Not all poisonous species are deadly, however, they can be extremely Negative influence on human body... The varieties, the use of which can lead to death, are relatively few - they must be detected at first glance. In no case touch them, much less put them on other mushrooms. Below are the top 5 most life-threatening mushrooms found in Russia.
This is, without exaggeration, the most poisonous mushroom in the world. Even a small part of it contains enough toxic substances to kill an adult. The danger of toadstool is not only that the poison is not neutralized after any type of processing (drying, boiling, frying, freezing), but also in the resemblance to harmless green or yellow russules and mushrooms. If you notice a pale toadstool in the forest, do not approach and touch it. The fungus grows in cool and dark places.
Characteristic external features: cap in the shape of a flattened bell without spots and scales of white, pale green, yellow-green or olive shades. Towards the middle, the color of the cap is darker - usually olive-brown. The diameter of the cap is 11 cm, the length of the leg is 15 cm, the thickness of the leg is 2 cm. The leg tapers upwards, usually white or greenish - you can see a filmy ring on it. The base of the toadstool has a saccular vagina, popularly called the "cup of death". Grows singly or in groups and, fortunately, is quite rare.
Another name is spring amanita. The mushroom looks quite impressive due to the snow-white of the entire fruiting body, which is not lost with age. Mushroom pickers often confuse this poisonous specimen with champignons and an umbrella mushroom. However, it is worth taking a closer look: the leg of the mushroom is surrounded by a volva, its cap over time acquires a flattened cone-shaped shape characteristic of the same toadstool with a tubercle in the middle. The leg is hollow, covered with scales closer to the bottom, the mushroom smells unpleasant.
If you eat the fruiting body itself, it is possible fatal outcome, if the fly agaric got into the basket with other mushrooms, and they were eaten, most likely the case will end with moderate poisoning. In case of tactile contact, it is necessary to immediately wash off the toxic substances with water.
Whitish talker
In coniferous and mixed forests, a poisonous whitish talker is found. This is a small mushroom up to 7 cm high with a white cap resembling a saucer, and thin frequent plates on its inside... The danger of this variety is that it can be confused with russula, volushka or edible types of talkers. You can meet this "enemy of mushroom pickers" in the fields and meadows.
There are many inedible varieties of false mushrooms.: brick-red, sulfur-yellow, Candoll honey mushrooms, poppy seeds. The most dangerous is the sulfur-yellow false honey. Its use will certainly lead to nausea and vomiting, sweating, bloating, diarrhea, visual impairment and even loss of consciousness. With a severe degree of poisoning, a lethal outcome is not excluded. Toxic substances this mushroom is so corrosive that just one mushroom can ruin the whole pot of good, edible honey mushrooms.
How to distinguish false mushroom from the present? First of all, you should pay attention to the ring on the leg characteristic of honey agarics: not edible mushrooms it is usually less pronounced or absent altogether. Also, false mushrooms smell much worse, and their caps have a brighter color.
The pig is thin
Previously, this species was considered conditionally edible, but more recently it has been classified as a poisonous species. It's all about lectins that are not destroyed by heat treatment and cause a strong allergic reaction. Especially pigs are contraindicated for people suffering from renal failure ... Fatal symptoms include respiratory failure, exacerbation of renal disease, and intravascular coagulation.
The pig looks unremarkable: a brown cap with a diameter of about 14-15 cm with lowered edges is set on a short solid leg with a matte surface. At the cut site, the mushroom darkens.
The most poisonous mushrooms for humans (video)
Types of poisonous mushrooms in the Moscow region and the Leningrad region
The two largest Russian megalopolises - Moscow and St. Petersburg - are the birthplace of many forest lovers. What do you need to know to safely pick mushrooms in these areas? First, you should drive away from cities at a safe distance of about 35-40 km. Secondly, you need to know what poisonous varieties of mushrooms can be seen in these parts of Russia.
The mushroom, which occupies a leading position in the list of the deadliest mushrooms on the planet, has not bypassed the Moscow region either.
Considered inedible rather than poisonous. Popular name- orange talker. It differs from real chanterelles by the smooth edge of the bright cap and the release of milky juice at the cut site.
Satanic mushroom
This species with a terrifying name is quite dangerous. and may be mistakenly placed in a basket instead of a white or oak tree. Characteristic signs: large, fleshy leg, covered with a red openwork mesh, and a cushion-shaped white thick cap.
Amanita muscaria
This bright representative forest flora can be found in mixed, coniferous and birch groves from July to the end of October in Leningrad region... Fortunately, the fly agaric, familiar to everyone from children's fairy tales, is quite easy to distinguish from edible species by a red hat with white scales and a snow-white leg with a characteristic "skirt".
How to distinguish edible from poisonous mushrooms (video)
List and characteristics of poisonous mushrooms of the Volgograd region
In addition to the aforementioned pale toadstool, satanic mushroom, false mushrooms and fine pigs in Volgograd region you can encounter several more dangerous varieties.
Poisonous row
Inhabits coniferous and deciduous forests. The popular name for this poisonous family of mushrooms is talkers. External signs: a flat cap covered with gray scales, a mealy plaque on the stem. The leg itself reaches a height of 8 cm, brown to the bottom. The danger of poisonous ryadovka is that it is confused with champignon. After a couple of hours from the moment of eating, vomiting and severe upset of the intestinal tract begin.
White row
Like a poisonous ryadovka, a ryadovka white is also not suitable for eating, since it causes poisoning. White ryadovka hat open, convex... Stem - fleshy and dense, light in color, with an extension closer to the base. The fruiting body itself is pungent, unpleasant odor and taste.
Unfortunately, this variety is well camouflaged, and only an unpleasant smell and yellowing at the cut site can help distinguish an impostor from a real champignon. In this case, the way out of the situation will be the motto of mushroom pickers: "If you are not sure about the mushroom, do not take it to the basket."
Poisonous mushrooms of Siberia
The Siberian part of Russia is the most extensive, on its territory is located most of forests of the country. Along with healthy gifts from the taiga, one can find dangerous plants and mushrooms. In addition to the varieties already mentioned in Siberia, grow:
Broken fiber
The mushroom looks quite recognizable: a rounded brown cap with a dark tubercle in the middle and uneven edges is planted on a thin high leg. Deadly due to the presence of muscarine in the poison.
Found only in southern regions Siberia. Refers to woody mushrooms and is sometimes mistaken for woody or winter honey. The gallery looks like this: an almost flat brown or reddish-brown sticky hat on a hollow leg with a ring and a bloom. On the part of the leg under the ring, you can see scales that distinguish the gallery from the woody honeydew.
Poisonous mushrooms of Ukraine
As in the territory of Russia, in Ukraine there are often mushroom poisonings due to the ignorance of the population about the poisonous species. In addition to the widespread pale toadstool, fly agarics, ryadovki, satanic mushroom and pigs, in Ukraine you can see:
Entoloma spring
Starting from April, groups of very dangerous mushrooms begin to grow in aspen and birch groves. Entoloma vernalis has well recognizable outward signs, such as a conical dark brown cap, the same brown thin stem and gray-brown mid-frequency plates on the inside of the cap. Entoloma smells like damp and generally looks unattractive, which can save an inexperienced mushroom picker from big trouble.
The cone-shaped cap is stripe from the center to the edges, the stem is brownish-white. The fruiting body secretes easily inhaled spores, which are poisonous in the same way as the pulp of the fruiting body. Fiber contains muscarine and is 20 times more dangerous than red fly agaric. Even a tiny bite raw will cause repeated bouts of vomiting due to the pungent taste.
False weight
A characteristic feature of the poisonous "brother" of the lump is purple tint at a round, slightly wavy cap. In a mature mushroom, the stem is hollow; on the cut, the flesh turns reddish and spreads the smell of coconut or camphor. Dangerous to human health and life.
You should take a responsible approach to such an activity as "quiet hunting" - inattention threatens the gatherer with severe poisoning or even death. If you are not sure that the plucked gifts of nature can be eaten, consult with experienced mushroom pickers, and it is better not to approach suspicious specimens at all.
What happens if you eat a poisonous mushroom (video)
Gallery: poisonous mushrooms of Ukraine (41 photos)
















