Our body contains a large amount of macro- and microelements. All these substances are involved in various processes, helping our body in its life. One of these elements is iron. Its amount in our body is very small (if we take all the iron contained in our body, then you can only make a small bolt for a wristwatch), but its function is very great.
Iron is a part of many proteins (proteins of the skin and hair), participates in enzymatic reactions and carries oxygen throughout our body. Iron is found in our body in muscles (in the form of myoglobin), in erythrocytes - red blood cells (in the form of hemoglobin), in the liver and a small amount circulates in the blood in a form associated with proteins. The liver is a kind of iron storage. This reserve is laid even in utero during pregnancy and is consumed as needed. With a decrease in the iron content in the body, a disease such as iron deficiency anemia develops. To better understand this disease, you need to know about how iron is metabolized in the body.
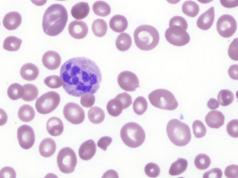
The most active form of iron that is used in our body is very often the iron found in hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is a protein molecule in which 4 iron atoms are embedded, so one such structural unit can bind 4 oxygen atoms. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells. These blood cells have a specific lifespan of 120 days.
After this period, erythrocytes are destroyed in the spleen, and iron from hemoglobin is excreted into the intestines. In the lower parts of the intestine, about 95% of iron is absorbed back and goes to build new hemoglobin molecules, the rest is excreted into the environment. Therefore, the body's need for iron is very small and iron from the "depot" (storage, liver) is practically not consumed.
The main reserves of iron in the child's body are formed during pregnancy, therefore it is so important that the expectant mother eats right, it is necessary to monitor the level of hemoglobin in the mother's blood and, if it decreases, it is imperative to correct it.
During pregnancy, the hemoglobin contained in a child has a slightly different structure and is called hemoglobin-P. This hemoglobin is able to bind oxygen more actively. This is necessary so that the exchange of oxygen between mother and child through the placenta occurs in the mother-child direction, and not in the opposite direction. To ensure a more active transfer of oxygen in an unborn child, the content of hemoglobin itself in the blood is also increased. In an adult, the hemoglobin content ranges from 120-145 g / l, and in a newborn child, its content is 220 g / l. Due to the fact that hemoglobin-P more actively binds oxygen, the erythrocyte membrane is more susceptible to the oxidative effect of oxygen, therefore, the life span of such erythrocytes is reduced to 60-80 days in term infants and to 35-40 days in premature infants. Therefore, on the 3-4th day of a child's life, active destruction of an excess of erythrocytes begins. This produces a large amount of bilirubin. Normally, it is excreted from our body with feces and urine (it is because of it that our urine is yellow, and the feces are brown), but since a newborn child has too much of it, the body does not have time to excrete it into the environment, and an excess of bilirubin stains the baby's skin yellow. This is how physiological jaundice of newborns appears.
Causes of iron deficiency anemia in children
The reasons for the development of iron deficiency anemia in children are different. They can be divided into two large groups: external (exogenous) and internal (endogenous)
Exogenous causes include:
1. Reducing the intake of iron in the child's body. 5% of the iron that is excreted in the feces must be replenished. If iron does not come from the environment with food (meat, eggs, liver, fish, vegetables, fruits) or it binds to other products and turns into indigestible complexes (when using milk, legumes, tea, coffee, nuts), then this percentage is not replenished, and the body borrows it from the liver. When liver stores are depleted, iron deficiency anemia develops.
2. With increased iron consumption. Girls begin to menstruate during puberty. This entails a loss of blood, and hence hemoglobin, therefore, at this time, girls need additional supplies of iron to the body.
3. Bleeding. Bleeding entails the consumption of iron from the body, which requires its correction.
4. Artificial feeding. Breastfeeding a baby protects him from developing anemia, since the baby receives iron from the mother's milk, and the proteins of breast milk do not bind it into insoluble complexes, unlike cow's milk proteins, on the basis of which all formulas are made. Therefore, transferring a child to artificial feeding too early can lead to the development of anemia.
Endogenous causes include:
1. Diseases of the stomach and intestines. It can be gastritis, enteritis, colitis, gastric ulcer and 12 duodenal ulcer. With all these diseases, the integrity of the mucous wall of the stomach and intestines is disrupted. Because of this, the absorption surface decreases, and iron from the intestine does not return to the body. Also, in case of gastric ulcer and 12-intestinal ulcer, periodic bleeding from ulcers is observed, which is a chronic loss of iron in the body.
2. Decrease in the concentration of vitamin B12 in the body. Vitamin B12 is involved in the transfer of iron from the intestinal lumen to the bloodstream. With a decrease in its concentration, the process of iron capture is less active, and a large amount of iron is excreted into the environment.
