meters, but in arid places it grows as a short bush. Depending on the palatability of the fruit, bitter, sweet and brittle almonds are distinguished, all of which belong to the species of plant in question.
Almond varieties such as "Pink Mist" and "Anyuta" are very popular, but fruit growers prefer to grow "White Sail".
If the purpose of growing almonds is to decorate a plot, you should pay attention to such varieties as "three-lobed" almonds (it has a very beautiful one and a half meter crown and falling leaves, blooms with bright pink or crimson flowers); "Ledebura" (distinguished by a special aroma, large dark leaves and large light pink flowers) and "Petunnikova" (decorative dwarf shrub with beautiful pink flowers).
What soil is suitable for growing
 The almond tree does not impose too high demands on the soil; it may well grow on rubble, in sand and stones. It is optimal that the soil is light, fertile and has good drainage.
The almond tree does not impose too high demands on the soil; it may well grow on rubble, in sand and stones. It is optimal that the soil is light, fertile and has good drainage.
For this plant, acidic clay, saline, especially chlorine-containing soils are contraindicated, its root system does not tolerate the effects of high groundwater, as well as the lack of air and water permeability.
How and when to plant almonds
Deciding how to grow an almond tree begins with choosing a location. In addition to the requirements for the composition of the soil and the abundance of light, it is necessary to provide the seedling with good protection from the wind. It is best to place the plant on the south side of the site.
Planting almonds is best done in late autumn, a plant planted in spring takes root worse.
Important! There is another secret: given that almonds cannot be pollinated on their own, it is necessary to plant several varieties and specimens at once. The presence of other almond trees somewhere nearby does not solve the problem: for successful pollination, almonds need insects that have settled in the hive directly near the plant.
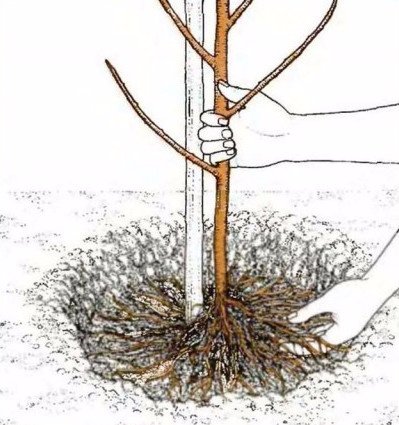 The almond tree planting technology is as follows. Pits a little more than half a meter deep are dug at a distance of two to three meters from one another (for shrubs and dwarf varieties, this distance can be reduced). Small gravel or crushed stone is poured at the bottom of the pit, up to 10 cm of sand on top, then fertilizing, ideally phosphorus fertilizers and manure.
The almond tree planting technology is as follows. Pits a little more than half a meter deep are dug at a distance of two to three meters from one another (for shrubs and dwarf varieties, this distance can be reduced). Small gravel or crushed stone is poured at the bottom of the pit, up to 10 cm of sand on top, then fertilizing, ideally phosphorus fertilizers and manure.
Trees are carefully placed in the pit (the root collar should be 10-15 cm underground), after which the pit is filled with fertile soil and compacted well.
A near-root circle with a radius of one and a half meters should be mulched. It is best to use peat for these purposes. A support is driven in near the seedling, with which a young tree is tied to protect it from the wind.
Each seedling needs to be watered abundantly.
Almond propagation
Almonds are propagated by seeds, cuttings, and by root division of the plant.
Almonds can be grown from seeds, but in this case the biological and commercial characteristics of the almond may be lost. In order to germinate the almond seed as best as possible, it should first be soaked in a strengthening solution and planted at a distance of 15-20 cm from each other in a well-dug place prepared in advance in late autumn or at the beginning of winter to a depth of 10-15 cm. Two seeds can be placed in one hole, in this case, a stronger seedling is left after germination.  The seeds can be planted in early spring, but before that, from the end of January to the beginning of February, they must be stratified (germinated in conditions similar to natural wintering) in the sand. The process lasts up to one and a half months at temperatures from zero to ten degrees above zero.
The seeds can be planted in early spring, but before that, from the end of January to the beginning of February, they must be stratified (germinated in conditions similar to natural wintering) in the sand. The process lasts up to one and a half months at temperatures from zero to ten degrees above zero.
When seed shoots reach 10-15 cm, the roots of the plant at the same depth must be cut with a shovel, after which water abundantly.
The seedlings are peeled off at the end of summer in the area of the root collar, after which the ophthalmologist is spudded. Annual seedlings need to be transplanted, otherwise they will not form a crown.
Propagation of almonds by cuttings
 To propagate the almond tree in this way, at the beginning of summer, cuttings 15-20 cm long (two nodes) are cut from the top of the plant and placed in a stimulating solution for several hours. After that, the cuttings are planted in a prepared mixture of sand and peat (ratio 1: 2) and placed in a cold greenhouse for 20-30 days. During this time, the cuttings should be fully rooted, after which the young almond tree continues to grow in the training bed.
To propagate the almond tree in this way, at the beginning of summer, cuttings 15-20 cm long (two nodes) are cut from the top of the plant and placed in a stimulating solution for several hours. After that, the cuttings are planted in a prepared mixture of sand and peat (ratio 1: 2) and placed in a cold greenhouse for 20-30 days. During this time, the cuttings should be fully rooted, after which the young almond tree continues to grow in the training bed.
