It is not for nothing that Thailand is called the "Land of Smiles", because very polite and hospitable people who love to smile live there. Probably, the habit of smiling among Thais is developed from an early age under the influence of Buddhism. This is not surprising given that there are over 18,000 Buddhist temples in Thailand. Something else is amazing in Thailand - nature, mountains, palaces, ancient monasteries and temples, pagodas, floating bazaars, Thai cuisine, Thai massage, coral islands, and, of course, white sandy beaches surrounded by palm and coconut groves.
Geography of Thailand
Thailand is located on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. Thailand borders Laos and Cambodia to the east, Malaysia to the south, and Myanmar and Laos to the north. In the east of the country is the Gulf of Thailand, which belongs to the South China Sea, and the western shores are washed by the waters of the Andaman Sea. The total area of Thailand, including the islands, is 514,000 sq. km., and the total length of the state border is 4,863 km.
There are several geographical regions in Thailand. In the west, south and north are mountain systems, and in the east - the Korat plateau. The highest peak is Mount Doi Inthanon, whose height reaches 2,565 m. In the central part, along the Chao Phraya River, there is the Menam lowland. It is the Chao Phraya that is considered the largest river in Thailand.
Capital
The capital of Thailand is Bangkok, which is now home to more than 15 million people. The history of Bangkok goes back to the 15th century.
Official language of Thailand
The official language of the people of Thailand is Thai, belonging to the Thai-Kadai language family.
Religion
More than 94% of the population of Thailand professes Theravada Buddhism (the most conservative direction of this religion).
Government of Thailand
Under the current constitution, Thailand is a constitutional monarchy. The head of state is the King and the head of government is the Prime Minister.
The bicameral parliament in Thailand is called the National Assembly, it consists of the Senate (150 senators) and the House of Representatives (480 deputies).
The main political parties in Thailand are the For Thailand Party and the Democratic Party.
Climate and weather
The climate in Thailand is tropical with a lot of rainfall. On the west coast of the country, the monsoon brings rain from April to November, while on the east coast the rainy season lasts from September to December.
In general, the best time to visit Thailand is from November to February. During this cool season, the air temperature in Bangkok ranges from +18C to +32C.
The summer period (i.e. the hot, dry season) lasts from March to June. In Bangkok at this time of the year, the average air temperature is +34C, but often reaches +40C. Try not to get to Thailand in April, unless, of course, you plan to constantly swim in the ocean. April is the hottest month in Thailand.
From July to October, the monsoon season continues in Thailand. During this time, floods often occur in the country.
Sea in Thailand
In the east of Thailand is the Gulf of Thailand, which belongs to the South China Sea, and the western shores are washed by the waters of the Andaman Sea. The total length of the coast is 3,219 km. The average annual water temperature is +26-29C.
Rivers and lakes
The largest river in Thailand is the Chao Phraya River, which flows through the Menam Lowland in the central part of the country. Another large local river is Mun, which is a tributary of the Mekong River. The Tapi River flows through the south of Thailand, it originates in Khao Lang and flows into the Gulf of Thailand near the city of Surat Thani.
Also in the south of Thailand is the largest lake in this country - Songkhla Lake, located near the city of the same name. Its area is 1,040 km. sq.
Story
Archaeological finds indicate that people on the territory of modern Thailand lived already 10 thousand years ago, and they began to grow rice more than 5 thousand years ago. The ancient Thais were nomads, and their ancestral home is still not exactly known.
Buddhism began to spread in the territory of modern Thailand from about the 3rd century BC. From the 9th to the 11th century, Thailand was part of the Khmer kingdom.
In the XIII-XVII centuries, there were two strong Thai states - Sukhothai and Ayutthaya, which formed the Thai principalities. Interestingly, the Europeans were never able to establish their protectorate over Thailand (it was called Siam in the Middle Ages and in modern times).
In 1932, after a bloodless revolution, the absolute monarchy in Thailand turned into a constitutional monarchy. In 1939, Siam officially became known as Thailand.
After World War II, Thailand experienced several military coups. Only in 1997, after the adoption of the new Constitution, the political situation in this Asian country stabilized.
Culture of Thailand
Thailand's culture is rooted in family and Buddhist traditions. Thai children are taught to respect their parents, the elderly, teachers, Buddhist monks. Every Thai settlement has a Buddhist temple, which is the center of local life. That is why Thais are so polite and friendly.
In April, the people of Thailand celebrate the onset of the New Year (Songkran). To be more precise, Thais celebrate this holiday for three days - from April 13 to 15. Before the onset of the New Year, Thais spend a spring cleaning in their homes to throw away all the failures of the outgoing year.