3. Decreased reserves of iron in the "depot" (liver). As mentioned earlier, the "depot" of iron is formed in the child during pregnancy. If the mother was ill with colds during pregnancy, did not eat well, if it is a multiple pregnancy (two or more children), there is a violation of the deposition of iron in the liver and the child is born without additional supply. Usually, after birth, there are no manifestations of this, since the amount of hemoglobin and iron content in the blood is normal, but after 3-4 months these reserves are depleted and signs of anemia appear.
4. Anemia can be observed with increased destruction of red blood cells. This can be observed when:
a) ingestion of toxic substances, in particular arsenic, the poison of some mushrooms;
b) diseases associated with a decrease in the life span of erythrocytes (sickle cell anemia, erythrocyte macrocytosis);
c) diseases of the spleen (splenomegaly).
The norm of hemoglobin in a child
a) at birth - 180-240 g / l;
b) in 1 month - 115-175 g / l;
c) from 2 to 12 months - 110-135 g / l;
d) from 1 year to 12 years old - 110-145 g / l;
e) from 13 years old and older - 120-155 g / l.
With a decrease in the hemoglobin content below these figures, they talk about the development of anemia.
 In addition to a decrease in hemoglobin in the peripheral blood, there are other changes that help to suspect anemia in a child.
In addition to a decrease in hemoglobin in the peripheral blood, there are other changes that help to suspect anemia in a child.
1. Changes in the skin, hair, nails. Iron is part of the proteins of the skin and its appendages (hair, nails). With a decrease in the level of iron in the body, dryness of the skin can be observed, the appearance of cracks, in particular in the corners of the mouth (seizures), brittle nails, their dullness, hair becomes dull, and their active loss is often observed.
2. Changes in the muscles. Iron is part of the muscle protein myoglobin. With a decrease in the iron content in the body, muscle weakness, urinary incontinence, both at night and when a child is laughing, may occur. The child becomes more lethargic, plays less, gets tired quickly.
3. Changes in the gastrointestinal tract. Iron is a part of enzymes that promote digestion, protects the lining of the stomach and intestines. When it decreases, dryness of the oral mucosa, decreased appetite, indigestion in the form of constipation and diarrhea, changes in taste preferences (sometimes children even eat clay), the appearance of ulcers on the mucous membranes of the mouth, stomach, and intestines can be observed.
4. Changes in the psychophysical development of the child. Since iron is involved in the transfer of oxygen to all tissues and organs of our body, its deficiency entails oxygen starvation of the body, and, in particular, the brain. Therefore, children with anemia lag behind their peers in growth, get more tired at school, and have poor academic performance.
5. Changes in the child's immunity. Iron is part of a large number of proteins that protect our body from bacteria and viruses. Children with anemia often have recurrent upper respiratory tract infections, frequent sinusitis, and tonsillitis. Very often, these children are on the dispensary register as often and for a long time.
Children with all of the above signs may have anemia, so they must definitely pass a general blood test to clarify the level of hemoglobin in the blood. But very often children may experience latent iron deficiency anemia, when the hemoglobin content in the blood is within normal limits (more often at its lower border), and there is no iron in the "depot". In this case, the child will have the above symptoms. To make a diagnosis in this case, it is necessary to pass a biochemical blood test. This analysis may observe:
1. Decrease in the level of protein, in particular, albumin;
2. Increase in the iron-binding capacity of blood plasma. Since the amount of iron is reduced in the liver, the body tries to capture as much of it as possible from the incoming food in order to replenish its reserves, therefore, the iron-binding capacity of blood plasma increases. Normally, it is 60-78 μmol / l.
3. Decrease in the content of serum iron in the blood. Normally, free iron, not bound to proteins, circulates in our blood, its content is normally 12-14 μmol / l. But with iron deficiency in the body, all free iron is captured by proteins for transport to the liver and the formation of hemoglobin, therefore, the level of free iron in the blood decreases.
4. Decrease in iron saturation of transferrin. Transferrin is a transport protein that transfers iron from one organ to another in our body. With a decrease in iron stores, there is a decrease in its transport between organs and therefore transferrin saturation decreases. Normally, it is 18-25%.
Treatment for anemia depends on the severity.
5. Decrease in serum ferritin level (below 10-12 ng / ml). Ferritin is a protein that binds iron in the blood and is a kind of "depot" of iron in the bloodstream, from where, in case of emergency, it can be quickly delivered for the production of hemoglobin.