Propagation of almonds by growth
When pruned heavily, the almond tree produces abundant growth. In the second year after the appearance, such shoots can be separated, keeping the roots, and transplanted into a separate place.
Propagation of almonds by layering
Young shoots of almonds can also be used for propagation by layering. To do this, it must be bent to the ground, pinned with a metal or wooden hairpin and lightly sprinkled with earth. The own root system of such shoots is formed in about a year, all this time they must be regularly watered, weeds are weeded around them and the soil is plowed. Subsequently, the seedlings are separated from the mother tree and planted in a permanent place.
How to care for almonds
To obtain a good harvest of almonds, it is necessary to observe not only the planting rules, but also to provide the rooted plant with competent care in the open field.
How to water almonds properly
 Almonds only need abundant watering if they grow on sandy soil. The abundance of moisture is very harmful to the plant, however, with a lack of water, the tree blooms poorly and does not bear fruit. Almonds should be watered when the soil around the plant has dried to a depth of about one and a half centimeters. The watering rate is from seven to ten liters of water per bush.
Almonds only need abundant watering if they grow on sandy soil. The abundance of moisture is very harmful to the plant, however, with a lack of water, the tree blooms poorly and does not bear fruit. Almonds should be watered when the soil around the plant has dried to a depth of about one and a half centimeters. The watering rate is from seven to ten liters of water per bush.
Fertilizing and feeding almonds
Almonds need a lot of strength for the fruits to form and fill properly; this feature of the plant determines the agricultural technology of its cultivation. In the spring, an adult tree is fertilized with organic matter and ammonium nitrate (20 g per bucket of water). In autumn, the soil must be fed with double superphosphate and potassium sulfate - 20 g of both per square meter.
Almond pruning
Pruning and shearing almonds is very beneficial for the plant. Even the flowering branches cut for decorative purposes will not damage the tree. It is imperative to remove damaged and dried branches. It is necessary to form the tree as soon as it fades. Almonds need pruning as they grow very quickly and become unkempt without proper trimming. For the plant to be pleasing to the eye, annual shoots should be pruned.
Almond grafting
Almonds can be grafted not only on a plant of the same variety, but also on other varieties of almonds, as well as on plums, cherry plums or thorns. This is best done in mid-spring or late summer, when sap flow is especially active. The weather shouldn't be too hot.
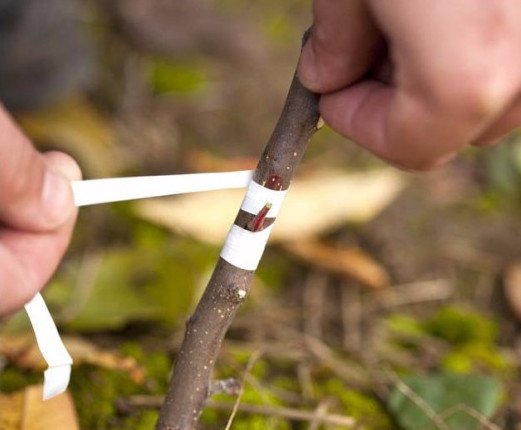 A couple of days before the procedure, the stock should be poured very well (the bark should be easily separated) so that during budding the bark is well separated from the wood. A straight stalk with a formed bud is taken as a scion, from which it is necessary to carefully cut the leaves, leaving cuttings a few millimeters in order not to damage the bud.
A couple of days before the procedure, the stock should be poured very well (the bark should be easily separated) so that during budding the bark is well separated from the wood. A straight stalk with a formed bud is taken as a scion, from which it is necessary to carefully cut the leaves, leaving cuttings a few millimeters in order not to damage the bud.
In the area of the root collar of the scion (first it must be cleaned of dirt), a sharp knife is made to make an incision in the shape of the letter "T", and in the place where the incision lines converge, the bark is gently folded back. A shield with a kidney is cut from the prepared cutting in such a way that it fits into the prepared incision. When trimming the flap, you need to grab, in addition to the bark, a little woody tissue. The stalk is inserted into the incision, covered with bark and fixed with a dense bandage made of plaster or tape (the kidney must remain on the surface).
After 2-3 weeks, a control check is carried out: with a successful vaccination, the peephole should be green, and the petiole should disappear. The bandage can then be loosened. If budding was carried out at the end of summer, the peephole trim should not be removed until spring. Eyes that have not taken root need to be re-oculated.
In the spring, after the appearance of foliage, the harness can be removed, the rootstock with a dried eye can be grafted using a cuttings prepared in advance.
 When the height of the eyepiece reaches 10 cm, it must be additionally hilled; the procedure is repeated at least twice as it grows. The shoots that the rootstock gives should be removed, as well as the lateral shoots appearing on the eyepiece.
When the height of the eyepiece reaches 10 cm, it must be additionally hilled; the procedure is repeated at least twice as it grows. The shoots that the rootstock gives should be removed, as well as the lateral shoots appearing on the eyepiece.
Did you know? In the southern regions, almonds, as a hardy, unpretentious and frost-tolerant plant, are used as a rootstock, peaches and apricots are grafted onto it, which feel quite confident in such support. You can recommend the article to your friends!
238
once already
helped