This article discusses the most common and certainly edible mushrooms that can be safely eaten without fear of poisoning.
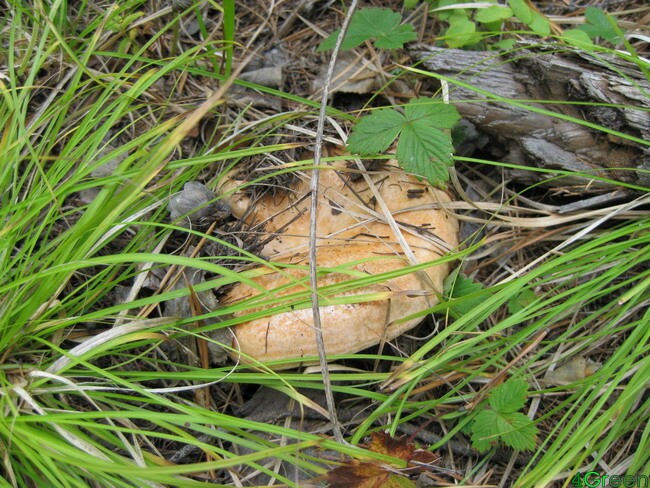
White mushroom
White mushroom (or boletus) can live in symbiosis with pine, spruce, oak and therefore grows in coniferous and mixed forests. A mushroom head with a diameter of 7-30 cm, convex, color from red-brown to almost white, can be lemon-yellow, orange, purple tones. The stump of the mushroom is cylindrical, with a thickening in the lower part.