Treatment of iron deficiency anemia in a child
 Allocate:
Allocate:
1. Latent iron deficiency. In this case, you can try to increase the amount of iron entering the body with food. It is very important to eat meat in combination with vegetables. Thus, the percentage of iron absorbed in the intestine increases. It is necessary to exclude milk, coffee, tea from the diet, as these products slow down the absorption of iron. The use of ascorbic acid has a very good effect on the absorption of iron. A dental examination is imperative, as gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) can lead to chronic blood loss when brushing your teeth. After a month, it is necessary to repeat the biochemical blood test, and if no improvement is observed, then the use of iron preparations is necessary.
2. In case of mild severity (hemoglobin content 90-110 g / l), it is necessary to start using iron preparations. It is very important to choose the right drug, since there are a huge number of them on the modern drug market. Iron preparations can be divided into those containing 2-valent iron and containing salts of 3-valent iron. When 2-valent iron enters the body, in order for it to be absorbed into the blood, it needs to turn into 3-valent, therefore, often preparations containing such iron can cause dyspeptic disorders (nausea, diarrhea, discoloration of the stool, staining of the teeth in black). To convert 2-valent iron into 3-valent, an acidic environment is necessary, therefore, it is recommended to combine the intake of these drugs with the intake of acidic juices or ascorbic acid, in particular the drug Tsevikap. It is also impossible to combine the intake of preparations containing 2-valent iron with food intake, especially with milk intake, since proteins will bind iron and convert it into insoluble complexes, which are excreted without being absorbed. Such iron intolerance can easily be avoided by using preparations containing 3-valent iron for treatment. Such iron is completely absorbed from the intestinal lumen without undergoing any changes. The therapeutic dosage is 3 mg / kg per day. These drugs can be measured in drops, ml, tablets. For young children, it is preferable to use iron preparations in drops. Preparations of 2-valent iron: hemofer, sorbifer, etc. Preparations of 3-valent iron: maltofer, ferrum lek, etc. It is necessary to start taking medications with 1/3 of the daily dose (for example, if a child weighs 10 kg, then his daily dose there will be 30 mg of iron, so you need to start with 10 mg). This will avoid the side effects of iron on the child's gastrointestinal tract, and if there is a side effect of the drug, quickly cancel it until too much of the active substance has entered the body. The full dosage is started after 5 days, if there is no side effect, and continue to be taken for 1 month. After that, it is necessary to repeat the general blood test and control whether the hemoglobin in the blood increases. If hemoglobin increases, then the iron preparation continues to be taken in half the dose for another 2 months. This is necessary in order to saturate the depot with iron, since in a month we only saturate the blood. If hemoglobin does not increase, then it is necessary to change the drug, but if after a month the hemoglobin remains at the same level, it is imperative to seek the advice of a hematologist, since this condition can hide more serious diseases.
3. With moderate severity (hemoglobin content 60-90 g / l), treatment tactics depend on the general condition of the child and concomitant pathology. It is possible to use iron solutions by mouth, as with mild severity, but hemoglobin control must be carried out once every 10 days. You can also use intramuscular injections of iron preparations (hemofer, ferrum lek, maltofer). These drugs quickly increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood, but with prolonged use, a complication such as hemosiderosis may develop. This is a condition when iron begins to be deposited in body tissues and form insoluble complexes. This is due to the fact that too much iron enters the body, and it does not have time to be utilized (used to build hemoglobin). Therefore, it is recommended to use intramuscular preparations for 10 days, and then, if the hemoglobin levels in the blood are normalized, switch to taking iron preparations by mouth.
4. With a severe decrease in hemoglobin (less than 60 g / l), transfusion of erythrocyte mass (washed erythrocytes) is indicated. This condition is very dangerous for the body: the amount of oxygen carried by the blood decreases, oxygen starvation begins in the tissues of the body, the brain suffers to a greater extent, since its oxygen requirements are very high. Therefore, it is urgently necessary to replenish the supply of the body's transport systems (hemoglobin). Transfusion of erythrocyte mass is carried out only in a hospital, under the strict supervision of a doctor, since very often during this operation complications can be observed that require urgent, and sometimes resuscitation measures. After the amount of hemoglobin in the blood is increased, it is necessary to find the reason for this drop in the iron content in the body. These can be latent bleeding, therefore it is very important to donate feces for the determination of occult blood, since the main body system where imperceptible blood loss can occur is the gastrointestinal tract. When taking an analysis for occult blood per day, it is necessary to exclude brushing the teeth, as this can lead to microtraumas of the gingival mucosa and the appearance of blood in the feces, 7 days before the analysis it is necessary to cancel the intake of iron preparations, to exclude apples from the child's diet 3-4 days, liver, meat, fish, beets, herbs. If blood is found in the feces, it is necessary to conduct a study of the stomach and intestines for the presence of ulcers and erosions.
