Boric acid widely used in the garden and in the garden. It is used as a mineral fertilizer, as a stimulant for seed germination, for pest and disease control.
Consider the features use of boric acid for vegetable crops, in the garden and for indoor plants. What proportions should be used and when to apply.

Boron- the most important trace element for plants. It improves metabolic processes, normalizes the synthesis of nitrogenous substances, and promotes normal photosynthesis.
Boric acid the most affordable and simple boron compound. It is used in various complex fertilizers. Boric acid is a colorless crystalline substance, odorless, easily soluble in water.
If the amount of boron in the soil corresponds to the norm, the plants are more resistant to adverse conditions, the yield increases, the fruits are stored longer during storage.

Apply boric acid on various soils, especially in areas with carbonate content, acidic soils after liming.
Boric acid helps to increase the number of ovaries in fruit and berry crops, improves the palatability of fruits, stimulates new points of growth of stems and roots.
With a lack of boron, diseases such as brown rot, gray rot, bacteriosis.
A lot of boron requires an apple tree. Boron is required by all plants throughout the growing season.
Boric acid must be used correctly, because each plant requires a certain amount of boron.
Conventionally, plants can be divided into 3 groups according to the need for boron.
High demand: pear, apple tree, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, rutabagas ,.
Average demand: carrots, tomatoes, salads, stone fruits.
Low demand: legumes, potatoes, herbs, strawberries.
Boric acid overdose
Boric acid belongs to the 4th hazard class of harmful substances, the lowest class.
But excess boron in the soil is dangerous for plants- can provoke a burn of the lower leaves, yellowing of the edges of the leaves, dying off and falling off. The first to suffer from excess boron are old leaves.
With an excessive content of boron in fodder plants, severe chronic diseases develop in animals when consumed.
Video - The use of boric acid in the garden and vegetable garden
Boric acid from ants

Boric acid is used as an insecticide in pest control: ants, cockroaches.
Dry baits act as intestinal poisons.
Boric acid affects the nervous system of ants. After eating the powder by the pest, after a few hours, it is paralyzed or death occurs.
The easiest way to deal with ants is to scatter the powder in places where insects accumulate, at the entrance to the anthill.
Liquid and soft baits work more efficiently, the ants eat the bait and part of it is taken to the anthill, so other ants will submit to the poison.
It will not work to quickly remove annoying ants, it will take 2-4 weeks until the insects disappear completely, but this is an effective drug.
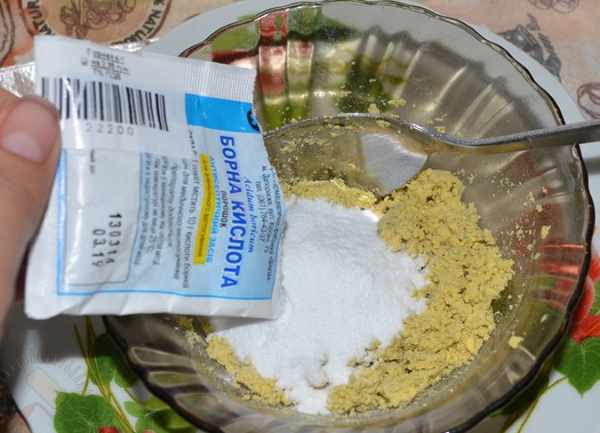

Bait # 1. In 100 ml of water with a temperature of 50 degrees, dilute 10 grams of honey and 5 grams of boric acid. Stir the mixture and pour into a flat dish.
Bait # 2. 1 tbsp. l. mix water with 2 tbsp. l. glycerin, 1 tsp. honey, 1/3 tsp. Boric acid, 1.5 cups of sugar. Stir well, roll up small balls of bait. This bait is good because it remains moist and soft for a long time.
Bait # 3. Boil 3 medium-sized potatoes in their skins, boil 3 hard-boiled eggs. Peel the potatoes and eggs (only the yolk is needed), grind, mix together and add 10 g of boric acid and a teaspoon of sugar. Mix everything thoroughly together and roll up small balls of bait.
Attention: Do not exceed the dose of boric acid, so the ants will not have time to bring the bait to the anthill after dying.

Boric acid is used as seed germination stimulant... To do this, you need the following solution: dilute 0.2 g of boric acid in a liter of water.
Soak seeds of beets, tomatoes, carrots, onions for 24 hours; soak seeds of cucumbers, cabbage, zucchini for 12 hours.
With a lack of boron in the soil, with the same solution, spill the beds before planting seedlings.