Songkran begins with the distribution of food to Buddhist monks who appear on the streets on this holiday from the very morning. Then the youth pours water on everyone (including themselves), after which festivities, games, and dances begin.
Other popular festivals in Thailand are Visakha Puja (May), Rocket Festival, Full Moon Night (November) and Elephant Festival (November).
Kitchen
Thai cuisine is considered one of the best in all of Asia. Indian and Chinese culinary traditions had a noticeable influence on her. The staple food is rice, which is eaten at every meal. Other staple foods in Thailand are fish noodles and seafood. Meat is not often eaten in this country (because of its high cost).
Be warned that most Thai dishes are very spicy. Therefore, if you do not like a lot of spices, in a restaurant just tell the waiter "No spicy".
In Thailand, tourists are recommended to try rice in oyster sauce, khao phat (rice with vegetables and crabs), laap (fish salad with spices), mi krop (noodles with sweet and sour sauce), nay ( pork sausages), "mu daeng" (pickled meat), "salaphao" (patties with different fillings).
In the bazaars in Thailand, tourists are offered a variety of exotic fruits that grow in this country all year round.
Fruit season in Thailand:
lychee - june
durian - May-August
mangosteen - May-September
rambutan - May-September
longan - June-August
longkong - August-October
mango - March-May
sapodilla - January-May
Do not forget also that in Thailand there are also other fruits - watermelons, bananas, coconuts, pineapples and papaya.
Landmarks of Thailand
In Thailand, tourists are waiting for a huge number of various historical, cultural and architectural monuments. According to official figures, there are now several thousand temples, palaces, pagodas and other attractions in Thailand. The top 10 most interesting sights in Thailand, in our opinion, may include the following:
- Temple of the Emerald Buddha in Bangkok
- Buddha's footprint at Phra Buddha Bath
- Royal Palace in Bangkok
- Wat Mahathat temple in Ratchaduri
- Hill Temple in Bangkok
- Sitting Buddha statue at Mahahtati Si Chum
- Temple of Dawn in Bangkok
- Wat Lok Moli temple in Chiang Mai
- Marble Temple in Bangkok
- Temple of the Mountain in Bangkok
Cities and resorts
The largest Thai cities are Nonthaburi, Pakkret, Chiang Mai, Nakhon Phanom, and, of course, the capital is Bangkok.
In Thailand, tourists are waiting for excellent beach resorts. The most popular of them are Cha-am, Krabi, Hua Hin, Pattaya, Samet, Koh Samui, Phuket, Phi Phi, Chan.
Many tourists believe that Thailand has some of the best beaches in the world. Which one to choose from them? In our opinion, the top ten beaches in Thailand include the following:
- Patong - the largest beach in Phuket, soft white sand, warm sea, a large number of hotels, restaurants. shopping, and a lively nightlife.
- Railay Beach - This small beach near Krabi is only accessible by boat and is surrounded by clear waters and majestic mountains.
- Maya Bay, Koh Ley - the beach is located in a small bay, surrounded by high cliffs. This beach can only be reached by boat.
- Hua Hin - This beach, located on the shores of the Gulf of Thailand, is considered an ideal beach for families with children.
- Kata Beach - This beach is located in the quiet southern part of Phuket, in the low season there are quite large waves, and therefore there are many surfers.
- Lamai Beach, Koh Samui - this beach combines beautiful nature and dozens of bars.
- Sairi Beach, Koh Tao - is considered a great place for a beach holiday and diving.
- White Sand Beach, Koh Chang - This beach, located on the island, is surrounded by palm and coconut groves.
- Haad Rin, Koh Phangan - once a month, this beach hosts a fun music party that lasts all night.
- Koh Mun Nork - This beach is located on a desert island in the Gulf of Thailand. The white sandy beach is surrounded by palm trees. You can get there in 45 minutes by ferry.
By the way, Thailand and the Andaman Sea are among the top ten places in the world for diving. The infrastructure on the islands is very poorly developed, and therefore the coral reefs and the underwater world remain untouched. On the west coast, diving can be practiced almost all year round (the best time is from mid-November to the end of April).
Souvenirs/Shopping
From Thailand, tourists usually bring handicrafts (including wooden carvings), ceramics, Thai silk, silk scarves, clothes, Buddha figurines, silver jewelry, objects depicting elephants (elephants are the symbol of Thailand), Thai sauces and spices.