Iron deficiency anemia is treated by a pediatrician. Hospitalization is indicated in the presence of a severe course of the disease (hemoglobin less than 60 g / l). Consultation with a hematologist is indicated if, with the correct treatment (monitoring the intake of iron preparations by the child, adequate dosages of drugs in accordance with the weight of the child), the amount of hemoglobin in the peripheral blood remains at the same level for 2 months, since this condition can hide more serious diseases. Treatment of anemia is long-term and the normalization of hemoglobin parameters in the peripheral blood is not an indication for the abolition of iron preparations, since it is also necessary to saturate the depot with iron (liver). Otherwise, after a month, the child will develop anemia again, and treatment will have to start over. After recovery, the child is registered at the dispensary for 1 year. If during this period the blood counts remain within the normal range, the child is removed from the dispensary registration.
Pediatrician Litashov M.V.
Hemoglobin is a substance that contains red blood cells - blood cells. These cells make up 80% of the blood. They all contain the pigment hemoglobin, which is red in color and contains iron atoms.
Reasons for a decrease in hemoglobin
- Lack of iron. It performs the respiratory function. Its deficiency leads to a violation in the body of the formation of red blood cells and, naturally, to oxygen starvation of the body.
It must be remembered that iron is not absorbed in combination with calcium. Therefore, buckwheat porridge in milk is not a dish from which the baby's hemoglobin will increase. - Lack of vitamin B12. He participates in the synthesis of hemoglobin. Here, too, you should pay attention to nutrition, B vitamins are contained in evil. However, remember that with the help of diet and certain foods, you can increase hemoglobin, but only with a slight decrease.
- Lack of protein. Hemoglobin is a complex consisting not only of iron, but also of protein, which is an order of magnitude more. And what about protein? In cottage cheese and cheese, eggs and meat. For the kid - diet varieties - rabbit, veal, turkey.
- Folic acid deficiency. It is also present in the composition of hemoglobin.
Frequent infections, pale skin, slow wound healing are symptoms of iron deficiency. This mineral is part of hemoglobin, which actively supplies oxygen to all organs of the baby. With a deficiency, there is a risk of anemia. The iron champion is red meat. Then there are eggs, beans, dark green vegetables, whole grain breads, green apples. Companions of iron - vitamins of group B, A, animal proteins. The opponents are calcium. Iron mixtures.
What is the threat of a low hemoglobin level?
The situation when child's hemoglobin level is 100 at a rate of 120 - occurs quite often, especially in children from the age of four months. At a low level of hemoglobin in the blood, the body can suffer hypoxia- insufficient oxygen saturation of the body, which can affect the well-being and even the appearance of the child. Therefore, if you find that the baby has become weak, lethargic, is a lot lazy and constantly wants to sleep, remember that one of the reasons for this behavior may be precisely hypoxia, provoked by a low level of hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin level in children
The level of hemoglobin in the baby's blood directly depends on his age. For example, at six months, the normal figure for a baby is 95-135, and for a child who is already one year old, it is 100-140. Well, if the child is already about three years old, his norm is about 145. By the way, mothers have a lot of beliefs that if the hemoglobin level of a one-year-old baby is less than 120, then you need to start to panic. But, before you decide for yourself what is the norm for your baby, it is better to consult a doctor. Keep in mind that quite often the indicator can change even without changes in the diet of the baby and his lifestyle. So, quite often pediatricians, before prescribing certain medications, suggest that additional tests be done after a while.
A low hemoglobin content leads to: anemia, constant fatigue, weakness and dizziness, up to loss of consciousness.
How to raise it, and for what reasons can its level decrease?
.
Why does the child have low hemoglobin? A child's hemoglobin deficiency can develop due to a low intake of iron in the body. Every day, about 5% of iron stores are excreted in the feces. It is necessary to replenish them with good nutrition. The causes of low hemoglobin in children often lie in increased iron consumption due to bleeding. In adolescent girls, menstrual bleeding can dramatically reduce the amount of Hemoglabin. When breastfeeding, the baby receives the necessary amount of iron from breast milk. Artificial feeding uses cow's milk, which binds iron into insoluble complexes. Therefore, the baby's body lacks hemoglobin. Diseases such as enteritis, gastritis, stomach ulcers, and duodenal ulcers can lead to a decrease in the hemoglobin content. All these diseases lead to a decrease in the absorption surface of the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines. Therefore, iron is not absorbed by the intestines. A decrease in the level of hemoglobin is due to a lack of vitamin B12, which helps to transfer iron into the blood. If during pregnancy a woman was improperly and poorly nourished, was susceptible to colds, an insufficient amount of iron is deposited in the child's liver and a lack of hemoglobin is observed immediately after birth. Also, a violation of the hemoglobin level is observed in case of poisoning with certain toxic substances that cause the destruction of red blood cells. How to increase hemoglobin in a child without resorting to drugs. ? At different ages, the norm of hemoglobin in the blood of a child is also different:
- level at birth - from 180 to 240 g / l.