It is used fresh (boiled and fried) and dried. After drying, the protein of the mushrooms becomes more available for the digestive system (up to 80% of the protein is absorbed)
White mushroom is widespread on all continents except Australia. Russian forests are abundant porcini mushroom decreases in the direction from west to east, from the European part of Russia to Eastern Siberia, by Far East already found abundantly.
Collect from June to September.
Boletus and boletus
Both mushrooms belong to the same species Leccinum (Obabok), differ only in the color of the cap, according to chemical composition, taste is almost the same ..
The boletus has a whitish-gray or brownish cap. Below the cap is gray with brown spots, the stump is cylindrical, slightly thickened downwards.


The cap of the boletus is red or orange, whitish-gray underneath, the stump is gray, thickened downward. On a fresh break, the flesh of the mushroom is stained with a bluish or greenish color.

Both mushrooms grow more often in deciduous, but sometimes in mixed forests.
Eat them fresh, dried and pickled form.
Recipe from the author: the collected mushrooms are washed, cut into pieces and boiled for 15 minutes in salted water. Then you can fry them with potatoes or just like that. And yet, the boletus legs, added to the tourist soup, give a very rich, thick broth.
Collection time is from June to September.
Butterlets

They grow in groups under pines and spruces, less often under other trees. The cap of the oiler is round, up to 10 cm or more in diameter. From above it is yellowish-brown, in damp weather it is covered with a layer of mucus, in dry weather it shines. Below the cap is light yellow.
Eat fresh (pre-boiled mushrooms to fry) and pickled.
They are collected from July to October.
Lactose

Grows in pine and deciduous forests. The color of the fungus is white, sometimes with brownish spots. The hat is funnel-shaped with the edges curled down. If a sticky fringe hangs from the edges of the cap, it is a "raw" breast, if there is no fringe, it is "dry". Milk mushrooms are good when salted. For direct consumption, mushrooms need to be soaked in water a little (about an hour at least) to wash out the bitter milky juice, then they are fried.
Collection time July-September.
Ryzhik