Office Hours
Thailand has significant and diverse mineral resources. Since the Middle Ages, Thailand has been known for its richest tin and gold placers. The deposits of these metals are associated with alluvial deposits, which Thailand's river valleys abound. The locals have long wash gold in many parts of the country. There were cases when large gold nuggets. However, at present, gold is mined in negligible amounts. When developing deposits a wide variety of methods are used, ranging from traditional, based on the use of unskilled labor to highly mechanized large-scale production methods. Many miners are engaged in washing gold. The high density of gold makes it easier to mine. The simplest technological processes, such as washing at locks, can provide a very high degree of gold recovery from the washed rock.
SILVER. There is an interesting feature in the Thailand-silver relationship. Large-scale silver mining in Thailand began relatively recently, but at the same time, silver jewelry has been made here for more than one century.
In Greek, silver is "ἄργυρος", " á rgyros”, from the Indo-European root meaning “white”, “shiny”. Hence comes its Latin name - "argentum". Silver- element of the 11th group, indicated by the symbol Ag(lat. Argentum).
Silver in jewelry. It is used as a precious metal in jewelry (usually in an alloy with copper, sometimes with nickel and other metals). Traditionally, experts divide silver into three types: sterling silver, Mexican and British. The difference between the types, first of all, is in the sample (that is, in the percentage of pure silver): sterling - 92.5%, Mexican - 95%, British - from 95.8 and above. Silver of Thailand refers to silver of the highest standard (up to 99%). The fact is that the production of silver in Thailand is taken under the control of the state and the sample of sold silver products, according to the law, cannot fall below 92.7%. But at the same time, the bulk of jewelry has 95% pure silver in its composition.
- 925 sterling silver For example, a 925 sample means that the alloy contains 92.5% silver and 7.5% alloying metal. An alloy of 925 silver is also called sterling silver (sterling, sterling silver, ster). It is an alloy of dazzling white color with high strength. Most jewelry is made from sterling silver due to its affordability and beautiful appearance. 925 sterling silver remains one of the main precious metals used to make highly artistic jewelry. Application (sputtering) of the thinnest (several microns) silver/gold layer, or “gluing” a thin silver/gold plate with another metal during pressing.
3. Rhodium-plated - silver plated with rhodium (to prevent oxidation)
See also Silver Blackening Technique.
silver nuggets. Silver sulfide compounds predominate in nature together with other metals: antimony, arsenic, bismuth, copper, tin, and gold. There is 20 times more silver in the earth's crust than gold. The facts of finding not just large, but huge silver nuggets are known and documented. So, for example, in 1477, a silver nugget weighing 20 tons was discovered at the St. George mine (the Schneeberg deposit in the Ore Mountains, 40-45 km from the city of Freiberg). workings, arranged a festive dinner on it, and then split it and weighed it. In Denmark, in the Museum of Copenhagen, there is a nugget weighing 254 kg, discovered in 1666 in the Norwegian mine Kongsberg. Large nuggets were also found on other continents. Currently, one of the native silver plates mined at the Cobalt deposit in Canada, weighing 612 kg, is stored in the Canadian Parliament building. Another plate, found in the same deposit and called "silver pavement" for its size, had a length of about 30 m and contained 20 tons of silver. However, for all the impressiveness of the finds ever discovered, it should be noted that silver is chemically more active than gold, and for this reason it is less common in nature in its native form. For the same reason, the solubility of silver is higher and its concentration in sea water is an order of magnitude greater than that of gold.
Silver in Ayurveda very important healing metal. It has a cooling effect and is beneficial in treating pitta excesses. Helps strength and endurance. It is used to treat vata diseases. However, for people of kapha constitution, it should be used with caution. Silver helps with exhaustion, chronic fever, weakness after fever, heartburn, inflammation of the intestines, overactive gallbladder and heavy menstrual bleeding. Silver is very helpful in inflammatory heart diseases, liver and spleen disorders. Silver water is prepared in the same way as golden water. Drinking warm milk warmed in a silver bowl increases strength and endurance.
TIN. But Thailand is especially famous for tin. Deposits of tin ore (cassiterite*) concentrated mainly in the southern part of the country. * Cassiterite(from Greek kassiteros - tin) - the main ore mineral for obtaining tin. The giant ridge of granite, sandstone and limestone that forms the Malacca Peninsula and the islands adjacent to it hides in its bowels, according to some sources, two-thirds of the world's tin reserves. Usually cassiterite is mined among the products of destruction of rocks - in alluvial deposits. Tin ores Thailand are of very high quality, they contain 65% metal.