- at the age of 1 month - from 115 to 175 g / l.
- from 2 months to 1 year - from 110 to 135 g / l.
- from 1 to 12 years old - from 110 to 145 g / l.
- from 13 years of age and older - from 120 to 155 g / l.
Treatment of low hemoglobin in a child is carried out with special iron-containing preparations, this will quickly help restore the balance of the trace element. There are drugs that can raise low hemoglobin, even in an infant, for example, Maltofer in drops, for the smallest, or Maltofer, Ferrum Lek in syrup, for the older ones. You can also drink Maltofer, Maltofer or Femis Fer in tablets for nursing mothers, which will increase the quality of breast milk, which in turn will affect the level of hemoglobin in the baby.
However, doctors recommend adding more foods high in iron to the diet of the baby and nursing mother.

Products that increase hemoglobin and how you can raise hemoglobin in a child
Primary products:
red meat and veal liver, as well as veal and liver puree Baby food from 6 months; vegetable puree Baby food from 6 months; oatmeal with a mark for Children from 8 months - since the manufacturers of Baby food enrich baby products with iron and vitamin "C".
These same foods are good for adults too: pregnant women, breastfeeding mothers, the elderly, and anyone else who has problems with low iron.
Daily allowance for iron from baby food puree for adults
200 g x 3 times a day.
Other products:
cereals and cereals: rice, rye, buckwheat, oatmeal, beans, peas, lentils, oatmeal; meat and fish products: fish of all sorts, heart, kidneys, red poultry meat, beef tongue and liver; vegetables: especially cooked potatoes in their skins, tomato, beetroot, pumpkin, onions, watercress, spinach, arugula, green vegetables, parsley, Brussels sprouts, beets, seaweed, garlic; fruits: green apples, bananas, plums, pomegranates *, peaches, pears, persimmons, apricots, quince; berries: cranberries, strawberries, currants, blueberries, strawberries; juices: pomegranate * (no more than 2 sips daily), carrot (with the addition of a small amount of water or milk or vegetable oil or other juice, such as apple juice), beetroot; low hemoglobin in a child can be raised with milk, cottage cheese at least 5%, red and black caviar, seafood, egg yolk, dark chocolate at least 75% cocoa, walnuts, dried fruits; hematogen - from 5 years old, indicated on the package. * Pomegranate juice for anemia is drunk in combination with iron-containing products: buckwheat, green apples, liver ..., because there is no iron in the pomegranate juice itself, but there are enzymes that enhance the absorption of iron from iron-containing products at times, that is, pomegranate juice by itself is meaningless.
Coriander tea is also useful:
It is not suitable for small children, only for adults.
In a glass or earthenware dish, brew 8 tsp. coriander seeds per 1 liter of boiling water. Insist 20 minutes. under a closed lid. Drink with honey or sugar, 1 tbsp. per day, 3 months
Do not brew in metal containers, as the metal is oxidized ...
Also, this tea is very good at leaching the body.
----
How to detect in time symptoms of low hemoglobin in a child, or even better, save him from this problem. These are the questions we will try to answer in this article.
Reasons for a decrease in hemoglobin levels
The development of a condition in which hemoglobin is reduced can lead to too rapid growth of the child. And also iron deficiency, which occurs with inadequate nutrition (and iron is mainly found in meat products, not an exception to dried fruits and vegetables).
So, iron, in turn, is the main constituent of hemoglobin. So it turns out that when there is a lack of it in the blood, hemoglobin decreases, and the child develops anemia. That is, the amount of oxygen decreases, which is why it is supplied in a small amount to cells and tissues. As a result, the organs do not develop very well, and there is a predisposition to infectious diseases. This condition is often found in children. But at the same time, anemia can always be detected at an early stage. A timely appeal to a pediatrician will help to identify it as soon as symptoms of low hemoglobin in a child were noticed. However, the signs of anemia are often attributed to the character of the child, his characteristics, and at this time the baby needs microelements. What are the symptoms of low hemoglobin that should alert parents?
The main symptoms
To begin with, you should pay attention to the child's behavior, his condition. With a lack of iron, increased fatigue appears, the baby may have a poor appetite. It is easy enough to reveal this in an active child, when his energy is lost somewhere, he gets tired quickly, and headaches appear. Already such seemingly insignificant things can be symptoms of low hemoglobin in a child and a reason to see a doctor.
The next signs of low hemoglobin are damage to the skin appendages. Nails become brittle, hair is also brittle, dull, dry. And the skin itself begins to peel off. Of course, it cannot be argued that this is 100% iron deficiency. Brittle, peeling nails can also occur due to fungal infection. Therefore, going to the doctor should not be postponed.