It is found under pine, larch and spruce forests. In a young mushroom, the cap is slightly convex, in the old one it may be in the shape of a funnel. Above and below the cap is orange, sometimes with greenish spots. When the mushroom breaks, orange juice is released. If there is a fringe along the edge of the cap, then this is not a mushroom, but a wave. Throw it away - don't get poisoned, but still ..
The mushrooms are salted, pickled and fried (without boiling). You can simply add salt to the mushroom and fry it on a twig over a fire.
We collect them from July to September.
General rules for picking mushrooms:
Better to harvest early in the morning or before lunchtime
Don't pick unfamiliar mushrooms
Look closely, mushrooms can hide!)
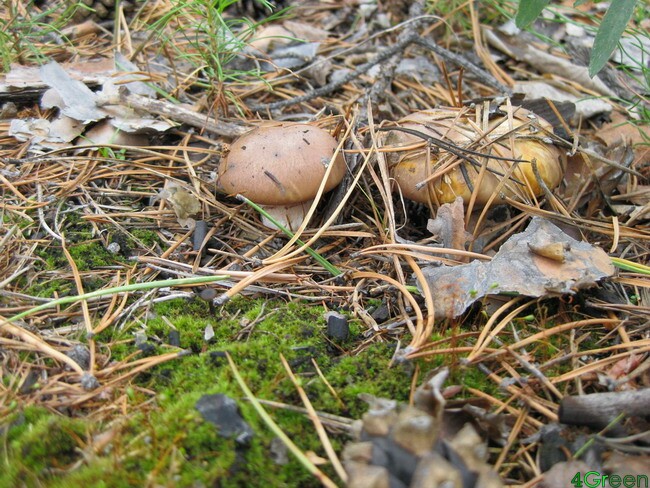
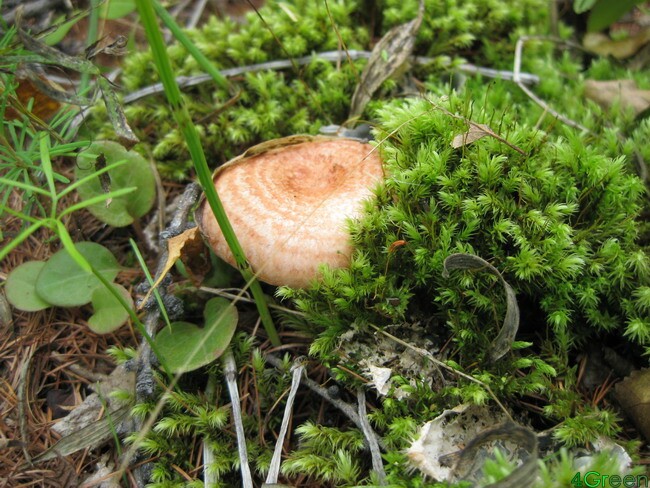



There are several more types of conditionally edible mushrooms (honey agarics, russula, stitches, morels, champignons, etc.), but their collection and cooking requires special knowledge and experience, since they are easy to confuse with poisonous mushrooms and can be poisoned if improperly cooked. So you better not take risks with them ..
For reference, here is a drawing of poisonous mushrooms.

1 - false mushrooms; 2 - pale toadstool; 3 - red fly agaric; 4 - panther fly agaric.
Recipes for camping dishes using mushrooms will be discussed in the following articles.
Every citizen of Novosibirsk went to pick mushrooms at least once in his life - for some it was the first and last time, but for the lucky ones it is just the beginning of a new hobby. If you went without experienced mushroom pickers and collected a whole basket of poisonous mushrooms, then you should not be disappointed in yourself. TNR always thinks about its readers and today will talk about what edible mushrooms grow in our vast expanses.

Firstly, when going to pick mushrooms, you should not dress like the Opera House! You definitely need tight clothes and a net from insects, especially since only mosquitoes will suck in the forest ... Mushroom places it is very easy to find - by the number of mushroom pickers along the road, who hunt russula every day and arrange deadly fights for them. For example, 2 mushroom pickers share a mushroom place:
A true mushroom picker does not care about anything: rain, wind, kilometers of forest, and even rivals. A mushroom hunt is like a third or quiet hunt for a Siberian ... If we just collect berries (a second hunt) in a neighboring area, then we still have to look for mushrooms under a layer of soil, leaves and moss. Now let's move on to the look and design of our Siberian mushrooms:
White mushroom

Exceptionally high quality edible mushroom. It is considered one of the most valuable types of mushrooms, which can be used fresh, boiled, fried, as well as dried, salted and pickled. When dried, the pulp of porcini mushrooms, unlike the others, remains white (the favorite mushroom of nationalists)! Fruiting in June - October.
Gall mushroom

