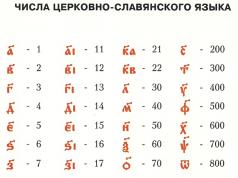
To remember how much they harvested or how many stars in the sky, people came up with symbols. In different areas, these symbols were different.
But with the development of trade, in order to understand the designations of another people, people began to use the most convenient symbols. We, for example, use Arabic symbols. And they are called Arabic because the Europeans learned them from the Arabs. But the Arabs learned these symbols from the Indians.
The symbols used to write numbers are called figures .
The word digit comes from the Arabic name for the number 0 (sifr). This is a very interesting number. It is called insignificant and denotes the absence of something.

In the picture we see a plate with 3 apples on it and an empty plate with no apples on it. In the case of an empty plate, we can say that there are 0 apples on it.
The remaining numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 are called meaningful .
Bit units
Notation which we use is called decimal. Because it is exactly ten units of one category that makes up one unit of the next category.
We count in units, tens, hundreds, thousands, and so on. These are the bit units of our number system.
10 ones - 1 ten (10)
10 tens - 1 hundred (100)
10 hundreds - 1 thousand (1000)
10 times 1 thousand - 1 ten thousand (10,000)
10 tens of thousands - 100 thousand (100,000) and so on ...
A digit is the place of a digit in a number notation.
For example, among 12 two digits: the units digit consists of 2 units, the tens digit consists of one dozen.
We talked about the fact that 0 is an insignificant number, which means the absence of something. In numbers, the number 0 means the absence of ones in the discharge.
In the number 190, the digit 0 indicates the absence of a units digit. In the number 208, the digit 0 indicates the absence of a tens digit. Such numbers are called incomplete .
And the numbers in the digits of which there are no zeros are called complete .

The digits are counted from right to left:

It will be clearer if you depict the bit grid as follows:

- In list 2375 :
5 units of the first category, or 5 units
7 units of the second digit, or 7 tens
3 units of the third category, or 3 hundreds
2 units of the fourth category, or 2 thousand
This number is pronounced like this: two thousand three hundred seventy five
- In list 1000462086432
2 pieces
3 dozen
8 tens of thousands
0 hundred thousand
2 units million
6 tens of millions
4 hundred million
0 units billion
0 tens of billions
0 hundred billion
1 unit trillion
This number is pronounced like this: one trillion four hundred sixty-two million eighty-six thousand four hundred thirty-two .
- In list 83 :
3 units
8 tens
Pronounced like this: eighty three .
Bit , call numbers consisting of units of only one digit:
For example, numbers 1, 3, 40, 600, 8000 - bit, in such numbers of zeros (insignificant digits) there can be as many or not at all, and there is only one significant digit.
Other numbers, for example: 34, 108, 756 and so on, non-digit , they are called algorithmic.
Non-bit numbers can be represented as a sum of bit terms.
For example, number 6734 can be represented like this:
6000 + 700 + 30 + 4 = 6734
1. Numbers of the second ten (twenties).
2. Numbers of the first hundred.
3. Numbers of the first thousand.
4. Multi-digit numbers.
5. Number systems.
1. Numbers of the second ten (twenties)
The numbers of the second ten (11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20) are two-digit numbers.
Two digits are used to write a two-digit number. The first digit on the right in a two-digit number is called the digit of the first digit or units digit, the second digit on the right is called the digit of the second digit or tens digit.
The numbers of the second ten in all mathematics textbooks for elementary grades are considered separately from other two-digit numbers. This is because the names of the numbers of the second ten contradict the way they are written. Therefore, many children for some time confuse the order of writing numbers in the numbers of the second ten, although they can name them correctly.
For example, when writing down the number 12 (two-twenty) by ear, the child hears “two (a)” as the first word, so he can write the numbers in this order 21, but read this entry as “twelve”.
The formation of the concept of two-digit numbers is based on the concept of "digit".
The concept of a digit is basic in the decimal number system. A digit is understood as a certain place in a number entry in a positional number system (a digit is the position of a digit in a number entry).
Each position in this system has its own name and its conventional meaning: the number in the first position on the right means the number of units in the number; the figure in the second position from the right means the number of tens in the number, etc.
The numbers from 1 to 9 are called significant, and zero is an insignificant digit. At the same time, its role in writing two-digit and other multi-digit numbers is very important: zero in the notation of a two-digit (etc.) number means that the number contains a bit designated by zero, but there are no significant digits in it, i.e., the presence of zero on the right in number 20, means that the number 2 should be perceived as a tens symbol, and at the same time the number contains only two whole tens; writing 23 will mean that in addition to 2 integer tens, the number contains 3 more units, in addition to integer tens.
The concept of "digit" plays a big role in the system of studying numbering, and is also the basis for mastering the so-called "numbering" cases of addition and subtraction, in which actions are performed by whole digits:
27 - 20 365 - 300
The ability to recognize and distinguish digits in numbers is the basis for the ability to decompose numbers into bit terms: 34 \u003d 30 + 4.
For numbers of the second ten, the concept of "digit composition" coincides with the concept of "decimal composition". For two-digit numbers containing more than one ten - these concepts do not match. For the number 34, the decimal composition is 3 tens and 4 ones. For the number 340, the bit composition is 300 and 40, and the decimal is 34 tens.
Acquaintance with the numbers of the second ten (11-20) is convenient to start with the way they are formed and the names of the numbers, accompanying it first with a model on sticks, and then reading the number according to the model:
Remembering the names of two-digit numbers in this case will not be difficult for children with a record that contradicts the name: 11, 13.17. (After all, in accordance with the tradition of reading in European scripts from left to right, in the name of these numbers, first the digit of tens should go, and then the digits of units!) Due to this feature of the numbers of the second ten, many children in the first grade get confused for a long time when writing them on hearing and reading by writing. The early introduction of symbolism plays a negative role in this case, both for remembering the names of the numbers of the second ten, and for understanding their structure. To form a correct idea of the structure of a two-digit number, you should always put tens on the left and units on the right. Thus, the child will fix the correct image of the concept in the internal plan, without special verbose explanations that are not always clear to him.
At the next stage, we offer the child the correlation of the real model and the symbolic notation:
one-on-twenty three-on-twenty seven-on-twenty

Then we move on to graphical models and to reading numbers according to the graphical model:



and then a symbolic notation of the bit composition of the numbers of the second ten:
Later, the concept of a category is introduced at school and children are introduced to the concept of "bit terms":
37 = 30 + 7; 624 = 600 + 20 + 4.
Using a decimal model instead of a bit model to get acquainted with all two-digit numbers allows, without introducing the concept of "digit", to introduce the child both to the method of forming these numbers, and to teach him to read a number from the model (and vice versa, build a model from the name of the number), and then write :

When children study second-order numbers, we recommend that the teacher use the following types of tasks:
1) on the method of forming the numbers of the second ten:
Show thirteen sticks. How many dozens and how many more individual sticks?
2) on the principle of formation of a natural series of numbers:
Draw a picture for the problem and solve it orally. “There were 10 cinemas in the city. They built 1 more. How many cinemas are there in the city?”
Decrease by 1: 16, 11, 13, 20
Zoom in 1:19, 18, 14, 17
Find the value of the expression: 10+ 1; 14+1; 18-1; 20-1.
(In all cases, one can refer to the fact that adding 1 leads to the next number, and decreasing by 1 leads to the previous number.)
3) on the local value of the digit in the notation of the number:
What does each digit in the number entry mean: 15, 13, 18, 11, 10.20?
(In the entry for the number 15, the number 1 indicates the number of tens, and the number 5 indicates the number of ones. In the entry for the number 20, the number 2 indicates that there are 2 tens in the number, and the number 0 indicates that there are no ones in the first digit.)
4) in place of a number in a series of numbers:
Fill in the missing numbers: 12.........16 17 ... 19 20
Fill in the missing numbers: 20 ... 18 17.........13 ... 11
(When completing a task, they refer to the order of numbers when counting.)
5) for the digit (decimal) composition:
10 + 3 = ... 13-3 = ... 13-10 = ...
12=10 + ... 15 = ... + 5
When performing a task, they refer to a bit (decimal) model of a number from a dozen (a bunch of sticks) and units (individual sticks),
6) to compare the numbers of the second ten:
Which number is larger: 13 or 15? 14 or 17? 18 or 14? 20 or 12?
When completing a task, you can compare two models of numbers from sticks (a quantitative model), or refer to the order of the numbers when counting (the smaller number is called when counting earlier), or rely on the process of counting and counting (counting two units to 13 we get 15, which means 15 more than 13).
Comparing the numbers of the second ten with single-digit numbers, one should refer to the fact that all single-digit numbers are less than two-digit ones:
What is the largest and smallest of these numbers: 12 6 18 10 7 20.
When comparing the numbers of the second ten, it is convenient to use a ruler.