What else can happen to a child? As for the skin, we add that it becomes pale, like the mucous membranes. Weakness appears, possibly dizziness and tinnitus.
Symptoms of low hemoglobin in a child are quite extensive. This includes a change in taste. In such a situation, it is possible to dislike dairy products and replace them with meat or vegetables. It also happens that there is a desire to eat chalk or earth ("perverted taste"). The child can observe a slowdown in growth and weight gain.
Symptoms include the appearance of cracks, seizures in the corners of the mouth. However, such a sign may indicate hypovitaminosis, which is observed quite often in children. Also, the child should check the state of the tongue. If it is shiny and smooth, then this is also a criterion for seeking medical attention.
These are the main and most frequent symptoms of low hemoglobin in a child.
Confirmation of the diagnosis
But no one can make a diagnosis - low hemoglobin, guided only by external signs. As noted above, symptoms that indicate a decrease in hemoglobin levels can be symptoms of other diseases. Therefore, when you contact your pediatrician, he will definitely give you a referral for a blood test.
The norm of hemoglobin in the blood is 120-140 g / l. And if it becomes less than 90 g / l, then one can draw conclusions about anemia. But, it is worth considering the following factor: in children who are breastfed, the hemoglobin level may be below 90 g / l during the first two months. And this will be considered the norm. This condition is commonly referred to as false anemia. It's another matter if the baby is artificially fed. Accordingly, he does not receive iron from his mother's milk. It is necessary with the help of drugs to replenish the level of a trace element necessary for the child.
As a result, the diagnosis will be made if the following parameters are present: the level of hemoglobin is lowered, the level of erythrocytes and the color index are lowered. But this is the doctor's business, as you understand. However, it is recommended to take the analysis several times to verify the diagnosis.
Prevention of a decrease in hemoglobin
There are several points, if followed, you can save your child from anemia.
- Cow's milk is not recommended for babies under nine months old, as it can damage the gastrointestinal mucosa and thereby cause iron loss.
- Drinking tea for up to two years is contraindicated! Since it interferes with the absorption of iron.
- The child should be taught to eat coarse bread, fresh herbs. Those foods that are rich in iron.
- Do not give your child porridge more than once a day, as it also interferes with the absorption of iron.
Naturally, parents should remember that the child should periodically donate blood, even if there are no visible symptoms of low hemoglobin. You should carefully monitor what your child eats. Indeed, at a young age it is very important, it is the guarantee of your child's health for a long time. Try to teach your baby a healthy diet and healthy lifestyle.
Such a complex protein as hemoglobin, consisting of two components heme and globin, is the basis of erythrocytes. Its functional significance for the human body is great - after all, it is he who participates in the transport of oxygen molecules from the lungs to the tissues, and also removes carbon dioxide and helps to regulate the acid-base state (CBS).
In the blood, protein is presented in two variations: as oxyhemoglobin (in conjunction with oxygen), and as reduced hemoglobin (giving up oxygen molecules to tissues). If the first is found mainly in arterial blood, giving it a bright scarlet color, then the reduced protein is present in venous blood, which makes its color darker.
Naturally, hemoglobin plays a huge role in the life of the body and is an important indicator of its normal functioning. That is why, starting from birth, a blood test is taken from a person, where such an indicator as the quantitative determination of this protein is mandatory. Pediatricians all over the world reasonably pay great attention to the fact that the hemoglobin in the child's blood remains normal, since its decrease is fraught with unpleasant consequences.
Causes of low hemoglobin in a child
Depending on the age of the child, the reasons for the decrease in vital protein can be different.
As for newborn babies, due to blood loss, increased destruction or generally a violation of the production of red blood cells, anemia may be observed in a child:
The baby can lose a significant amount of blood during childbirth, this happens when premature placental abruption or rupture of the umbilical cord begins.
A low level of hemoglobin can also be in the case of increased breakdown of erythrocytes, while the bone marrow cannot cope with the production of new proteins, due to its underdevelopment. Similar phenomena are often observed in premature babies aged 1 to 2 months.
Certain diseases can also lead to increased breakdown of hemoglobin, such as hemolytic disease of the newborn. At the same time, the antibodies that he received from the mother act in the child's body. It is they who destroy the erythrocytes of the fetus.
Such a hereditary disease as spherocytosis is the cause in infants. Hemoglobin breaks down quickly due to the irregular, spherical shape of red blood cells.
The reason for the rapid destruction of red blood cells can also be an intrauterine infection received by a child, for example, rubella, herpes simplex or syphilis.
With an insufficient intake of iron from food in children, even with an initially normal level of hemoglobin, it can decrease by the age of 6 months, since the reserves received from the mother by this time are depleted.