First tin mining was started in the ninth century. or even earlier by colonists from southern India who settled on the West Coast of the Peninsula. Around the 15th century local deposits were rediscovered by Chinese merchants crossing the Kra Isthmus on their way from China to India. To this day, tin is mined where the old developments were laid.
Vessels made from tin or from an alloy of tin and lead were used in China in antiquity, and the technique of bronze casting in India and China was known long before our era. Traces of Chinese activity were found by European explorers in almost all the promising tin deposits they identified.
The world's tin deposits are located in Southeast Asia, mainly in China, Indonesia, Malaysia and Thailand. There are also large deposits in South America (Bolivia, Peru, Brazil) and Australia.
When a person first met tin, it is impossible to say for sure. Tin and its alloys have been known to mankind since ancient times. Tin is mentioned in the early books of the Old Testament. Alloys of tin and copper, the so-called tin bronzes, appear to have been in use more than 4000 BC. And with the metal tin itself, a person met much later, around 800 BC.
Tin is one of the seven metals of antiquity, which is able to preserve the taste and smell of drinks.
Tin(lat. Stannum; denoted by the symbol sn) is an element of the 14th group.
Latin name stannum, associated with the Sanskrit word meaning "resistant, durable", originally referred to an alloy of lead and silver, and later to another alloy that imitates it, containing about 67% tin; by the 4th century, this word began to be called tin itself.
Word tin- common Slavic, which has correspondences in the Baltic languages \u200b\u200b(cf. lit. alavas, alvas- "tin", Prussian. alwis- "lead"). It is a suffix from the root ol– (cf. Old High German elo- "yellow", lat. albus- “white”, etc.), so that the metal is named by color.
Application. An important use of tin is the tinning of iron and the production of tinplate, which is used in the canning industry. For these purposes, about 33% of all mined tin is consumed.
The method of long-term preservation of food products by canning in tin-plated tin cans was first proposed by the French chef F. Appert in 1809.
More than 60% goes to metallurgy, to obtain various alloys, for example, the most famous of the tin alloys is bronze.
Tin can be rolled into a thin foil - staniole, such foil is used in the production of capacitors, organ pipes, dishes, art products.
"Tin Plague". The result of white tin turning gray is sometimes referred to as "tin plague". Stains and growths on army teapots, wagons with tin dust, seams that have become permeable to liquid are the consequences of this “disease”.
Why don't stories like this happen now? Only for one reason: they learned to “treat” the tin plague. Its physico-chemical nature has been clarified, it has been established how certain additives affect the metal's susceptibility to the "plague". It turned out that aluminum and zinc contribute to this process, while bismuth, lead and antimony, on the contrary, counteract it.
Tin in Ayurveda. Rejuvenating element. Refined tin ash is used in the treatment of diabetes, gonorrhea, syphilis, asthma, respiratory infections, anemia, skin diseases, lung diseases, and lymphatic blockages.
COPPER. Copper deposits are found in northern Thailand and on the Korat plateau.
The iron ores found in different parts of the country belong to the type of formation to laterites or contact metamorphic rocks. The iron content is usually high. Geological surveys in the country are far from being completed, and it is still impossible to judge the total reserves of iron ores and their industrial significance.
COPPER in Ayurveda. Alleviates excess kapha and fat. A good tonic for the liver, spleen and lymphatic system. Especially useful for people who tend to gain weight, retain water, or have lymphatic buildup. Copper also helps in the treatment of anemia. For the treatment of obesity and liver, as well as diseases of the spleen, drink two teaspoons of copper water three times a day for a month. To prepare this water, tenpence coins are washed in lime water, then placed in a quart of water and boiled until half the volume of water is boiled away. Wearing a copper bracelet around your wrist also helps.
IRON ORE. Since ancient times, iron ore deposits have been known in Thailand. On the far northern outskirts of Thailand, in the mountainous spurs that form the right bank of the Mekong, near the village of Chiengkong, red iron ore has long been mined on a small scale. Deposits of brown iron ore have long been known in the Lampang region (southeast of Chiengmai). Ore comes to the surface here, which facilitates its development. But especially rich deposits of iron ore were discovered after the Second World War near the city of Lopburi, 130 km north of Bangkok, as well as on the island of Koh Samui in the Gulf of Thailand.
IRON in Ayurveda. Beneficial for bone marrow, bone tissue, red blood cells, liver and spleen. It increases the formation of red blood cells and therefore its ashes are used in the treatment of anemia. It is effective for enlargement of the liver or spleen. Iron strengthens muscles and nerve tissues, has restorative properties.