7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25
Comparing the lengths of the corresponding segments, the child clearly determines the setting of the comparison sign: 17< 19.
To write numbers, people came up with ten characters, which are called numbers. They are: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 .
With ten digits, you can write any natural number.
Its name depends on the number of characters (digits) in the number.
A number consisting of one sign (digit) is called a single digit. The smallest single-digit natural number is "1", the largest is "9".
A number consisting of two characters (digits) is called a two-digit number. The smallest two-digit number is “10”, the largest is “99”.
Numbers written with two, three, four or more digits are called two-digit, three-digit, four-digit or multi-digit. The smallest three-digit number is "100", the largest is "999".
Each digit in the record of a multi-digit number occupies a certain place - a position.
Remember!
Discharge- this is the place (position) at which the digit stands in the notation of the number.
The same digit in a number entry can have different meanings depending on which digit it is in.
The digits are counted from the end of the number.
Units digit is the least significant digit that ends any number.
The number " 5" - means " 5" units, if the five is in last place in the number entry (in the units' place).

Tens place is the digit that comes before the units digit.
The number "5" - means "5" tens, if it is in the penultimate place (in the category of tens).

Hundreds place is the digit that comes before the tens digit. The number "5" means "5" hundreds if it is in the third place from the end of the number (in the hundreds place).