As for children of preschool and school age, they have other reasons for a decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood:

Most often at an older age, the main cause is the child's malnutrition. But it is worthwhile to understand that it is not enough just to feed your child with foods rich in iron content. It will be absorbed only if certain vitamins and minerals (copper and manganese) are present in the body. As shown by studies conducted by the WHO, this process is largely facilitated by ascorbic acid. If it is present in the body, the assimilation of both organic (contained in food) iron and in the form of drugs occurs very quickly and almost in full.
If a child has a deficiency of folic acid and vitamin B12, the production of red blood cells is impaired, and as a result, anemia will not keep itself waiting long. This is often due to the fact that the baby receives few vegetables during the period of active growth, or they are cooked for too long.
The reason for the decrease in the level of hemoglobin so necessary for the body can be various bleeding, both explicit and latent. As for the former, for girls in the phase of puberty, these are most often begun. If the discharge is abundant, then in most cases the level of hemoglobin decreases. But with the right approach to nutrition, no additional funds are required. Also, with errors in the menu, due to even small but regular blood losses, the coveted protein becomes less, and doctors can diagnose anemia. Naturally, due to all sorts of wounds and injuries, bleeding can occur, which will inevitably lower the level of hemoglobin. As for latent bleeding, in children they can be observed with gastrointestinal diseases.
Another reason leading to the above problem may be the wrong way of life, namely: if a child spends little time on the street, does not move, does not play sports, then it is natural that his metabolism is disturbed. This will inevitably lead to low levels of iron in the blood. But it is worth considering that, on the contrary, increased physical activity can lead to a similar reaction of the body, when a child is engaged in physical labor that is unbearable for himself or too difficult a sport.
Taking certain medications during childhood, especially without the supervision of a doctor, can lead to anemia.

Most often, those children suffer from anemia whose mothers during pregnancy did not take care of curing their iron deficiency anemia. Naturally, this is transmitted to the baby, since his already small reserves are quickly depleted. In addition to the above, the cause of early anemia can be frequent colds in the mother while carrying a child, or if the pregnancy is multiple. At the same time, at birth, all indicators of the crumbs are most often normal, but by the age of 3 months, a blood test will reveal a low level of hemoglobin.
Surprisingly, the myths about artificial feeding and, as a result, the development of anemia are really myths. If the child receives a full-fledged adapted milk mixture in the proportions necessary for his age and weight, as well as the first complementary food correctly introduced, then he will not be threatened with iron deficiency. But there are exceptions, it is not worth switching to a mixture too early, since a very young organism sometimes is not able to break down the cow protein, on the basis of which mixtures are made.
As for some symptoms, the following symptoms may appear in children under one year old:
The skin becomes dry, even small cracks may appear, especially in the corners of the mouth. Hair and nails grow poorly, fall out and break.
The kid is lethargic, gets tired quickly, lags behind in development, due to changes in the muscles, he does not start to raise his head in time, turn over to one side and crawl.
The mucous membrane of the mouth dries up, it can appear, and the appetite is often reduced, the stool is disturbed. Moreover, both can be observed.
Lagging in mental development is also observed, especially if anemia remains undetected. This is due to the fact that oxygen is not “supplied” to the brain at the proper level, it experiences a corresponding starvation and cannot fully function.
The immunity of a baby up to six months of age depends on the antibodies received from the mother. Naturally, it will be reduced in those children whose hemoglobin is not at the proper level. Such babies from an early age are prone to frequent diseases of the upper respiratory tract, suffer from and.
Hemoglobin rate per year
The normal range of essential protein for life can fluctuate depending on the age of the child. The indicator that is adequate for a newborn baby will be overestimated for a one-year-old baby. That is why parents should be guided by the numbers indicating the normal values of the child's hemoglobin.
In the first 3 days of life, hemoglobin values can fluctuate between 145 and 225 g / l, and by a month they are already significantly lower from 115 to 175 g / l. Further, starting from two months of age and ending with a year, this figure varies between 110 and 145 g / l.
Knowing these numbers and regularly donating blood as directed by a doctor, you can monitor the normal level of hemoglobin and prevent the development of a disease such as iron deficiency anemia. This disease is very insidious and may not give itself out, while weakening the defenses of the baby's body. Experts note that anemia is a fairly common disease that many children face. However, do not despair, because with timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, it disappears without a trace.
How to increase hemoglobin in babies?
Ways to increase hemoglobin in infants will directly depend on the cause that caused this condition.
If protein deficiency occurs due to blood loss during childbirth, then immediate blood transfusion is required. With excessive destruction of red blood cells, exchange transfusion is required. The child's own blood is gradually and slowly replaced with donor blood. Through this procedure, damaged bilirubin and red blood cells, as well as maternal antibodies are removed from the baby's body. When direct treatment of anemia is required, appropriate iron preparations are prescribed, and when serious symptoms of the disease develop, blood transfusions are made.