It is difficult to confuse porcini with inedible poisonous mushrooms. But it has an inedible double - gall mushroom... Its flesh is so bitter that even one small fungus that gets into the cauldron will ruin the whole dish. It will simply be impossible to eat it! The color of the bile mushroom tubules is dirty pink, and the flesh turns pink when cut.
Ryzhik

Some peoples consider it even cooler than a porcini mushroom, and in many countries, so in general, mushroom is considered a delicacy. Everyone especially loves mushrooms fried in sour cream, but it is not recommended to dry the favorites of Peter the Great.
Mostly mushrooms grow in coniferous forests, especially in pine and spruce, bear fruit from June to October.
In addition to the usual saffron milk cap, in our forests there is a red camelina (with wine-red milky juice, which turns purple in the air), salmon camelina (its milky juice is orange and does not change color in the air) and red pine camelina (milky juice is orange, and on air turns wine red).
Birch (birch, obabok) is a very common species, bearing fruit from June to September.
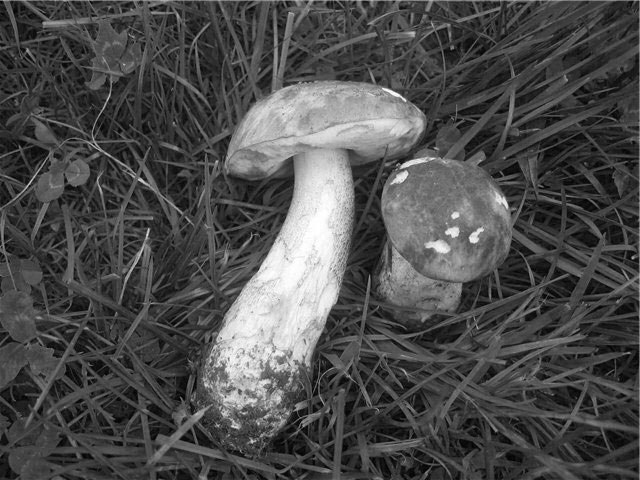

This mushroom can be eaten boiled, fried and without pre-treatment. This mushroom is suitable for all types of harvesting. Our grandmother:
If there is a need to avoid blue discoloration that appears during processing, the mushroom must be soaked in a 0.5% solution. citric acid... The boletus is processed in the same way. The boletus is especially good in fried or boiled... It can be confused with an inedible gall mushroom!

Boletus
(aspen, redhead) - one of the most common edible mushrooms. By its nutritional value and taste he, together with boletus, takes the honorable 3rd place after porcini mushroom and camelina.
There are quite a few subspecies of the boletus. It is processed like boletus.

Butterlets
distributed wherever pine trees grow in the northern hemisphere. They are characterized by a smooth, sticky or slightly slimy cap. Less common are boletus with a fibrous cap and a cap like Boyarsky's. Common butter dish (late, true, yellow) - the most common among butter. He has a slimy brown, dark brown or chocolate hat (no, we won't joke about a Negro ...).
Late butter can be fried, boiled, pickled, salted, dried and eaten. Attention!!! This mushroom bears a resemblance to the inedible pepper mushroom.

Larch butter dish
- grows in deciduous forests of Siberia and loves young trees. His cap is lemon yellow, yellowish orange or golden brown, sticky with an easily removable skin. This butter dish is good for boiling and pickling.
Granular butter dish (summer, butter, yellow) - prefers pine forests, often grows in dry places, on roads, glades and in pits. Usually these mushrooms grow in clusters from late May to early autumn.
Summer butter oil - high-yielding, tasty, edible mushrooms, used without preliminary boiling for hot dishes, salting, pickling, drying.