Remember!
If there is no digit in the number, then the number “0” (zero) will be in its place in the record of the number.
Example. The number " 807»Contains 8 hundreds, 0 tens and 7 units - such an entry is called bit composition of the number.
807 = 8 hundreds 0 tens 7 onesEvery 10 units of any rank form a new unit of a higher rank. For example, 10 ones make 1 tens, and 10 tens make 1 hundred.
Thus, the value of a digit from digit to digit (from ones to tens, from tens to hundreds) increases 10 times. Therefore, the counting system (calculus) that we use is called the decimal number system.
Classes and ranks
In the notation of a number, the digits, starting from the right, are grouped into classes of three digits each.
Unit class or the first class is the class that the first three digits form (to the right of the end of the number): units place, tens place and hundreds place.
Thousand class or the second class is the class which is formed by the following three digits: units of thousands, tens of thousands, and hundreds of thousands.
| Numbers | Thousand class (second class) | Unit class (first class) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hundreds of thousands | tens of thousands | units of thousands | hundreds | dozens | units | |
| 5 234 | - | - | 5 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 12 803 | - | 1 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 3 |
| 356 149 | 3 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 4 | 9 |
We remind you that 10 units of the hundreds place (from the class of units) form one thousand (the unit of the next place: the unit of thousands in the class of thousands).
10 hundreds = 1 thousandMillion class or the third class is the class which is formed by the following three digits: units of millions, tens of millions, and hundreds of millions.
The million place unit is one million or one thousand thousand (1,000 thousand). One million can be written as the number "1,000,000".
Ten such units form a new bit unit - ten million "10,000,000"
Ten tens of millions form a new digit unit - one hundred million or in the notation in numbers " 100 000 000".
| Numbers | Thousand class (second class) | Unit class (first class) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hundreds of millions | tens of millions | units million | hundreds of thousands | tens of thousands | units of thousands | hundreds | dozens | units | |
| 8 345 216 | - | - | 8 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 6 |
| 93 785 342 | - | 9 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| 134 590 720 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 0 |
| Numbers | Million class (third class) | Thousand class (second class) | Unit class (first class) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hundreds of millions | tens of millions | units million | hundreds of thousands | tens of thousands | units of thousands | hundreds | dozens | units | |
| 8 345 216 | - | - | 8 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 6 |
| 93 785 342 | - | 9 | 3 | 7 | 8 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| 134 590 720 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 9 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 0 |
How to read a multi-digit number
Remember!
Do not pronounce the name of the class of units, as well as the name of the class, all three digits of which are zeros.
For example, the number " 134 590 720"We read: one hundred thirty-four million five hundred ninety thousand seven hundred twenty.
The number " 418 000 547"We read: four hundred and eighteen million five hundred and forty-seven.
On our website, to check your results, you can use the calculator for decomposing a number into digits online.
Important!
Digits in the notation of multi-digit numbers are divided from right to left into groups of three digits each. These groups are called classes. In each class, the numbers from right to left represent the units, tens, and hundreds of that class:
The first class on the right is called unit class, second - thousand, third - million, fourth - billion, fifth - trillion, sixth - quadrillion, seventh - quintillion, eighth - sextillions.
For the convenience of reading the entry of a multi-digit number, a small gap is left between the classes. For example, to read the number 148951784296, we select classes in it:
and read the number of units of each class from left to right:
148 billion 951 million 784 thousand 296.
When reading a class of units, the word units is usually not added at the end.
Each digit in the record of a multi-digit number occupies a certain place - a position. The place (position) in the record of the number on which the digit stands is called discharge.
The digits are counted from right to left. That is, the first digit on the right in the number entry is called the first digit, the second digit on the right is the second digit, etc. For example, in the first class of the number 148 951 784 296, the number 6 is the first digit, 9 is the second digit, 2 - digit of the third digit:

Units, tens, hundreds, thousands, etc. are also called bit units:
units are called units of the 1st category (or simple units)
tens are called units of the 2nd digit
hundreds are called units of the 3rd category, etc.
All units except simple units are called constituent units. So, a dozen, a hundred, a thousand, etc. are constituent units. Every 10 units of any rank is one unit of the next (higher) rank. For example, a hundred contains 10 tens, a dozen - 10 simple ones.
Any constituent unit compared to another unit smaller than it is called unit of the highest category, and in comparison with a unit greater than it is called lowest rank unit. For example, a hundred is a higher unit relative to ten and a lower unit relative to a thousand.
To find out how many units of any digit are in a number, you must discard all the digits that mean the units of the lower digits and read the number expressed by the remaining digits.
For example, you want to know how many hundreds are in the number 6284, i.e. how many hundreds are in thousands and hundreds of this number together.
In the number 6284, the number 2 is in third place in the class of units, which means that there are two simple hundreds in the number. The next number to the left is 6, meaning thousands. Since every thousand contains 10 hundreds, there are 60 of them in 6 thousand. In total, therefore, this number contains 62 hundreds.
The number 0 in any category means the absence of units in this category. For example, the number 0 in the tens place means the absence of tens, in the hundreds place - the absence of hundreds, etc. In the place where 0 stands, nothing is pronounced when reading the number:
172 526 - one hundred seventy-two thousand five hundred twenty-six.
102026 - one hundred two thousand twenty-six.
Numbers greater than a thousand are considered multivalued. Multi-digit numbers are numbers in the thousands class and the million class. Multi-valued numbers are formed, named, written based not only on the concept of a category, but also on the concept of a class.
The class combines three categories.
The class of units is units, tens and hundreds. This is first class.
The thousands class is units of thousands, tens of thousands, hundreds of thousands. This is second class. The unit of this class is the thousand.
Class of millions - units of millions, tens of millions, hundreds of millions. This is third grade. The unit of this class is the million.
Table of ranks of class I:
The table contains the number 257. Table of digits of class II:
The table contains the number 275,000,000.
Multi-digit numbers form the second class - the class of thousands and the third class - the class of millions.
Ten hundred is a thousand. Numbers from 1001 to 1,000,000 are called numbers in the thousands class.
Numbers in the thousands class are four-, five-, and six-digit numbers.
Four-digit numbers are written in four digits: 1537, 7455, 3164, 3401. The first digit on the right in a four-digit number is called the first digit or units digit, the second digit on the right is the second digit or tens digit, the third digit on the right is the third digit or hundreds digit , the fourth digit from the right - the digit of the fourth digit or thousand digit.
The fifth digit is the tens of thousands, the sixth digit is the hundreds of thousands.
The table contains the number 257,000. Class III rank table:


Integer thousands: 1000,2000,3000,4000,5000,6000,7000,8000,9000.
Read multi-digit numbers from left to right. For numbers 1001 and further, the order of naming their bit numbers and the order of recording is the same: 4321 - four thousand three hundred and twenty one; 346 456 - three hundred forty-six thousand four hundred fifty-six.
Rule for reading multi-digit numbers: multi-digit numbers are read from left to right. First, the number is divided into classes, counting three digits from the right. Reading begins with units of the senior classes (on the left). Units of the senior classes are read immediately as a three-digit number, then adding the name of the class. Class I units are read without adding the class name.
For example: 1 234 456 - one million two hundred thirty-four thousand four hundred fifty-six.
If some class in the number entry does not contain significant digits, it is skipped when reading.
For example: 123 000 324 - one hundred twenty-three million three hundred twenty-four.
The concept of "class" is basic for the formation of multi-valued numbers. All multi-digit numbers contain two or more classes.
The class combines three digits (ones, tens and hundreds).
In writing, when writing a multi-digit number, it is customary to make a detente between classes: 345 674, 23 456, 101 405.12 345 567.
The rule for writing multi-digit numbers: multi-digit numbers are written by class, starting with the highest. To write down a number in numbers, for example, twelve million four hundred and fifty thousand seven hundred and forty-two, they do this: they write down the units of each named class in groups, separating one class from another with a small gap (discharge): 12 450 742.
Class composition - the allocation of "class numbers" (class components) in a multi-valued number.
For example: 123,456 = 123,000 + 456
34 123 345 - 34 000 000 + 123 000 + 345
Bit composition - selection of bit numbers in a multi-digit number: _____