Top dressing of plants at the root is carried out only if it is precisely known about the lack of boron in the soil. Pre-water the plants, then spill with a solution: 0.1 g of boric acid per 1 liter of water.
Boric acid only dissolves in hot water and then bring the solution to room temperature.
Foliar feeding for the first time carried out in the budding phase with a solution: 0.1 g of boric acid diluted in 1 liter of water. Second time spraying carried out during the flowering period with the same solution. Third time feeding carried out during the fruiting period.
When other trace elements are used together, the proportion of boric acid is reduced to 0.05 g per liter of water.

With a lack of boron, strawberry leaves are curved, edge necrosis. Boric acid supplementation increases the yield and improves the taste of strawberries.
In early spring planting strawberries with a solution: 1 g of boric acid, add 1 g of potassium permanganate, dilute with 10 liters of water.
Approximate consumption of 10 liters of solution for 30-40 bushes. Also during this period, it is useful to carry out foliar feeding with a solution of 5 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water.
Before flowering, during the formation of buds, carry out foliar dressing with a solution of 2 g of boric acid, 1 glass of ash, 2 g of manganese per 10 liters of water.
Before preparing the solution, make an extract from the ash - pour the ash with a glass of boiling water, leave for a day, strain through several layers of gauze.

Lack of boron in tomatoes it manifests itself as follows - the growth point dies and blackens, new shoots from the root begin to grow rapidly, the petioles of young shoots are brittle and fragile.
On the fruits of tomatoes on the upper part, formations of brown spots of dead tissue are visible. It helps to soak seeds for a day, as a prophylaxis, in a solution of boric acid 0.2 g per 1 liter of water.
Foliar feeding with boric acid solution process plants during flowering - 2 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water. Spraying with this solution leads to better fruit setting.
During the ripening of the fruits, use the same solution for foliar feeding, the tomatoes will ripen faster and sugar will accumulate in them.

At lack of boron in beets the heart of the root crop rots, light brown spots with black dots appear on the leaves, then the disease passes to the root crop. This fungal disease is phomosis.
For prophylaxis, before sowing seeds, treat them in a solution of 0.1 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water. Soak the seeds in the solution for 10-12 hours.
For tasty and healthy fruits carry out foliar feeding at the stage of formation of 3-4 leaves with the following solution - 5 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water.
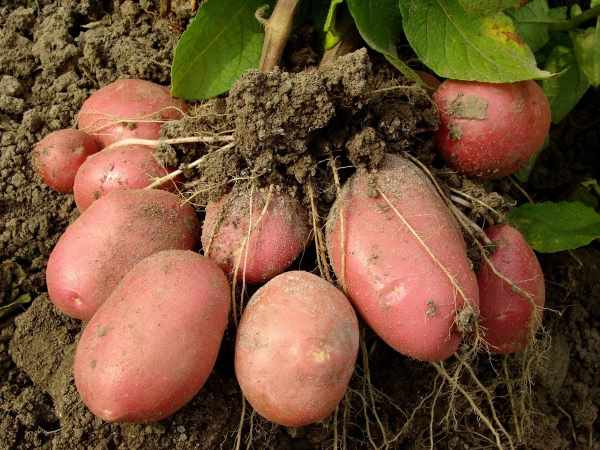

At lack of boron in potatoes there is a general developmental delay, the plants get sick with scab. The need for potatoes in boron depends on the acidity of the soil, the amount of mineral fertilizers.
At the first sign of scab disease feed with solution: Dilute 6 g of boric acid in 10 liters of water. Consumption of solution for 10 m 2 of the site.
When introducing fertilizers into the soil, boron-phosphorus is used. Alternatively, you can use wood ash. The boron content in ash is from 200-700 mg per 1 kg.
Boric acid for apple and pear