Chanterelles - edible mushrooms with good taste but small nutritional value... It is consumed without preliminary cooking - fresh, pickled, salted.
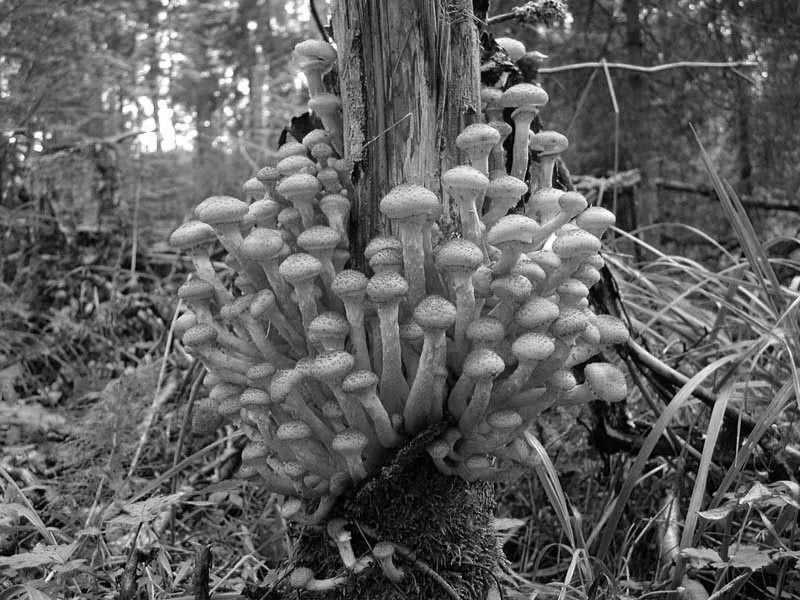

Honey mushroom
summer grows from June to October, on birch stumps or lying trunks, sometimes on stumps of other deciduous plants, they are rarely seen on conifers.
This is a delicious, gourmet mushroom, the caps of which can be used without preliminary boiling for hot dishes, for drying, pickling, salting. This mushroom is not known to all mushroom pickers ... it is very fruitful, often found in the Novosibirsk forests and grows large groups.

In addition, many types of mushrooms in Siberia are used in medical purposes: a decoction of porcini mushrooms is recommended in the treatment of angina pectoris and heart failure. V folk medicine the fruiting bodies of porcini mushrooms are used for frostbite, eye diseases. It is known that a decoction of porcini mushrooms is very effective as an anti-inflammatory and regenerating agent for burns and skin inflammations.

In Akademgorodok, on lawns and garden beds, you can often find shaggy dung beetle ... It is considered a conditionally edible mushroom at a young age (before the spores mature). It is known that the shaggy dung beetle contains the poison koprin, which is used in medicine in the treatment of alcoholism (you can also treat "bruises" with ordinary manure). Therefore, it is not recommended to use it with alcoholic beverages. The aqueous extract exhibits anti-tumor activity, and the protein isolated from the fruit body extract inhibits the development of stomach cancer.

Many people know medicinal properties chaga ... Chaga water infusions have long been used to treat gastrointestinal diseases, with tuberculosis, liver disease, heart, as disinfectant... Mushroom decoction reduces blood pressure and blood sugar. Chaga increases the body's defenses, activates the metabolism in the brain tissue, acts as an anti-inflammatory when used internally and locally, and inhibits the growth of tumors. Respect to Chaga and deep Siberian bow!

A very common species in our forests is gray talker ... This species is found in large concentrations in coniferous, deciduous and mixed forests. Many mushroom pickers have only recently tried this little-known edible mushroom. The study of medicinal properties showed that talkers have antibacterial properties - they contain substances used in the treatment of tuberculosis. In France, it is used in the treatment of epilepsy.

Edible mushroom, which is not very popular with us - oyster mushroom ... But besides nutritious, it has a lot useful properties... Oyster mushrooms can be found in the forests of Akademgorodok on dry, fallen leaves of deciduous and coniferous species, sometimes even on living trees. In the traditional Chinese medicine the mushroom is a remedy for rheumatism, it is used for pain in the lower back and legs, for numbness of the extremities, impotence (it works better than any Viagra). Oyster mushroom extract shows antimicrobial, antitoxic, radioprotective and radiosorption properties.

The medicinal form is very popular today. lacquered tinder fungus ... But this species is found mainly in the mountainous regions of Siberia, in addition, many researchers put it in the category rare species... In the forests of Akademgorodok, another representative of this genus grows, medicinal properties which is not inferior to the varnished tinder fungus. It is characterized by a wide range pharmaceutical action, including regulatory effects immune system, antitumor effect, anti-inflammatory and antiviral activity, hypoglycemic effect, normalization blood pressure and others. In folk medicine, it is used to reduce phlegm, as an analgesic and antipyretic agent, as well as to increase the general tone of the body, relieve fatigue and drowsiness.