On the basis of the discharge composition, the cases of discharge addition and subtraction are considered:
400 000 + 3 000 20 534 - 34 340 000 - 40 000
534 000 - 30 000 672 000 - 600 000 24 000 + 300
When finding the values of these expressions, they refer to the bit composition of three-digit numbers: the number 340,000 consists of 300,000 and 40,000. Subtracting 40,000 we get 300,000.
Bit terms - the sum of the bit numbers of a multi-digit number:
247 000 - 200 000 + 40 000 + 7 000
968 460 - 900 000 + 60 000 + 8 000 + 400 + 60
Decimal composition - highlighting tens and ones in a multi-digit number: 234,000 is 23,400 dess. or 2,340 cells.
When studying the numbering of multi-valued numbers, the cases of addition and subtraction are also considered, based on the principle of constructing a sequence of natural numbers:
443 999 +1 20 443 - 1 640 000 + 1 640 000 - 1
10599+1 700000-1 99999 + 1 100000-1
When finding the meaning of these expressions, they refer to the principle of constructing a natural series of numbers: adding 1 to the number, we get the next (subsequent) number. Subtracting from the number 1, we get the previous number.
Here are the main types of tasks performed by children in the study of multi-digit numbers:
1) for reading and writing multi-digit numbers:
Break the number into classes, say how many units of each class are in it, and then read the number:
7300 29608 305220 400400 90060
7340 29680 305020 400004 60090
When completing the task, you should use the rule for reading multi-digit numbers.
Write and read the numbers in which: a) 30 units. second class and 870 units. first class; 6) 8 units second class and 600 units. first class; c) 4 units. second class and 0 units. first class.
When completing the task, you should use the table of ranks and classes.
Write the numbers in numbers: "The smallest distance from the Earth to the Moon is three hundred and fifty-six thousand four hundred and ten kilometers, and the largest is four hundred and six thousand seven hundred and forty kilometers."
The students wrote down the number nine thousand forty like this: 940, 900040, 9040. Explain which entry is correct.
When performing tasks, you should use the rule for writing multi-digit numbers.
2) on the bit and class composition of multi-digit numbers:
Replace these numbers with the sum according to the sample: 108201 = 108000 + 201
360 400 = ... + ... 50070 = ... + ... 9007 = ... + ... Task for the class composition of a multi-digit number.
Replace each number with the sum of the bit terms:
205 000 = ... + ... 640 000 = ... + ...
200 000 + 90 000 + 9 000 299 000 - 200 000
4 000 + 8 000 408 000 - 8 000
How many units of each category in the number 395 028, in the number 602 023? How many units of each class are in these numbers?
When performing tasks, a scheme of bit composition of multi-digit numbers is used.
3) on the principle of formation of a natural series of numbers:
Find the values of the expressions: 99 999 +1 30 000 - 1
100000-1 699999 + 1
In all cases, one can refer to the fact that adding 1 leads to obtaining the number of the next one, and decreasing by 1 leads to obtaining the number of the previous one.
4) on the order of the numbers in the natural series:
Three tractors have the following serial numbers: 250,000,249,999, 250,001. Which of them rolled off the assembly line first? Second? Third?
Write down all six-digit numbers that are greater than 999996.
5) on the local value of the digit in the notation of the number:
What does the number 2 mean in the entry of each number: 2, 20, 200, 2,000, 20,000, 200,000? Explain how the value of the number 2 in the notation of a number changes when its place changes.
What does each digit in the number entry mean: 140,401, 308,000, 70,050?
(In the entry of the number 140401, the number 4, which is in the third place from the right, indicates the number of hundreds, the number 4, which is in the fifth place from the right, indicates the number
tens of thousands. The number 1, which is in the first place from the right, indicates the number of ones in the number, and the number 1, which is in the sixth place from the right, indicates the number of hundreds of thousands. The number 0, which is second from the right and fourth from the right, means that there are no ones in the second and fourth digits.)
Use the numbers 9 and 0 to write one five-digit number and one six-digit number. Use the same numbers to write other multi-digit numbers.
6) for comparison of multi-digit numbers:
Check if the equalities are correct:
5 312 < 5 320 900 001 > 901 000
Compare numbers:
a) 999 ... 1000 b) 9 999 ... 999 c) 415 760 ... 415 670
d) 200 030 ... 200 003 e) 94 875 ... 94 895
When comparing the first pair of numbers, they refer to the order of the numbers in the natural series: the next number is greater than the previous number.
When comparing the second pair of numbers, they refer to the number of characters in the number entry: a three-digit number is always less than a four-digit one.
When comparing the third, fourth and fifth pairs of numbers, the multi-digit comparison rule is used: To find out which of the two multi-digit numbers is greater and which is less, do this:
Compare numbers bit by bit, starting with the highest digits.
For example, of the two numbers 34567 and 43567, the second one is larger, since it contains 4 ones in the tens of thousands place, and the first one contains three ones in the same place.
Of the two numbers 415,760 and 415,670, the first is greater, since the class of thousands in both numbers contains the same number of units - 415 units. thousand, but in the discharge of hundreds of thousands, the first number contains 7 units, and the second - 6 units.
Of the two numbers 200,030 and 200,003, the first is larger, since the class of thousands in both numbers contains the same number of units - 200 units. thousand, in the hundreds place both numbers contain zeros, in the tens place the first number contains 3 units, and the second number in the tens place has no significant digits (contains zero), so the first number is larger.
For greater clarity, when completing a task, you can compare two models of numbers from the bones in the accounts (quantitative model).
Comparing multi-digit numbers, you can refer to the fact that a number containing more characters in the record will always be greater than a number containing fewer characters.
When comparing numbers of the form:
99 999 ... 100 000 989 000 ... 989 001
567 999 ... 568 000 599 999 ... 600 000
you should refer to the order of the numbers when counting: the next number is always greater than the previous one.
7) on the decimal composition of multi-digit numbers:
Write down the numbers: 376, 6517, 85742, 375264. How many tens are in each of them? Highlight them.
To determine the number of tens in a multi-digit number, you can cover the last digit (first from the right) with your hand. The remaining numbers will show the number of tens.
To determine the number of hundreds in a number, you can cover the last two digits in the number entry (first and second from the right) with your hand. The remaining digits will show the number of hundreds in the number.
For example, in the number 2 846 - tens 284, hundreds - 28. In the number 375 264 - tens 37 526, hundreds - 3 752.
Consider the numbers: 3849. 56018. 370843. Which of the underlined numbers shows how many tens are in the number? Hundreds? Thousand?
How many hundreds are there in 6800?
Write down 5 numbers, each containing 370 tens.
8) on the relationship between the categories:
Write by filling in the blanks:
1 thousand = ... hundred. 1 hundred = ... des. 1 thousand = ... dec.
How will the numbers 3,000, 8,000, 17,000 change if one zero is discarded in their entries on the right? Two zeros? Three zeros?
Compare the numbers in each column. How many times does a number increase when one zero is added to its right side? Two zeros? Three zeros?
17 170 1 700 17000
Numbers 57, 90, 300 increase 10 times, 1,000 times.
Decrease the numbers 3,000, 60,000, 152,000 by 10 times, by 100 times, by 1,000 times.
When completing the last two tasks, they refer to the fact that increasing the number by 10 times transfers it to the next digit on the left (tens to hundreds, hundreds to thousands, etc.), and decreasing the number to. 10 times transfers it to the next category on the right (tens to units, hundreds to tens).
When the number is increased by a factor of 10 (100.1000) in this way, you can simply assign zero to the right (two zeros, three zeros). When the number is reduced by 10 times (100, 1000), one zero can be discarded on the right in the number entry (two zeros, three zeros).
Acquaintance with the number 1,000,000 (million) completes the study of the class of thousands.
Ten hundred thousand is a million. A thousand thousand is a million.
A million is written like this: 1,000,000.
The number 1,000,000 completes the study of numbers in the class of thousands.
A million (1000,000) is a unit of a new class - the class of millions.
A million (1,000,000) is the first seven-digit number in the series of natural numbers.
A million is the smallest seven-digit number.
A million is a new counting unit in the decimal number system.
In the entry of the number 1,000,000, the number 1 means that in the VII digit (million digit) there is one unit, and in the digits of hundreds of thousands, tens of thousands, units of thousands, etc., zeros mean that there are no significant digits in these digits.
The class of millions contains three digits of units of millions, tens of millions and hundreds of millions (VII, VIII and IX digits).
The millions class ends with the number billion.
A billion is 1000 million.
1000 billion is a trillion.
1000 trillion is a quadrillion.
1000 quadrillion is a quintillion.
It is impossible to imagine such a quantity of something. AND I. Depman in The History of Arithmetic gives the following example to illustrate large numbers: “A heavy railroad car can hold 50 million rubles in ten-ruble tickets (bills). It would take 20,000 wagons to transport a trillion rubles.”
Visual class table model:

The number is read like this: 412 million 163 thousand 539
They write it down like this: 412 163 539
For numbers of the million class, the reading rule, the writing rule, and the multi-digit comparison rule apply (see above).
In a stable textbook of mathematics for elementary grades, numbers over a million are not considered.