At lack of boron apple and pear leaves thicken, veins darken, corking occurs, small leaves at the ends of the shoots are collected in rosettes. Leaves fall off with severe fasting.
In a pear, the fruits are deformed, the flowers dry up quickly. Spots appear on the apples, over time they turn brown and become like a cork, the fruits are deformed and swollen.
Carrying out foliar feeding increases fruit formation and reduces the number of fallen ovaries - 10 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water.
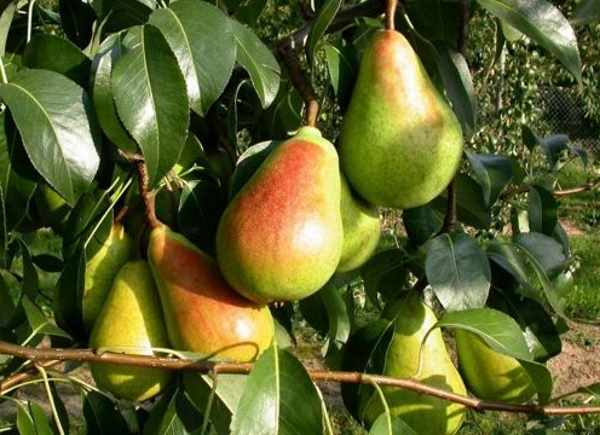

Spraying is carried out in the evening, evenly over the entire accessible crown of the tree. The first time such spraying is carried out at the very beginning of budding, the second time after 7 days.
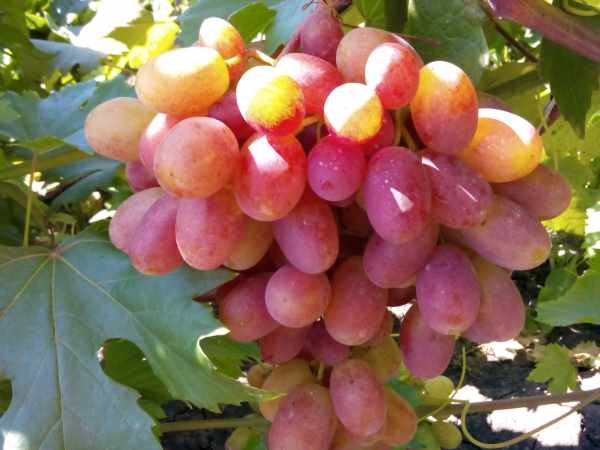

Signs lack of boron in grapes- there are no normal ovaries on the brushes (small berries), the appearance of spots between the veins on the leaves, which increase in size over time.
A young seedling may die after planting in a permanent place if there is a lack of boron in the soil.
A single treatment with a boric acid solution during the budding period is able to preserve the flowers, increasing less shedding of the ovaries, which in turn will increase the yield. When preparing a solution of boric acid for grapes, it is necessary to add zinc salts to it.
Solution recipe: 5 g of boric acid, add 5 g of zinc sulfate, dissolve everything in 10 liters of water.
Thanks to boron, plants easily absorb calcium, and buds are abundantly formed.
Spraying with boric acid solution has a beneficial effect on flowering plants during flowering and budding.
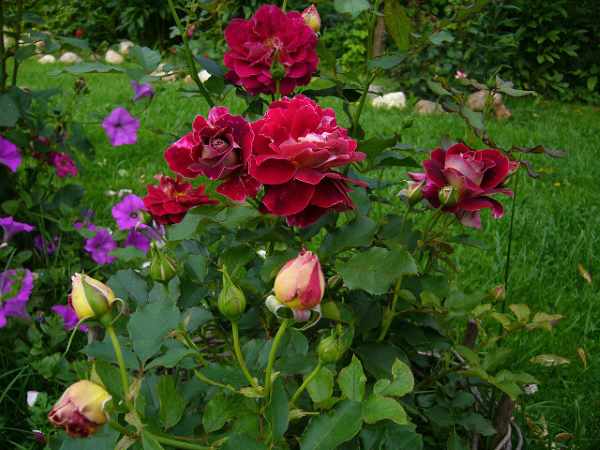

To do this, dilute 10 g of boric acid in 10 liters of water. When other microelements are added to the solution, the concentration of boric acid is reduced by half, that is, 5 g per 10 l of water.
Spraying a rose in early spring, a solution of 10 g of boric acid per 10 liters of water will give good results.
Gladioli Feed with a solution of 2 g of boric acid per 10 L of water during the flowering period to obtain large bulbs.
Dahlias spray with a solution: 2 g of potassium permanganate, 5 g of boric acid, dilute in 10 liters of water. Such foliar treatment will have a beneficial effect on flowering. Carry out this dressing twice before the period of mass flowering with an interval of 2 weeks.
Video - Boric acid in the garden and vegetable garden!
Boric acid can be purchased not only in pharmacies, but also in garden centers they sell boron containing fertilizers and packaged boric acid. Do not forget that an overdose of boron is very dangerous for plants, as well as a deficiency.