A well-known mushroom among the people "Grandfather's tobacco" , or rather - a prickly or pearl raincoat. Fruit bodies of this species can be found from June to September in Western Siberia. The pulp of the mushroom stops blood well in case of cuts and can replace a sterile plaster if there is no plantain nearby, of course.

In general, we found out that mushrooms are amazing organisms that can be used by humans for a variety of purposes. Today, scientists of the SB RAS are actively studying their medicinal properties, and, possibly, in the near future, mushrooms will cure many human diseases.
P.S. Don't eat these mushrooms.
Unknown edible mushrooms
The list of edible mushrooms collected by mushroom pickers is usually very small; and even in the most expanded form, does not exceed 50 species, and many collectors take them even less, only 10-15 pieces. While there are more than 200 species of edible mushrooms in our forests. Therefore, there exists a set delicious mushrooms that no one collects simply out of ignorance.
Stroharia aeruginosa belongs to such mushrooms. Which has an unusual, even “threatening”, typically “greasy” appearance, which inadvertently causes fear among ill-informed collectors. However, this mushroom is edible and even delicious. In preparation, it is versatile, suitable for any use: frying, boiling, pickling, salting and drying. There are no poisonous mushrooms similar to it.
Its appearance is very characteristic, unusual and memorable. Such a mushroom cannot be confused. His hat is medium in size, up to 8 cm in diameter. It is wide-bell-shaped, in old age it is spread, mucous-sticky, unusual for mushrooms "suspicious" bluish-green color, with white flakes along the edge. The plates adhered to the stem, in young mushrooms, are colored in the color of the cap - bluish-green, then they become smoky gray, and finally purple-brown. Leg up to 10 cm long and 1 cm in diameter, hollow, also blue-green. Young mushrooms have a blanket, which, when the cap is unfolded, remains on the stem, in the form of a ring. Above which, the leg is smooth, and below it, it is covered with white flaky scales, disappearing in old age. The pulp is fleshy, bluish in color, without any special taste or smell.
The fungus is found from August until late autumn. It grows in a wide variety of plant conditions: in forests, pastures, dumps, etc., not only on soil, but also on stumps, especially conifers; singly or in groups.
But its relative is especially interesting for gardeners - stropharia with a wrinkled ring (Stroharia rugoso-annulata), which has been successfully cultivated in Germany for several decades, both in open and closed ground; on straw, flax waste, sawdust and other plant residues. Unlike champignons and oyster mushrooms, which are usually produced on large enterprises industrial type, it is very convenient for growing in small farms of amateur gardeners. Her cap is shaped like a blue-green stropharia, but much larger, in an adult mushroom, reaches 13 cm in diameter, and sometimes even more. In adolescence, it is chestnut brown or wine red, with age it becomes brownish purple. The plates are at first whitish or bluish-light gray; with age, they acquire a violet-gray or lilac-brown color. The leg is very high, up to 19 cm long, and 1-6 cm in diameter; whitish at first, then brownish or bluish-brownish. In its upper part, it bears the remains of a blanket in the form of a ring, which can disappear with age. The pulp is pure white, very tasty. In nature, the fungus grows on dead wood, from June to October, usually in very large groups. In Germany, the first varieties of this mushroom have already been bred for cultivation. Russian amateur gardeners, perhaps, should also take a closer look at strophania with a wrinkled ring, purchase its mycelium and try to grow it on their garden plot.
Stropharia blue-green
In addition to the above, there are several other types of edible stropharias, however, they do not have of particular importance for mushroom pickers, due to its small size and rare occurrence.
It should be remembered that in addition to edible stropharias, there is also Gornemann's poisonous stropharia, which, however, sharply differs from them in the yellow-brown color of the cap in young mushrooms, and in lilac-dark gray in old ones.
Polish mushroom (Xerocomus badius, synonym - Boletus badius) - little known, but very delicious mushroom... V Western Europe he is considered one of the best mushrooms... This, of course, is some exaggeration, but it tastes no worse than boletus or boletus. Since the Polish mushroom has a "noble" appearance of a tubular mushroom, in our country it is often mistaken by collectors for a butter dish, a flywheel, and even a spruce form of white. In the forests of Russia, it is found infrequently, but in places it is abundant, especially in western regions country. Its Russian name this mushroom got because in the 19th century. v large quantities, was brought to Moscow and St. Petersburg from Poland, most of which, at that time, was part of the Russian Empire.