Breastfeeding mothers need to adjust their diet to include those foods that are rich in iron. Indeed, in infancy, children mainly eat only mother's milk. With the introduction of complementary foods, it will be easier to raise the hemoglobin level, since the child will be able to directly obtain iron from food, without “sharing” it with the mother.
As for preventive measures, they begin at the stage when the child is in the womb. A pregnant woman should register on time, donate blood and treat anemia, if any. For babies, adequate feeding, prevention of rickets and dystrophy is shown. It is necessary to take timely measures to treat possible intestinal and infectious diseases, and, of course, do not forget about regular blood tests. This is especially true for children at risk.

Depending on the severity of the anemia, the child's hemoglobin can be raised in the following ways:
If the indicators fell below 110 g / l, but did not go beyond the 100 mark, then the baby's nutrition should be adjusted and thus try to increase the hemoglobin level. For this, it is very important to eat not just meat products, but in combination with vegetables. So the percentage of iron absorbed in the intestine is significantly increased. But about such drinks as milk, tea and coffee should be forgotten. Often, pediatricians prescribe the intake of ascorbic acid. You should consult a dentist to rule out gingivitis, as the child may lose blood when brushing their teeth. After adjusting the nutrition, a second blood test is performed, and if no improvement is observed, then the appropriate drugs are prescribed.
If the indicators have reached the limit of 100 g / l, but not lower than 90, then preparations containing iron should be taken. Their choice should be taken especially carefully, so in order to avoid many complications and improve absorption, preference should be given to the 3-valent iron contained in the tablets. Most often, the duration of the course is a month, after which a control blood sample is taken, if an increase in hemoglobin is observed, then the drugs are taken for another 60 days. All treatment must necessarily take place under the supervision of a doctor.
If the level has reached the level of 60 - 90 g / l, then one should proceed from the general condition of the child. Depending on it, either iron solutions are taken by mouth, or intramuscular injections are prescribed. Blood counts are monitored every 10 days, self-medication is unacceptable.
When hemoglobin falls below the mark of 60 g / l, an emergency transfusion of erythrocyte mass is prescribed, since such conditions are a direct threat to life, in the first place, the brain suffers.
It should be remembered that all treatment is carried out under the supervision of a physician, hospitalization is required only in the latter case, with severe anemia. At the same time, it is important for parents to remember that a balanced diet in combination with regular examinations is the best prevention of iron deficiency anemia.
Comments (1)
gulnura 2015-11-15
Elena 2015-11-15
Lamia 2015-11-16
Natalia 2015-11-19
Alexander 2015-11-19
Gibrat 2015-11-25
Alexander 2015-11-25
Raisa 2015-12-10
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2015-12-10
Evgeniya 2016-03-10
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-03-10
Irina 2016-03-18
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-03-18
Irina 2016-04-07
Marina 2016-04-12
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-12
Ardak 2016-04-15
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-15
Elena 2016-04-16
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-16
Julia 2016-04-18
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-18
Valentine 2016-04-19
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-19
Eleonora 2016-04-19
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-19
Svetlana 2016-04-26
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-26
Aknabat 2016-04-26
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-26
Love 2016-04-28
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-28
Elena 2016-04-30
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-04-30
Oksana 2016-05-01
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-05-01
Liana 2016-05-26
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-05-26
Ekaterina 2016-05-27
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-05-27
Anna 2016-06-02
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-06-02
Gulmira 2016-06-03
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-06-03
Anna 2016-06-10
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-06-10
Hope 2016-06-30
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-06-30
Galina 2016-08-08
Marina 2016-08-14
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-08-14
Vilena 2016-09-25
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-09-25
Moldir 2016-09-28
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-09-28
Anna 2016-10-02
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-10-02
Olya 2016-10-27
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-10-27
Miroslava 2016-11-08
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-11-08
Julia 2016-11-12
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2016-11-12
Anya 2016-11-25
Anastasia 2017-03-04
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-03-04
Nargila 2017-03-12
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-03-12
Natalia 2017-03-20
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-03-20
Valentine 2017-03-26
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-03-26
Nazerke 2017-03-30
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-03-30
Maria 2017-05-09
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-05-09
Julia 2017-05-15
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-05-15
Anna 2017-06-01
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-06-01
Furug 2017-06-09
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-06-09
Olga 2017-06-13
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-06-13
Dana 2017-06-22
Diana 2017-06-28
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-06-28
Olga 2017-07-04
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-07-04
Amira 2017-07-07
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-07-07
Evgeniya 2017-08-07
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-08-07
Masha 2017-08-21
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-08-21
Evgeniya 2017-08-24
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-08-24
Irina 2017-08-24
Evgeniya Vladimirova 2017-08-24