Alluvial deposits are also associated placers of precious stones. In the spurs of the Cardamom Mountains are found rubies and sapphires. Their main production is carried out in the provinces of Trat and Chanthaburi, located along the coast of the Gulf of Thailand, in the east of the country in the province of Sisaket, near the border with Burma - in Kanchanaburi and near the northern border with Laos - in Muang Phre.
70% of all gems mined come from Chanthaburi. The stones are mined by hand, with the exception of the Makhlong deposit, where a combined mining method is carried out.
Private companies and prospectors work mainly by hand in open pipes, pits and cuts, the depth of which starts from 5m and reaches a maximum of 15m. The sapphire gravel is then washed in baskets. mined gemstones are then cut in the capital of Thailand - Bangkok, which since the 80s of the last century has become one of the world's largest centers for the processing of precious stones. In Bangkok, due to cheap labor, 80% of sapphires mined in Australia are processed, as well as emeralds, zircons and garnets from South Africa, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Kenya and Burma, whose rubies are considered world standards.
Found in Thailand more than 20 oil and gas fields. Most of the commercial oil reserves are concentrated in the Phitsanulok basins in the north of the Menam lowland, where the Sirikit group of fields is the largest. In the far north, near the town of Muangfang, rich oil field.
The bulk of the resources natural gas concentrated within the Cenozoic basin on shelf of the Gulf of Thailand. The most important deposit is Erawan. Identified also 2 gas fields on the Korat Plateau.
Oil and gas. The first oil field - Sirikit of the Phitsanulok basin (Kamphang Phet province, 320 km from Bangkok) was discovered in 1981 (operation began in 1983).
Natural gas. Thailand's first field is the Erawan field, discovered in 1972 in the Gulf of Thailand, about 300 miles from Bangkok. Erawan, the largest offshore field in the country, started gas production in 1981.
Possiblesourceenergy raw materials can servegeothermal resources, experimental work, the use of which has been carried out since 1984 in the area of Chiang Mai.
An alternative source of energy raw materials is bioethanol (ethanol obtained from biological raw materials and used to create an environmentally more neutral fuel). The cost of producing bioethanol from cassava in Thailand is about 35 USD per barrel of oil equivalent (for comparison: Thailand buys a barrel of oil from the United Arab Emirates and Malaysia for almost 100 USD); that is why at Thai gas stations you can see prices not only for gasoline ( gas), but also for various mixtures of gasoline and bioethanol (called differently, depending on the manufacturer and the percentage of gasoline / ethanol in the mixture - gasohol, E95 etc.).
Of the non-metallic minerals, limestone deposits have been found in different parts of the country, marble (on the coast and in Saraburi province), clays for the production of ceramics (in the center of the country), kaolin (in the north and south), quartz sand (Songkhla province), gypsum (in north and south), etc.
The territory of Thailand is promising from the point of view of the search for deposits of radioactive raw materials.Monazitesfrom tinplacersdistricts Phuket - Phangnga - Takuapa and Ranong.
Thailand is rich salt.
The role of salt in the trade of Southeast Asia is still great.
Salt in Thailand is extracted from sea water, from salt springs found in the Mesozoic red sandstone formations, and from crystalline formations on the soil surface in the Korat region. Huge salt marshes form on the surface of the Korat plateau in summer. Locals have been collecting salt for a long time and sending it to Central Thailand. A lot of salt is evaporated on the coast of the Gulf of Thailand from sea water. The most important source, far superior in value to all others, is the evaporation of sea water in salt ponds. Such ponds are arranged along the coast of the Gulf of Thailand.
Located in the southeast of Asia, Thailand's geography is considered one of the most successful. The territory of the country has a holistic form, and there is also access to many water resources, which automatically gives the state a number of advantages among its neighbors in location.
Successful geography of Thailand
It so happened historically that geography of thailand- these are water resources from all sides: seas, bays. These advantages make it possible to actively develop external water trade routes with other countries from all over the world. Thailand is considered one of the largest exporters of seafood, a supplier of a huge amount of rice.
Thailand time
The tourist state is located on the territory where the time deviates from Greenwich Mean Time by 7 hours. Thailand time passes very quickly, thanks to the uniqueness and interestingness of the territories. Geography The country is diverse and worthy of paying special attention to it, studying and traveling all year round.
Climate of Thailand
The state is located in the tropical and subequatorial zones. Therefore, so diverse and contrasting. In May, it rains regularly here, and the air temperature becomes a little cool, but November always has its own warmth. That's why thailand tourism feels a special offering just in this period of time.
