The almond tree, with proper planting and proper care, will bloom profusely every spring and decorate the garden when the rest of the plants are still sleeping. Blooms in April or early May. Its branches are literally strewn with pink or white-pink flowers, exuding a unique aroma. If you plant several almond trees of different varieties nearby, then at the end of summer it will be possible to collect fruits, inside of which there is an edible tasty bone.
Description of the almond tree
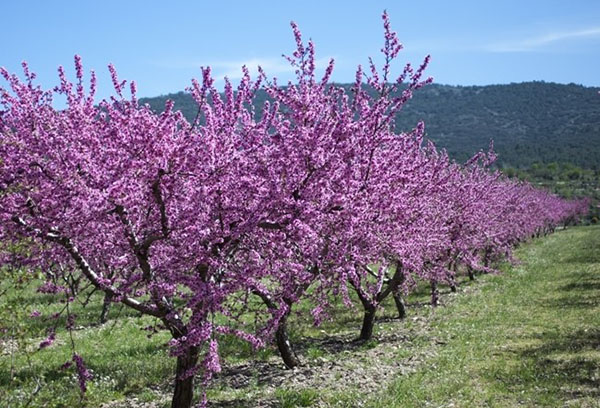
Almond is a tree up to 6 meters high or a spreading shrub up to 3 meters high. It begins to bloom early, in regions with a warm climate, flowers appear in March, in the middle lane - in April or early May. Flowers first appear on the branches, and after they crumble, leaves. There are so many flowers on the shoots that the almond tree in spring looks like pink fireworks. The diameter of each flower is 2.5 cm, it consists of five petals.
Almonds are of two types:
- bitter is a wild plant, its bones are inedible;
- sweet - a cultivated plant whose nuts can be eaten.
The first fruits appear on the 4-6th year after planting, and abundant fruiting - after 10 years. In favorable conditions, it lasts up to 50-60 years. Almond is a long-lived tree, its maximum age can be 120 years.
Fruit sets only when cross-pollinated. A prerequisite is that the trees must be of different varieties and bloom at the same time. Landing them is carried out at a distance of 3-5 meters from each other. Pollinators are bees or other insects. Almond is a honey plant.

Requirements for growing conditions
The almond tree is sun-loving. Growing it in a shady place leads to the fact that flowering becomes scarce.
The root system has several skeletal branches that go deep into the soil. This makes the plant drought tolerant. Stagnation of water at the roots does not tolerate, the soil must be drained, loose, breathable. Outdoor cultivation should be carried out in a place protected from winds and drafts. Almonds grow well on stony soils with a high content of calcium and lime. Planting on acidic or saline soils is unacceptable - the tree may die.
Almond is a thermophilic plant. For cultivation in regions with cold winters, cold-resistant species have been bred.
- Steppe almond is frost-resistant, hibernates without shelter at temperatures down to -25 °. Its other names are low, Russian, almond or bobovnik.
- Three-lobed almonds are cold-resistant, in frosty winters the ends of the shoots can freeze out, cover with agrofiber is required. After freezing, it quickly recovers.
All of these types are decorative. Their bones are inedible and can cause severe poisoning.
Cold-resistant seedlings are considered to be grafted on thorns or cherry plums.

Features of cold-resistant types of almonds
Steppe almond is considered the most winter-hardy. This is a low-growing shrub, its height does not exceed 1.5 meters. The branches are erect, the bark is gray-red. The steppe species is interesting in that its pericarp is pubescent, as if covered with felt. The fruits adorn the branches all autumn.
The steppe species has a lot of root growth, which is used for its reproduction. Pruning is required only sanitary, which is carried out in early spring. This species is undemanding to the soil, tolerates polluted air, easily withstands drought - it requires minimal care. It is used for landscaping streets and courtyards in the city.
One of the common varieties of the three-lobed species is Pink Foam. It has beautiful large double flowers of pink, raspberry or purple color. The root system of this variety is superficial and highly branched. The variety "Pink foam" is suitable for strengthening slopes, artificial embankments.