Polish mushroom
The cap in young mushrooms is semicircular, then it becomes convex, and in old ones it is even cushion-shaped. Its diameter is up to 15 cm. It is velvety, then naked and dry, in damp weather it is sticky. The skin on the cap is chestnut brown, dark brown, and in old age it is reddish brown. The tubular layer consists of small rounded pores, first light cream, then yellow, and in old age - greenish-yellow or olive-green, when pressed - turns blue. Leg up to 12 cm long and 2 cm in diameter, cylindrical. In the middle, often slightly swollen, dense, hard, brown in color. The pulp is dense, whitish, turns blue at the break, has a pleasant mushroom smell; the taste is pleasant, but poorly expressed. The mushroom is usually used boiled, fried and pickled, less often dried; you can also salt it, but it is rarely prepared in this way. Nutritionally, the Polish mushroom is close to white. When dried, it is also very similar to it; which is sometimes used by unscrupulous traders, selling it instead. It grows in coniferous and deciduous forests, often at the base of trunks, sometimes even on stumps; from June to the end of November.
Meadow honey fungus (Marasmius oreades). Although it is called honey fungus, it has nothing in common with real mushrooms - autumn, summer, winter, etc., in a systematic sense, and is not closely related. Even outwardly, it does not resemble them (unless only in small size and thin structure), it does not grow on stumps. And on the leg, unlike other types of honey agarics, he does not have a ring. Therefore, it is not clear why it was called that. Its other name is more suitable for it - non-fungus, since fruiting bodies, unlike most other mushrooms, usually do not rot in old age, but dry out.

Meadow honeydew
The cap in meadow honey is thin, bell-shaped; in mature mushrooms, it is flat, with a tubercle in the center, 3-7 cm in diameter (usually small); folded-striped along the edge, cream, ocher-cream or skin-yellow color. The plates are rare, fawn. The stem is cylindrical, fibrous, elastic, dense, 4-10 cm long, very thin, 3-8 mm in diameter, pale-yellow in color, with a powdery coating. Tapers slightly towards the base. The pulp is thin-fleshy, white or pale yellow, its color at the break, does not change, with a pleasant taste and a spicy mushroom smell, somewhat reminiscent of cloves or bitter almonds.
The mushroom is very tasty, it is used universally - boiled, fried, dried, pickled and salted. Especially good in soups. When cooking, only hats are often used, since the legs are thin and harsh. It is curative, the pulp contains medicinal substances that actively suppress staphylococci, Escherichia coli, and some other pathogenic bacteria. And also having a tonic effect on the body.
Meadow honeydew more often grows in treeless places: on dry meadows, pastures and pastures; on soddy soil, in June - September. And in the forest - in the clearings and edges, among the grass. Mushrooms often form well-visible "witch circles". There is a non-nippy very often and in large quantities, but the weight of the collected mushrooms, in total, usually turns out to be small.
It must be remembered that some are a little like meadow honey poisonous mushrooms that grow in forests. First of all, these are fibula (synonym - inocybe): common, changeable, and Patuyara. Their hats, like those of meadow mushroom, are first bell-shaped, and later - prostrate, with a tubercle, which, however, differ greatly from it in color. Their legs are several times thicker than those of the honey fungus, although they are not thick. It should be borne in mind that in addition to the described poisonous, there are among the fiber and edible species... But those, since they are rare, and also small, special interest, for mushroom pickers, do not represent.
There are a lot of similar, "unknown" edible mushrooms. One has only to study the literature on mycology a little, and carefully observe different kinds mushrooms growing in nature. And then a full basket of mushrooms will always be provided to you, not those others, albeit unknown to most other mushroom pickers.