Thailand weather
The tourist center of southeast Asia can please its visitors with a variety of weather conditions. It is better for travelers to know what time of the year is the most convenient and warmest to visit this country. But still, it is worth saying that it never stands in the way of tourists. Regardless of rain or heat, foreigners manage to see the state in all its glory, visit all the most famous sights of this region.
Thailand nature
Both locals and tourists pay special attention to the beautiful horizons and landscapes of the country. Thailand nature very varied and attractive. The extensibility of the state allows you to combine different types of plants, create entire reserves, which then open their doors to everyone. Thailand is a place where you can relax not only with your body. But also in soul. Tranquility and nature are the sources of real strength and energy that people need so much. And all this is located in one single place on the planet - in the fabulous, maritime Thailand, in southeast Asia, on the island of Indonesia.
- a state located in the southwestern part of the Indochina peninsula and in the northern part of the Malacca peninsula. Thailand is traditionally divided into 4 regions: Central, South, North and Northeast. It borders Myanmar in the northwest, Laos in the northeast, and Cambodia in the southeast. In the south and east it is washed by the waters of the Gulf of Thailand, and in the west by the waters of the Andaman Sea.
The name of the country comes from the ethnonym of the people - tai.
Official name: Kingdom of Thailand
Capital:
The area of the land: 514 thousand sq. km
Total population: 67.1 million people
Administrative division: Divided into 73 changwats (provinces).
Form of government: A constitutional monarchy.
Head of State: King.
Composition of the population: 80% - Thais, 10% - Chinese, 3.5% - Malaysians, 6% - Khmers, Karens, Vietnamese, Indians.
Official language: Thai. English is widely spoken in tourist centers. A small part of the population speaks Japanese, Chinese and Malay.
Religion: 95% are Buddhists, 4% are Muslims.
Internet domain: .th
Mains voltage: ~220 V, 50 Hz
Phone country code: +66
Country barcode: 885
Climate

Thailand is located in the tropical climate zone. In the tropical zone of Asia, there is a change in air currents: the trade wind dominates in winter, the monsoon dominates in summer, which determines the seasons of the year. The characteristic features of the climatic regime of Thailand are due to the presence of mountains in the north, which protect its territory from the influence of the winter trade winds, so the cool season is weakly expressed.
In the northern, northeastern and central regions of Thailand, 3 seasons are distinguished per year, depending on the amount of precipitation, in the southern regions - 2. In the east of the country, a special climate has formed with a fairly even distribution of precipitation throughout most of the year and with a sharp increase in September .
During the influence of the trade wind (from November to February), mild weather is established throughout the country. The average temperature in December, the coldest month, is +19 degrees in the north and +26 in the south. At the same time, during the daytime, the air in these areas warms up to +27 and +30, respectively. In winter, the night temperature in most of Thailand does not fall below +20; only the mountainous regions in the north are characterized by lower temperatures - in January they are +10: +12 degrees, and on some days the thermometer can drop to 0.
The period from December to February is the dry season in most of Thailand. At this time, partly cloudy weather with light rains prevails; the average monthly rainfall does not exceed 40 - 50 mm. In the south, the driest month is February, in December and January the amount of precipitation varies depending on the location from 30 mm in the northernmost regions to 370 mm in the southernmost.
Summer lasts from March to May in the northern, northeastern and central regions of the country. The sun burns already in the morning, and by noon the temperature reaches +32:+35 degrees. At night, the air cools down to +25. In April, precipitation becomes more intense, and in May the third season begins in these areas - the monsoon rainy season, which lasts until the end of October. Thunderstorms occur almost daily, but they quickly end, and after them the sun shines again brightly. Daytime temperatures during this period go down by 2 - 3 degrees.
The maximum amount of precipitation occurs in September-October and is 230 - 250 mm.
In the south, the rainy season begins as early as March and lasts until January, with the maximum precipitation in different areas occurring at different times. In September-October it floods Phuket, in November-December - Koh Samui (more than 300 mm of precipitation falls per month) - At the same time, in the remaining months of the rainy season, the amount of precipitation exceeds 100 mm. The further south the territory is located, the shorter the dry season lasts. The hottest month is August, when in the daytime the air warms up to +32...34, and at night it cools down to +25.
The Central Plain, North and Northeast receive an average of 1000-1100 mm of precipitation per year, of which more than 90% falls during the wet season lasting from May to October. In the South and Southeast, the average annual rainfall is 2300–2500 mm, and their amount does not change significantly from month to month.