Planting almonds in the garden
Planting almonds is carried out in pre-prepared pits:
- they are dug up 60x60 cm in size, the same depth;
- drainage is poured at the bottom, for which crushed stone, split brick, stones, expanded clay can be used;
- for drainage - a layer of coarse river sand, it is rammed;
- a mound is made from the nutrient soil, and a long stake is driven into its center, which will serve as a support for the seedling;
- the roots of the seedling are directed on different sides of the mound, making sure that they do not bend;
- the pit is covered with loose fertile soil.
The root neck is left 1-2 cm above the soil level.
The soil mixture is made up of 5 kg of humus or compost, 500 grams of superphosphate, 250 grams of lime and a small amount of river sand.
If you plan to grow several almond trees, then the pits are dug at a distance of 5 meters from each other.
Autumn planting of seedlings is preferable, this guarantees their survival.
During spring planting, the roots of the seedling must be smeared with clay mash. This will retain moisture and prevent the plant from drying out. The trunk circle must be mulched, but the root neck should not be covered with mulch. Caring for a planted tree consists in constant watering. Until the almonds take root, it is important to keep the soil moist. At the same time, you can not fill it: with excessive dampness, the roots can rot.

Care
Caring for an almond tree is not difficult, but should be done regularly, especially in the first few years after planting.
Care includes the following activities:
- loosening several times per season to a depth of 15 cm - a crust should not be allowed to form on the soil surface;
- regular watering, as the earth dries up, but not more than 10 liters per trunk circle;
- top dressing twice a year: in spring - nitrogen, in autumn - phosphorus and potash;
- in early spring and late autumn, it is necessary to carry out moisture-charging watering - in the fall, such care will make it easier to endure the winter, and in the spring it will provoke lush flowering;
- pruning.
Sanitary pruning is carried out after the snow melts. Cut out all broken, frozen branches. Formative pruning is carried out immediately after the flowers fall off. Remove branches growing deep into the tree, crossing each other and thickening the crown too much.
Older trees sometimes need rejuvenating pruning. In this case, cut off all the branches, leaving a stump. After a while, it will overgrow with young shoots.
In regions with cold winters, care includes preparing the almond tree for winter. To do this, in the second half of summer, buds are removed at the tops of the shoots. This accelerates the lignification of young green shoots and makes them resistant to frost. In cold winters, it is necessary to throw agrofiber on the almond bush and press the ends of the canvas tightly to the ground.
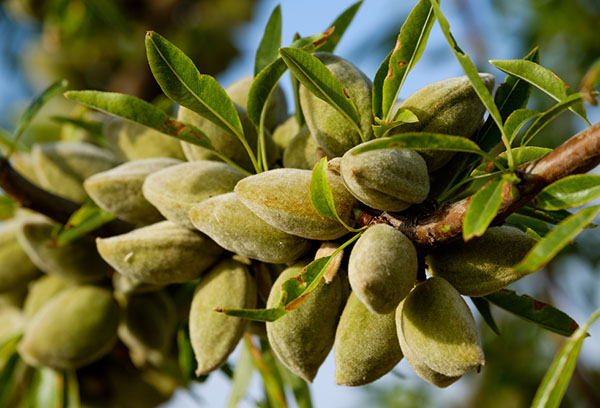

reproduction
The almond tree can be propagated by pitting, layering, grafting, or cuttings.
- The easiest way to propagate is rooting. It is carefully dug up and cut off with a sharp shovel from the mother plant along with the roots. Well, if you manage to keep part of the soil on the roots, rooting will be faster.
- Reproduction by layering is possible for bush almond species. The lower branch, extending almost horizontally, is pinned to the ground in several places and lightly sprinkled with earth. Separation from the main plant is carried out the next year.
Growing almonds in the above ways is the most effective. Rooting occurs quickly, and all the characteristics of the mother plant are transferred to the seedling.
The grafting method is more complex, and inexperienced gardeners do not always succeed on the first try. Growing almonds from seeds takes a lot of time. Stratification of seeds is required, their germination on a separate bed. Only three-year-old seedlings can be transplanted to a permanent place. Maternal characteristics when propagated by seeds are not always transmitted.
conclusions
In regions with cold winters, ornamental almonds are suitable for cultivation. They winter well, quickly recover after freezing, and in early spring they become garden favorites.