The dry season is especially noticeable in the Northeast. In the fields, the dry soil turns to stone and cracks. Ponds, shallow lakes, swamps and ditches dry up due to the lowering of the groundwater level. Some rivers become very shallow and become unsuitable for navigation, and sometimes they lose their flow.
The monsoon rains begin in April-May, and in early June the land is so moistened that it can be cultivated and sown. In July, irrigation canals fill with water following the rivers, which overflow widely in the Central Plain. As a result of the land in the delta of the river. The Chao Phraya are flooded almost entirely. To protect against the water element, the local population builds houses on stilts. In recent years, due to large-scale deforestation, the adverse effect of seasonal floods and droughts has increased.
Geography

Thailand is a country in Southeast Asia. It occupies the central part of the Indochina peninsula and the northern part of the Malacca peninsula, it also includes a number of small islands. In the west, Thailand borders with Laos and Cambodia, in the east - with Myanmar, in the south - with Malaysia. The country is washed by the waters of the Gulf of Thailand, the South China Sea in the south and the Andaman Sea in the southwest.
The area of Thailand is 531.1 thousand square meters. km. It stretches for 1500 km from north to south and 800 km from west to east. More than half of the country's territory is occupied by low plains; in the north and west there are mountain ranges that have a predominantly meridional direction and continue to the Malay Peninsula. The highest point in Thailand is Mount Doi Inthanon (2595 m) in the mountain range on the western border. To the east is the Korat plateau, almost devoid of vegetation as a result of intensive deforestation, and the coastal area is occupied by a plain known for its beautiful sandy beaches.
The rivers Menam, Mekong and Salween are of the greatest importance in the life of the country. The rivers are mainly fed by rain, so floods can occur during the rainy season. There are few lakes in Thailand, the largest of them is Lake Thaleluang on the Malay Peninsula.
On the territory of Thailand, 5 national parks have been created with a total area of about 8 thousand square meters. km.
The national parks include the Erawan waterfall (west of Bangkok), the highest mountain in Thailand, Doi Inthanon, and other interesting natural objects. The reserves located on the Khunthan and Tanentahunji mountain ranges in the west of the country preserve many of the plants and animals of the jungle. Here is the home of the elephants that survived in Thailand; animals can even be seen at work in forest clearings. Unique nature reserves are located on the islands in Phang Nga Bay.
Flora and fauna

Vegetable world
Currently, forests occupy 20% of the country's territory. Up to 70% of the forest stand are deciduous species. In the mountains in northern Thailand and near the border with Myanmar, moist monsoon mixed deciduous forests dominate, in which teak, planer xylia, large-fruited pterocarpus and other hardwood species grow. These forests are interspersed with thickets of bamboo.
On the open slopes in northern Thailand there are oak forests, at altitudes of more than 1000 m above sea level. alternating with pine forests of Merkuza and Khazi pines. Moist evergreen broad-leaved monsoon forests are common in the Makhlong River valley in the west and in the most humid places in the southeast.
Dry monsoon forests are found in the Korat Plateau, the Central Plain, and in the high mountains of western Thailand. These forests are dominated by stunted trees, bamboo and thorny shrubs. Evergreen rainforests are widespread in the south and southeast. They are dominated by dipterocarp (yang, takyan), hopei, anisoptera, sal tree, palm trees (areca, sago), there are bamboo, pandanus. Lianas are widespread.
There are mangroves along the coast, but introduced tree species such as eucalyptus and acacia often crowd out indigenous communities that have been severely affected by logging. The Thai government in 1989 sharply limited the scale of logging, but nevertheless, the rate of deforestation decreased only slightly.
Animal world
Hunting and loss of natural habitats have contributed to a sharp decline in the number of wild animals in Thailand. However, in some remote areas and in protected areas, elephants, tigers, leopards (including the very rare clouded leopard), white-breasted and Malay bears, gaur and banteng bulls, Asiatic buffalo, serow, and a very rare animal black-backed tapir are still found.

There are numerous monkeys (white-handed gibbons, macaques, orangutans, langurs), muntjac and sambar deer, small and large deer, antelopes and other mammals. Domesticated elephants and buffaloes are widely used in agriculture.
There are several dozen species of snakes in Thailand, including poisonous ones.
The fauna of birds is extremely diverse: there are many waterfowl (herons, white pelicans, ducks), pheasants, wild chickens, partridges, parrots, peacocks (including green ones), birds of prey, etc. are widespread. The world of insects is diverse, including more than 600 species of butterflies .
Attractions

Thailand is the leader in attendance among the countries of Southeast Asia. Thousands of Buddhist temples and monasteries, magnificent palaces and pagodas in Bangkok, beautiful beaches of Pattaya, Patong, Koh Samui and Phuket, vibrant nightlife with a wide variety of shows and entertainment, the notorious sex tourism of all kinds, the famous Thai massage and martial arts, elephant riding , excellent diving conditions, unique floating bazaars and hundreds of exotic uninhabited islands of the Andaman Sea, famous Thai cuisine and colorful Buddhist festivities - all this attracts the attention of millions of tourists.
Banks and currency

The monetary unit of Thailand is the baht (THB). There are 100 satang in one baht. There are coins in circulation in denominations of 25 and 50 satang, 1, 2, 5 and 10 baht; banknotes are issued in denominations of 10 baht, 20 baht, 50 baht, 100 baht, 500 baht and 1,000 baht.
Banks are open on weekdays from 8.30 to 15.30. The resorts have a network of exchange offices that are open from 8.30 to 20.00 or even later.
In Thailand, only local money is accepted for payment. You can exchange currency at the hotel, however, as a rule, the exchange rate at banks and exchange offices is more profitable, and in Bangkok it is more favorable than in other cities. At airports, the exchange rate is acceptable. When exchanging US dollars, it should be borne in mind that old-style banknotes (until 1993) and banknotes of some later years of issue are not always and everywhere accepted, due to the large number of counterfeit banknotes of this year of issue.
In Thailand, the exchange of dollars is quite specific - depending on the denomination of dollar bills, the exchange rate also changes. The lowest rate is offered for banknotes in denominations from 1 to 20 dollars, the highest - for banknotes of a new sample in denominations of 50 and 100 dollars. There are also exchange machines, but they do not accept all banknotes.
Most hotels and shops accept international credit cards such as Visa, American Express, etc.
Useful information for tourists

It is forbidden to photograph military installations and the interior of some temples. Ask for permission before photographing a Thai. You can import no more than 5 photographic films into the country. In Thailand, buy film only in large department stores, because in a tropical climate, if stored improperly, it quickly becomes unusable
For Thais, a good tone is restrained. Here it is not supposed to touch a person, pat him on the shoulder, and even more so stroke his head, even small children.
The royal house enjoys a particularly deep respect, so under no circumstances is criticism of it unacceptable. Shoes should be removed not only before entering the temple, but also in a private home.
It is customary to bargain in small shops and markets. Traditional Thai souvenirs are Thai silk, wooden figurines, lacquer boxes, silver items, ceramics, snake and crocodile skin items. The export of Buddha figurines, fur, ivory, tortoise shells is prohibited.
The people of Thailand are neat in their clothes. Ripped jeans and worn T-shirts disgust them. Shorts (this, by the way, applies to both men and women) can only be worn on the beach and in the hotel. However, women in miniskirts are perceived normally. There is another interesting detail: when talking with Thais, it is not customary to talk about the heat.
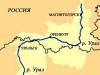
The Kingdom of Thailand is one of the most distinctive states of Southeast Asia. It is located on the Indochina Peninsula, in its southwestern part. Also, several provinces of Thailand are located on the Malay Peninsula, which Myanmar and share with it.
What countries borders Thailand?
Thailand's neighbors are:
- in the south - Malaysia;
- in the west - Myanmar (Burma);
- in the east - Cambodia and Laos.
For some reason, some tourists are sure that Thailand also borders on Vietnam, but this is not so - these states have neither land nor sea borders.
Terrain and climate
From north to south, Thailand stretches for 1860 km. The landscapes of the country are very diverse: there are high mountains, swampy lowlands, and impenetrable jungles. Northern Thailand is considered the beginning of the Himalayas - the average height here is 1500 m. The southern part of the country is covered with evergreen tropical forests, which alternate with fertile plains.
The central and southern part of Thailand has a sub-equatorial climate, which is characterized by minimal temperature fluctuations throughout the year, but noticeable fluctuations in humidity. In the north, in the mountainous part of the country, temperature fluctuations are more significant - at night it can even drop to 0°C. Thailand has a dry season and a rainy season, but they fall on different months in different regions.
What seas is Thailand bordered by?
From the west, the Kingdom is washed by the Andaman Sea, from the east by the Gulf of Thailand, which is part of the South China Sea. Both seas are part of the Indian Ocean basin. The most famous Thai resort of the Andaman Sea is the island of Phuket, the Gulf of Thailand is Pattaya. Also in the Gulf of Thailand is the island of Koh Samui (Koh Samui), which is rapidly gaining popularity among tourists from the CIS countries.